Hyalomma (Hyalommina) brevipunctata Sharif, 1928
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.186557 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6213753 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039087FB-607F-FFAD-4BAC-A4BB3C8AFF62 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hyalomma (Hyalommina) brevipunctata Sharif, 1928 |
| status |
|
Hyalomma (Hyalommina) brevipunctata Sharif, 1928 View in CoL
( Figs. 1–6 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 )
Type specimens. Syntypes (male and female; not quantified) ex dog from Anantapur in the Madras Presidency [now Andhra Pradesh State, India]; deposited in the Indian Museum, reg. № 56/18 (Kolkata, India) (p. 318, Sharif 1928).
Material studied. A total of 77 males, 46 females, 6 nymphs and 24 larvae that were collected in India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka were examined in the present study.
Synonym. Hyalomma hussaini var. brevipunctata Sharif, 1928
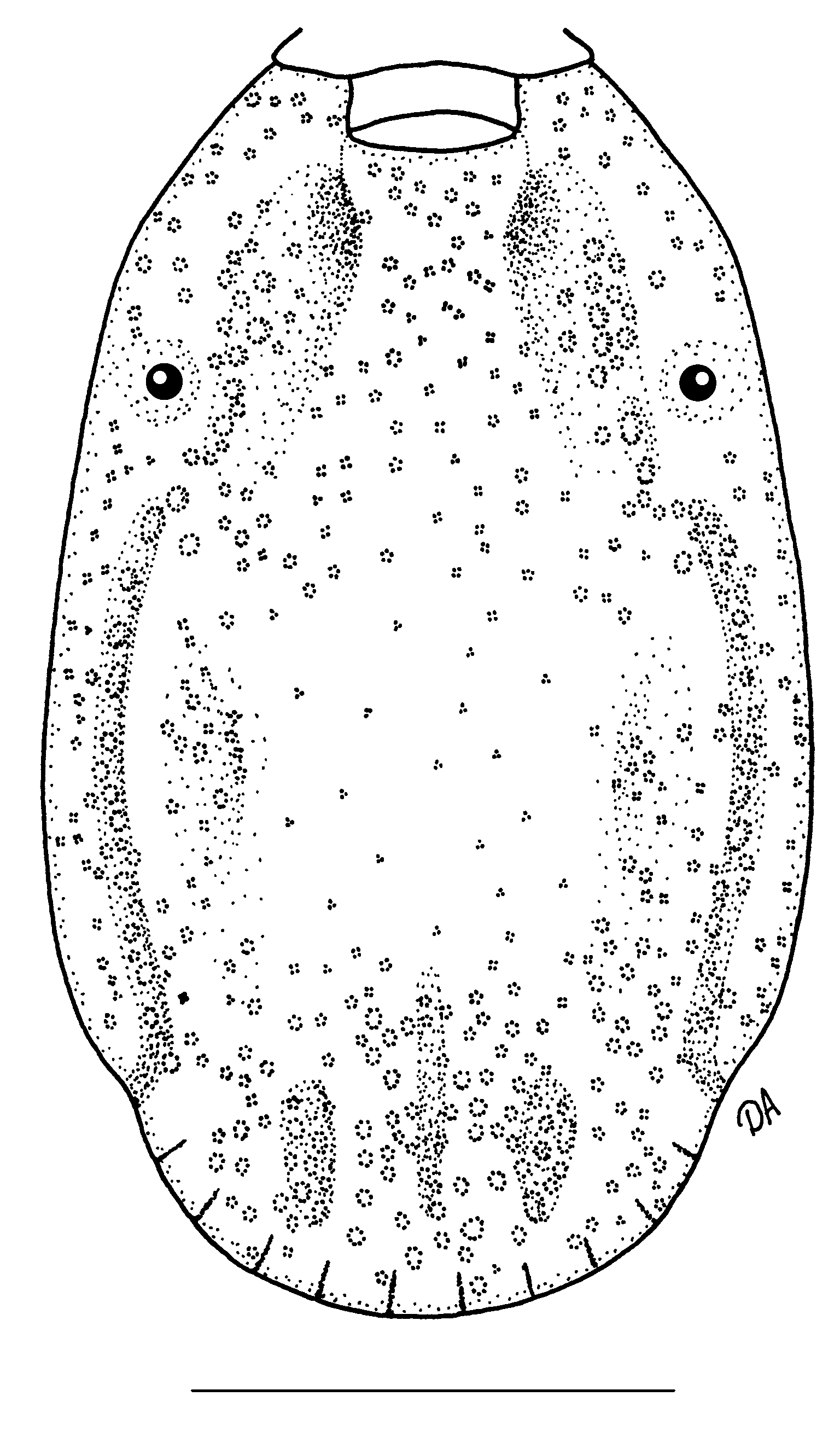
Description. Male ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Conscutum ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ): length 2.16–2.98 (2.52 ± 0.24, n = 34), width 1.20–1.73 (1.48 ± 0.14, n = 34), ratio length:width 1.51–1.87 (1.70 ± 0.08, n = 34); red-brown; fairly dense large and medium-sized punctations mainly on anterior part of conscutum, and on caudal and lateral fields, sparse, fine punctations on central part of conscutum. Spiracular plate ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C): perforated portion of prolongation moderately broad.
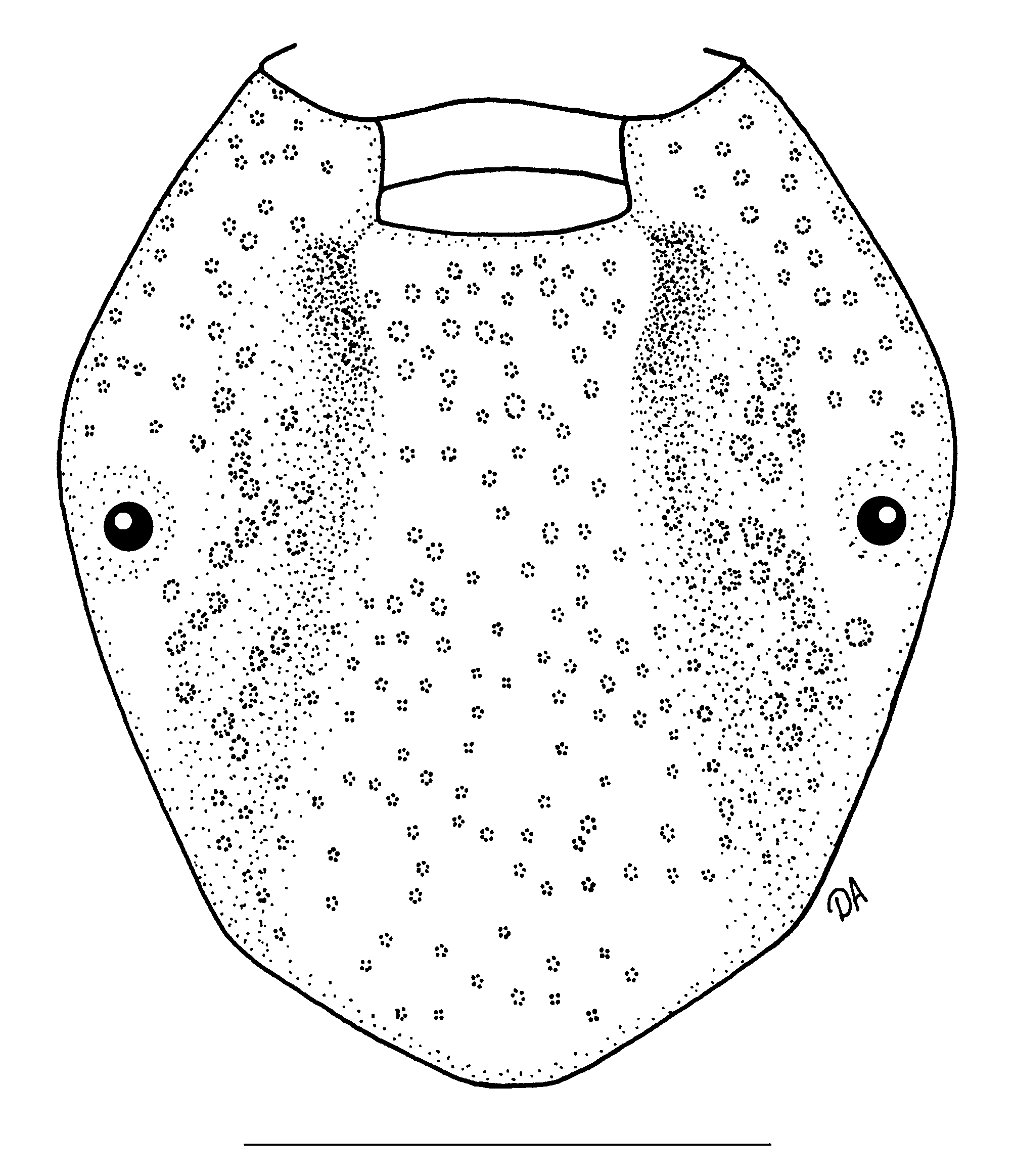
Female ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 , 4 View FIGURE 4 )
Scutum ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ): length 1.45–2.05 (1.78 ± 0.14, n = 30), width 1.42–1.91 (1.64 ± 0.13, n = 30), ratio length:width 1.00–1.17 (1.08 ± 0.04, n = 30); red-brown; moderately dense large punctations mainly on cervical and anterior part of central fields; moderately dense medium-sized and small punctations evenly distributed on lateral and central fields. Genital structures ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A): genital aperture narrow, arcuate (Ushaped) with arcuate or straight posterior margin; vestibular portion of vagina markedly bulging; preatrial fold of genital aperture bulging anteriorly and sharply sloping posteriorly ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 B).
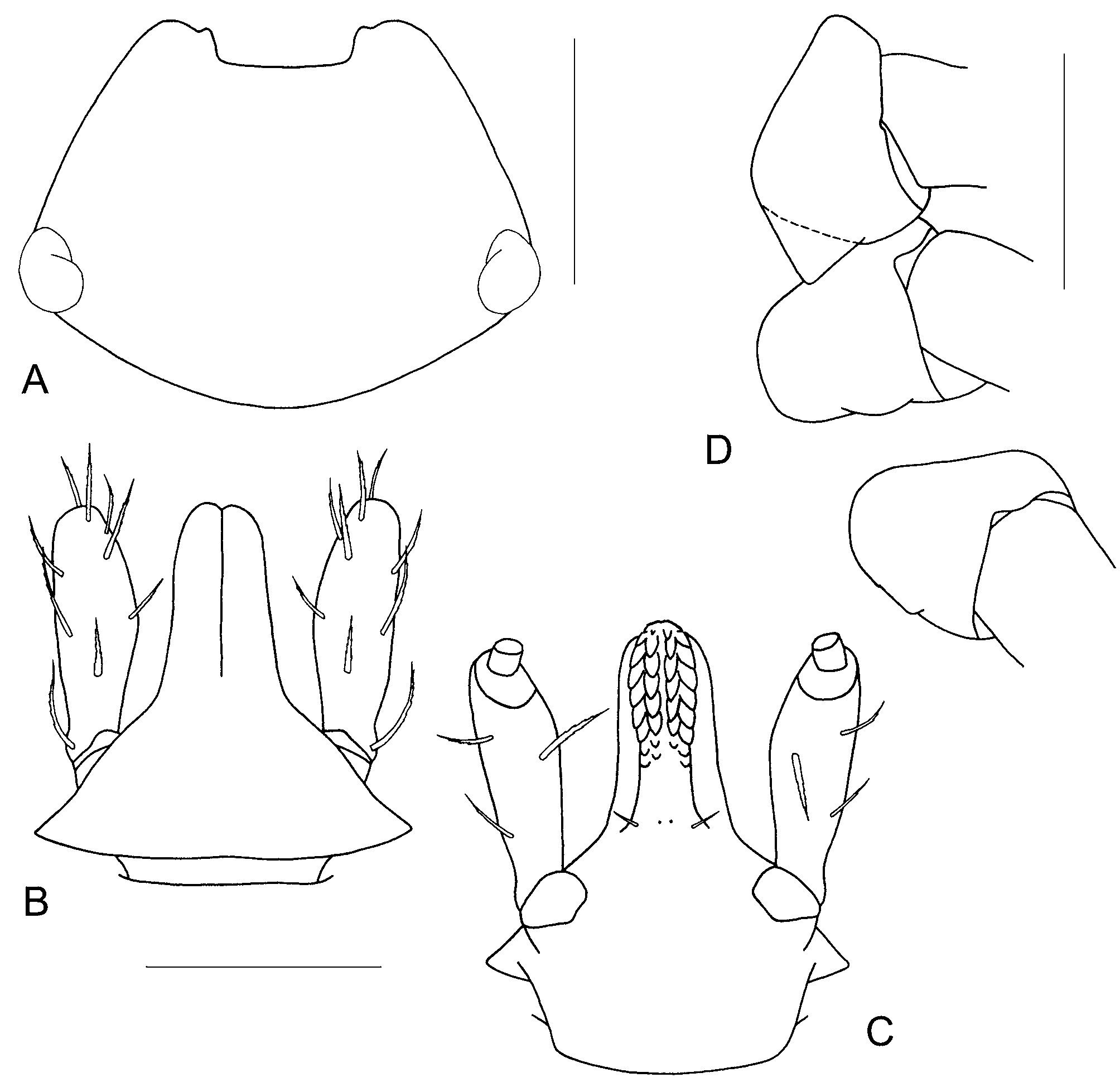
Nymph ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Scutum ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A): length 548–644 (609±42.29, n=5), width 477–533 (512±21.48, n=5), ratio length:width 1.14–1.23 (1.19±0.04, n=5), distance between posterior margin of eyes and posterior margin of scutum 215–238 (230±10.67, n=5), width:length of posterior portion of scutum 2.14–2.37 (2.23±0.09, n=5); posterolateral depressions on either side of scutal extremity absent.
Basis capituli ( Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 D, E): length 372–432 (402±26.32, n=5); width 328–362 (346±14.79, n=5), ratio length:width 1.13–1.19 (1.16±0.03, n=5); ventrally lateral saliences slightly convex without spur. Palpi (segment II) ( Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 D, E): length 154–178 (168±9.32, n=5), width 45–48 (47±1.41, n=5), ratio length:width 3.21–3.87 (3.57±0.29, n=5). Hypostome ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 E): length 168–196 (182±13.04, n=5), width 40–48 (44±3.16, n=5), ratio length:width 4.04–4.26 (4.14±0.09, n=5); tapering at apex; 7 large denticles in median file. Coxae ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 F): coxae II with moderate spur.
Larva ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 )
Scutum ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 A): length 220–240 (233±4.81, n=24), width 308–328 (317±5.44, n=24), ratio length:width 0.70–0.77 (0.74±0.02, n=24), distance from posterior margin of eyes to posterior margin of scutum 52–60 (57±2.23, n=24), ratio width:length of posterior portion 5.13–6.08 (5.52±0.22, n=24). Portion of scutum posterior to eyes nearly equal to 1/4 of scutal length.
Basis capituli ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 B, C): length 144–160 (153±3.39, n=24), width 152–162 (157±2.91, n=23), ratio length:width 0.94–1.01 (0.98±0.02, n=23). Palpi (segments II and III) ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 B, C): length 109–114 (112±1.57, n=24), width 34–38 (36±0.78, n=24), ratio length:width 2.89–3.26 (3.12±0.08, n=24). Hypostome ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 C): length 84–90 (86±1.55, n=24), width 20–22 (21±0.93, n=24), ratio length:width 3.82–4.40 (4.12±0.18, n=24); 6 large denticles in median file.
Genu I: length 118–134 (128±3.92, n=24), width 42–48 (44±1.68, n=15), ratio length:width 2.50–3.19 (2.95±0.17, n=15).
Hosts. The main hosts of the adults are large and medium-sized domestic and wild ungulates: cattle, buffaloes, goats, camels, sheep, horses, chital, Axis axis (Erxleben), nilgai, Boselaphus tragocamelus (Pallas) , sambar, Cervus unicolor Kerr and an antelope. The adults have also been recorded from domestic dogs, tiger, Panthera tigris (Linnaeus) and humans (our data; Sharif 1928; Kaiser & Hoogstraal 1964; Miranpuri & Naithani 1978; Mitchell 1979; Geevarghese & Dhanda 1987).
The main hosts of the immature stages of H. brevipunctata are various rodents and other small mammals. They have been recorded from Asian house shrew, Suncus murinus (Linnaeus) , Blanford’s rat, Cremnomys blanfordi (Thomas) , Cutch rat, Cremnomys cutchicus Wroughton , house rat, Rattus rattus (Linnaeus), Tanezumi rat, Rattus tanezumi Temminck, soft-furred rat, Millardia meltada (Gray) , greater bandicoot rat, Bandicota indica (Bechstein) , Asiatic long-tailed climbing mouse, Vandeleuria oleracea (Bennett) , flat-haired mouse, Mus platythrix Bennett , little Indian field mouse, Mus booduga (Gray) , rock-loving mouse, Mus saxicola Elliot, Indian gerbil, Tatera indica (Hardwicke) and jungle palm squirrel, Funambulus tristriatus (Waterhouse) ( Singh & Dhanda 1965; Rebello & Reuben 1967; Kaul et al. 1979; Geevarghese & Dhanda 1987).
Geographic distribution. Asia: India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka (our data; Sharif 1928; Kaiser & Hoogstraal 1964; Mitchell 1979; Geevarghese & Dhanda 1987; Dilrukshi 2006). Collection lot of the USNTC [RML 98964 (HH 58217), consisting of 2 males and 3 females, Burma, Pegu, Rangoon abattoir, ex domestic goat, December 1975, San-San Lin leg.] previously identified as H. hussaini , but we have reidentified them as H. brevipunctata . This is the first record of this species from Myanmar.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.