Triticella pedicellata (Alder, 1857)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4890.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1FD6877B-BCE2-4AAA-AEAE-04E5488463CC |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4328007 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039A87B9-FFB3-757E-FF28-13C8FF76FD1F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Triticella pedicellata (Alder, 1857) |
| status |
|
Triticella pedicellata (Alder, 1857) View in CoL
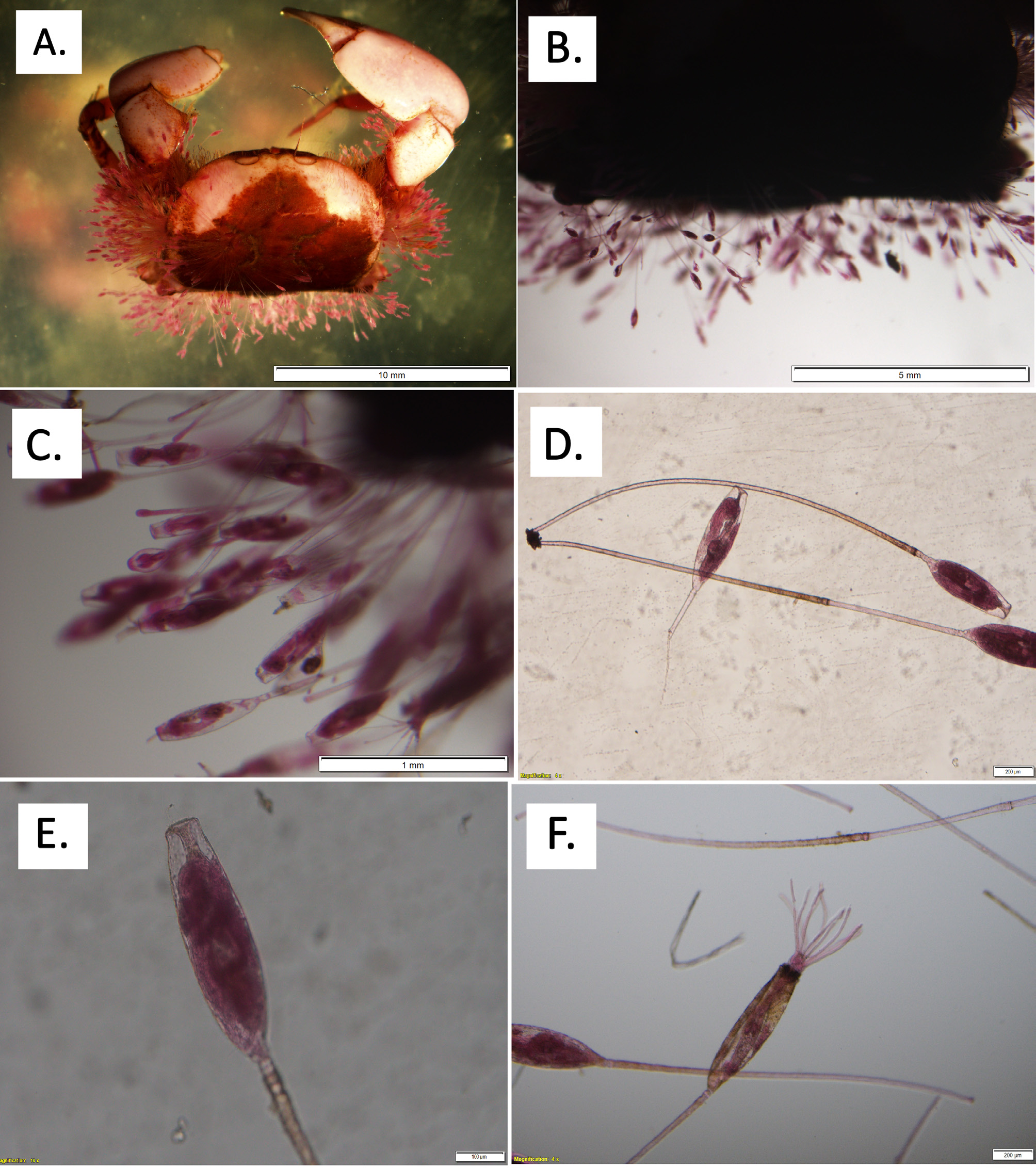
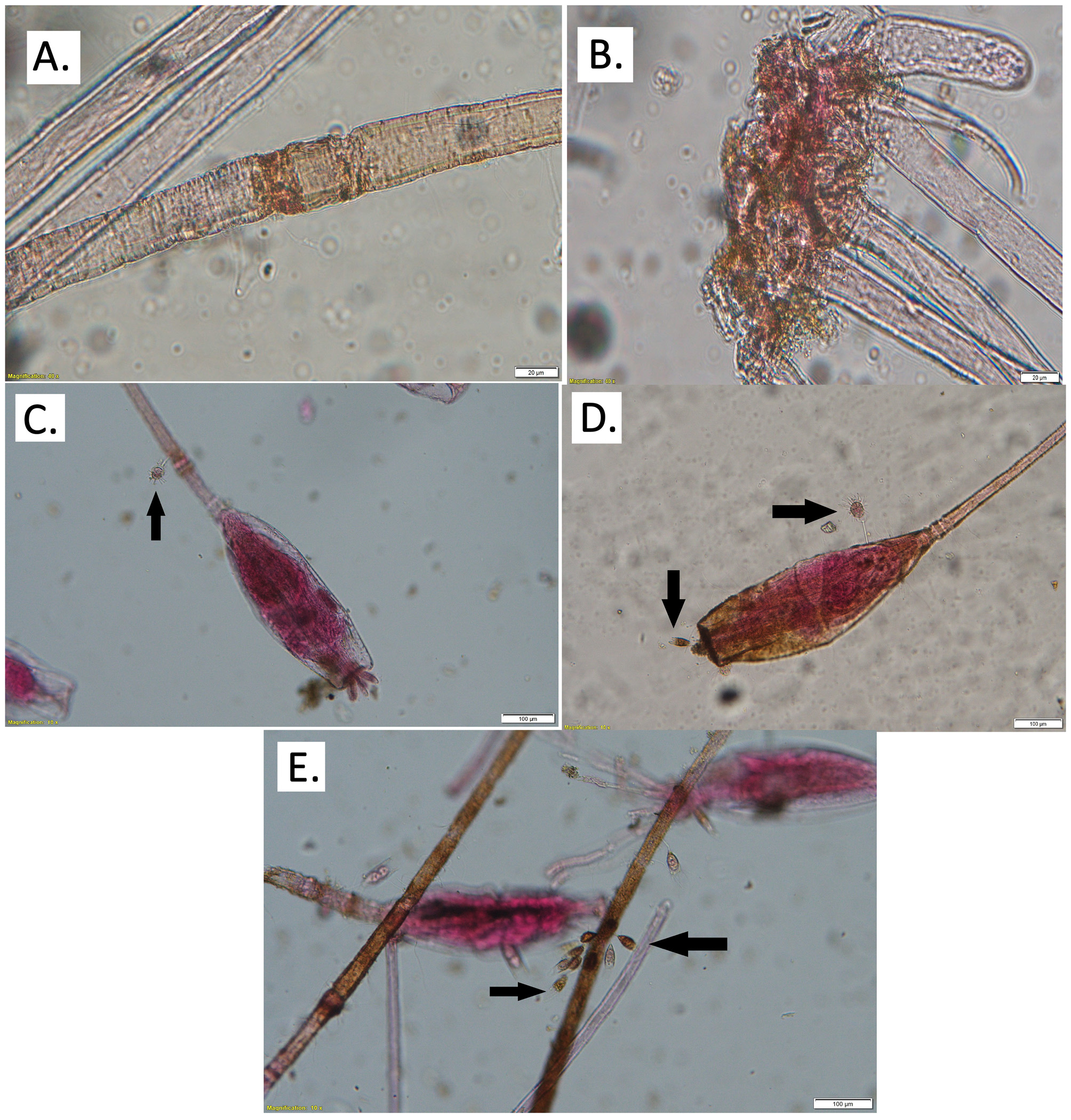
( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
Triticella pedicellata: Menon, 1972: 622 View in CoL , fig. 45–49.
Triticella pedicellata: Hayward, 1985: 120 View in CoL , fig. 40. (cum syn.)
Description: Colony encrusting on brachyuran crab Atergatis sp. ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 A–B), with adherent convoluted stolons from which arises kenozooids with group, erect zooids (2C). Erect zooids with a long tubular pedicel, translucent cystid, strongly chitinized, 1.5–3.1 mm long, 0.022 –0.032 mm wide ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ), smooth. Distal zooidal dilatation elongate, almost fusiform, convex proximal, distally truncate, sometimes flattened frontally, about 0.52–0.68 mm long and 0.16–0.20 mm wide ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 E–F); old zooids with scars and some septae along pedicel, indicating sequential breakages and repairs on it ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Zooids may be marked by a wrinkled area, with no septum, between pedicel and dilatation. Frenaculum absent. Orifice terminal, circular, with very short collar. Polypide with oval stomach; lophophore with about 11 tentacles, about 0.350 mm long ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ). Ovary located at proximal third in zooid dilatation.
Remarks. Menon (1972) reported two Triticella from Indian waters: Triticella korenii Sars, 1874 , found inhabiting on appendages of spiner crab, and Triticella pedicellata Alder, 1857 , collected on legs of swimming crab. Triticella korenii is regarded to be junior synonym of Triticella flava Dalyell, 1848 ( Hayward 1985) . According to Hayward (1985), Triticella flava and T. pedicellata are distinct in presence of frenaculum (present only in T. flava ), and number of tentacles (17–20 tentacles in T. flava and about 12 tentacles in T. pedicellata ). Specimens reported as T. pedicellata by Menon (1972) are similar to those here described and figured, but he reported slightly shorter pedicel ( 0.60–1.80 mm long). Triticella pedicellata was considered a badly described species ( d’Hondt 1983), but despite absence of any morphological differences between Indian specimens and those described for Britain, we assigned species here described to T. pedicellata . Triticella pedicellata seems to be part of a species complex due variations reported in that species; thus further molecular genetics studies is needed to solve it. Specimens here reported have dilatations along pedicels, some of those with distinct septum (and scars); they are mainly only in old zooids, indicating breakages and repair of the zooids. Therefore, these dilatations are distinct from those described for Triticella capsularis Gordon & Wear, 1999 , from New Zealand; Triticella capsularis is characterized by having 9–17 tentacles, with longer (up to 10 mm) and wider ( 0.043 mm) pedicel when compared to T. pedicellata . The polypide of Triticella gracilis d’Hondt & Hayward, 1981 , described from deep waters of Atlantic Ocean, also has few tentacles (10–12 tentacles; acc. d’Hondt 1983), but it is distinct in having shorter zooids (smaller than 0.50 mm long).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Triticella pedicellata (Alder, 1857)
| Chatterjee, Tapas, Dovgal, Igor, Vieira, Leandro M., Dutta, Arpita & Nanajkar, Mandar 2020 |
Triticella pedicellata :
| Hayward, P. J. 1985: 120 |
Triticella pedicellata :
| Menon, N. R. 1972: 622 |