Herdmania, 2002
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1046/j.1096-3642.2002.00009.x |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5106232 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038F87C0-0F1C-3520-FF3E-FD36FE54FEFA |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Herdmania |
| status |
sp. nov. |
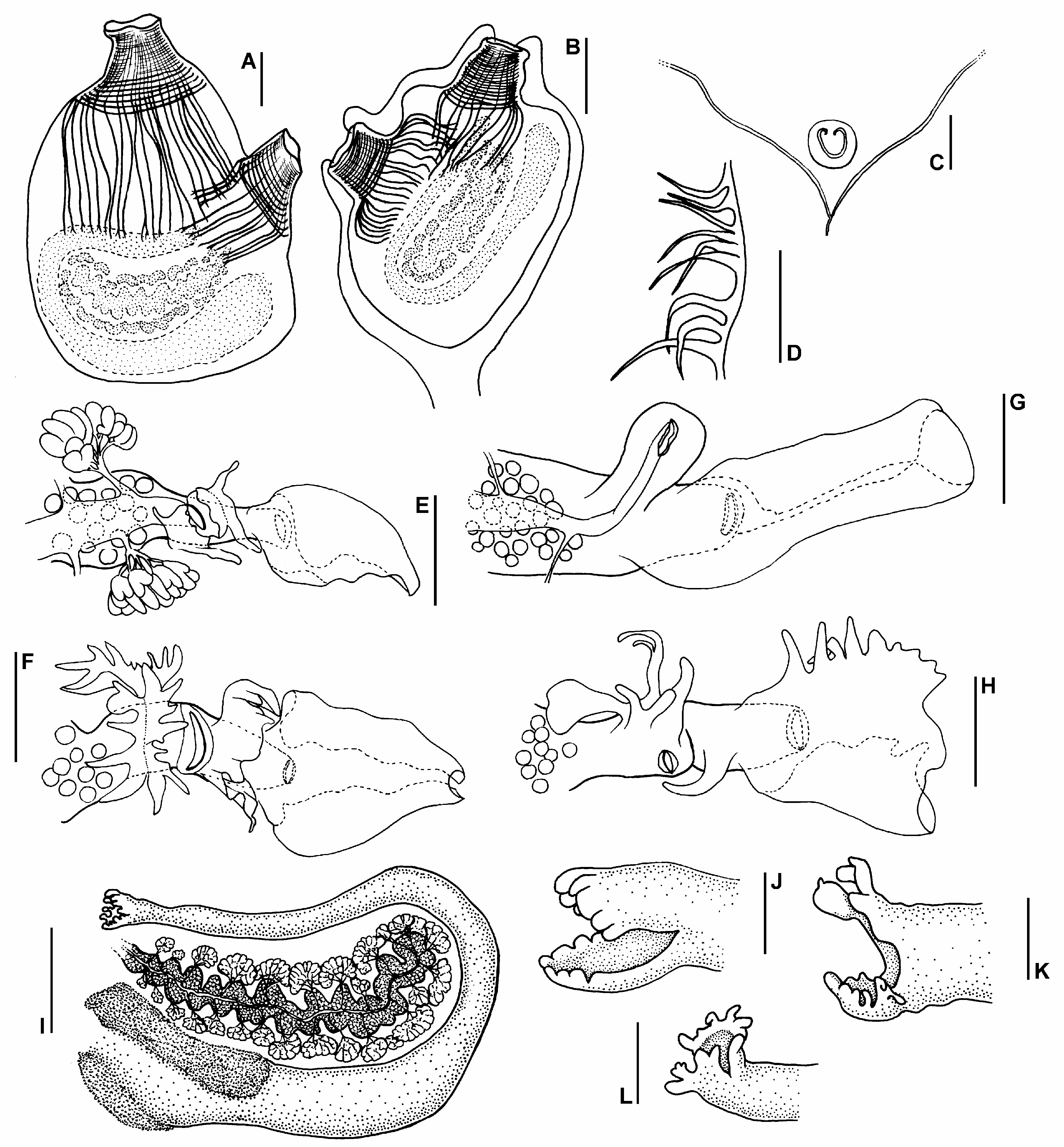
HERDMANIA FIMBRIAE SP.NOV. ( FIG. 1 View Figure 1 )
Herdmania momus var. galei Kott, 1952: 281 (part, fig. 127 from Tasmania, and Bowen).
Herdmania momus: Kott, 1972a: 41 (part, intermediate-sized forms 3 km off Glenelg); 1972b: 189 (part, small upright specimens).
Distribution
Type Locality. South Australia ( Point Turton jetty on piles and weed 3–4 m, coll. K. Gowlett Holmes 3.12. 93 holotype SAM E2892 View Materials ; coll. K Gowlett Holmes & W. Zeidler 20.4. 94 paratypes SAM E2891 View Materials ) .
Examined Material. South Australia ( Investigator Group , QM GH933 GH2299 ; Gambier Group, QM GH4405 ) . Tasmania ( Nine Pin Point , QM G1999 GH2017 ) . Queensland ( Bowen , AM Y1827 Y1829 ) . The species, also has been recorded from Tasmania ( Kott, 1952) and South Australia ( Glenelg , Kott, 1972a)
Description
Individuals sometimes upright, occasionally with short stalk. Up to 3 cm long. Upright individuals with atrial aperture terminal, branchial aperture directed laterally from halfway down the dorsum, both on short wart-like siphons. Other individuals sessile, fixed along their left sides. In preservative body laterally flattened, body wall closely adherent to gelatinous, thin white translucent test. Characteristic echinated needle-like spines in test, shorter and sparser than those crowded in body wall. Longest spines randomly orientated ones in posterior part of body wall, shorter ones anterior. Spines in siphonal walls orientated longitudinally.
Distinct circular muscle bands surround each siphon. On each side about 22 longitudinal branchial muscle bands extend almost parallel to one another and terminate in front of the horizontal gut loop on left and gonad on right. Twelve longitudinal atrial muscles on each side, the three anterior bands cross the posterior ends of the five dorsal longitudinal branchial muscles and the posterior atrial ones extend a short distance across body behind branchial muscles terminating near anus and gonoducal openings. When contracted, longitudinal branchial muscles raise body wall and test in rounded ridge around siphons. Dorsal tubercle a small cushion in wide peritubercular ‘V’ with a simple U-shaped slit, its ends turned in.
Branchial sac with seven to nine broad folds on each side with up to 12 internal longitudinal vessels on folds and one or two in interspace. Between dorsal fold and dorsal lamina never more than three internal longitudinal vessels which sometimes are absent altogether. Gut a horizontal loop with usual compact liver of crowded tubules embedded in body wall over pyloric region. Anal border variable, bilabiate, each lip usually divided and variously subdivided into regular or irregular tongue-like to rounded lobes. Long ovarian tubes, one in gut loop on left and one in corresponding position on right, undulate regularly and have clumps of testis follicles around each outer curve. From each clump, a number of short vasa efferentia join into a short common duct extending across surface of ovary to join central vas deferens. Large circular to fan-shaped, sometimes frilled and occasionally fringed membranous hood projects from the body wall over upper mesial surface of distal end of the short oviduct. It usually folds around to form conical to cylindrical chamber in front of oviducal opening. In older specimens, oviducal hood becomes less membranous, and is vascularized, to form a firm and slightly concave circular lid over the usually large, circular or sometimes triangular opening. Proximal to the origin of the oviducal hood, the male duct opening is a transverse slit sometimes raised on a short papilla projecting from surface of oviduct or is sessile, on side of, or across surface of oviduct. Variable frilled or fringed membranes, and/or pointed or rounded and sometimes branched papillae usually project into atrial cavity from body wall over oviduct distal and/or proximal to male opening. In robust (to 3 cm) specimens from Bowen, gonoducal hoods and membranes contain spines.
Remarks
The species resembles the Atlantic Herdmania momus: Van Name, 1921, 1930 and 1945, Cynthia pallida: Traustedt, 1883 and Rhabdocynthia pallida: Sluiter, 1898b in having testis follicles clumped along the outsides of an undulating ovary and a common vas deferens opening at the base of the short oviduct. However, in the Atlantic species neither oviducal hood or chamber nor the fringed or frilled membranes and/or papillae around the male openings are present. The present species is similar in size and appearance and has an oviducal hood and lobed anus as in Herdmania momus ( Savigny, 1816) , but the undulations of its oviduct are not as pronounced, testis follicles do not form an undulating band along the top of the ovary, the vas deferens is not interrupted and it has only a single opening. Herdmania momus: Nishikawa, 1991 and possibly some H. momus: Tokioka, 1953 (pl. 69 fig. 3) also have an oviducal hood and differ from the present species in having an interrupted vas deferens, each section with a separate opening like H. momus . Herdmania inflata differs in its interrupted vas deferens as well as its lack of gonoducal membrances. Herdmania mentula sp. nov. (p. 365), similar to the presents species, is known only from the north-western Australian coast and is distinguished by its freely projecting vas deferens and four shallow, smooth anal lobes (see below). The deeply scalloped anal border distinguishes the present species from H. insolita Monniot & Monniot, 2001 which has an even undivided anal margin.
| SAM |
South African Museum |
| QM |
Queensland Museum |
| AM |
Australian Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Herdmania
| Kott, Patricia 2002 |
Herdmania momus:
| Kott P 1972: 41 |
Herdmania momus var. galei Kott, 1952: 281
| Kott P 1952: 281 |