Neotripyla, Gagarin, Vladimir G. & Gusakov, Vladimir A., 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3716.4.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:18AF3DCA-7E90-4A00-8E0B-E92DD94F1461 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6146352 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038B8784-9E1D-FFEE-FF01-F9929EFAF9B6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Neotripyla |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Genus Neotripyla gen. n.
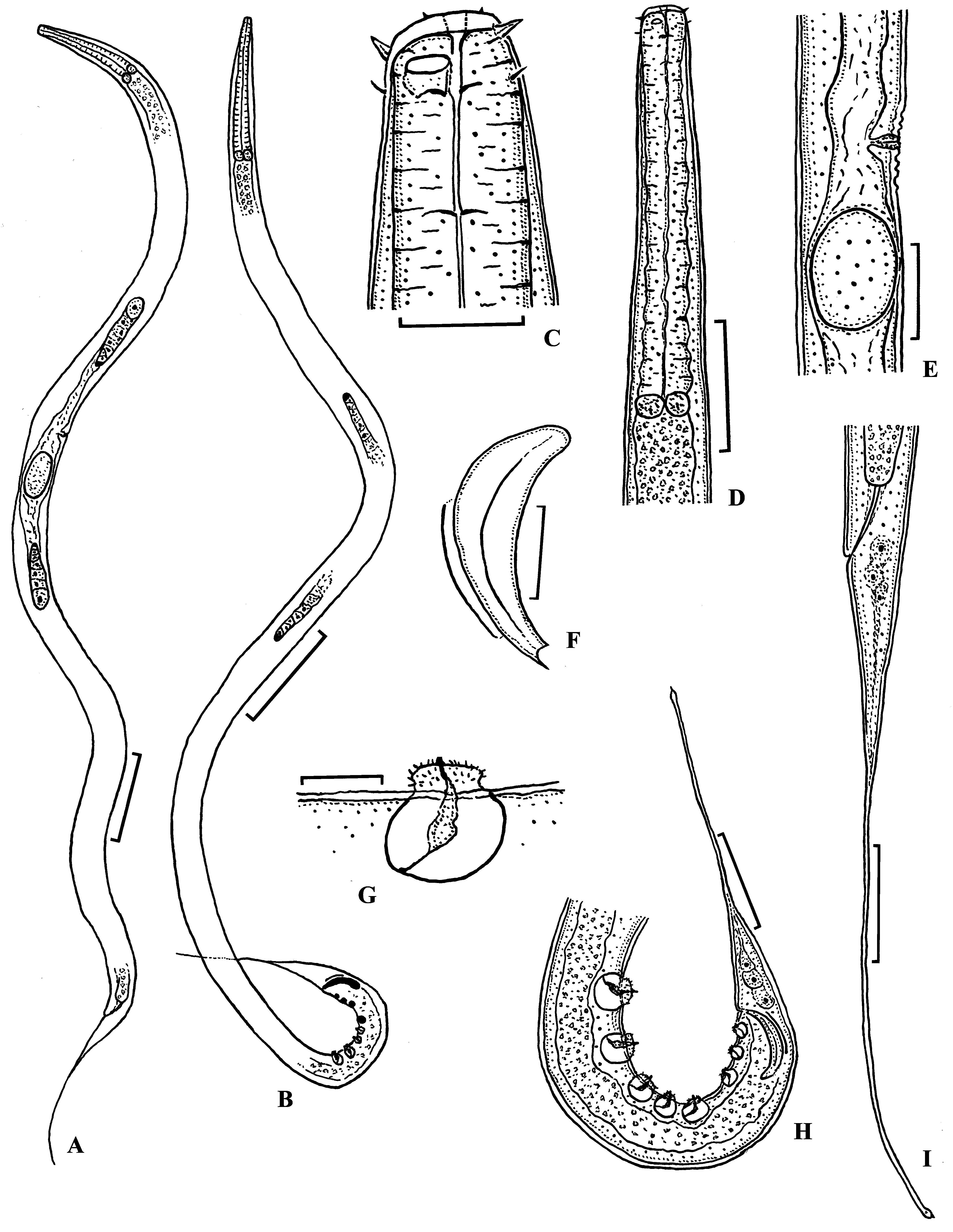
Diagnosis. Body comparatively long and thin. Cuticle finely transversely striated. Crystalloids and somatic setae absent. Lips three. Labial region not set off. Six inner labial sensillae in the shape of small papillae. Six outer labial sensillae in the shape of stout and short setae. Four cephalic sensillae in the shape of thin and short setae. Both circles of setae are arranged on considerable distance from each other. Stoma narrow, its walls not sclerotized. Teeth in stoma absent. Pharynx muscular, only slightly extended at its basis. Pharyngeal gland large. Females didelphic, amphidelphic, ovaries antidromous. Males diorchic. Spicules comparatively thick and short. Gubernaculum in the shape of a thin plate. Precloacal supplements vesiculate, echinate, 8 in number and arranged in three groups (2+3+3). The three supplements nearest to cloaca are the smallest, with the two supplements most distant from the cloaca the largest. Tail similar at both sex, long, with conical proximal and cylindrical distal portions. Caudal glands and spinneret well developed.
Type and single species. Neotripyla vulgaris sp. n.
Neotripyla gen. n. has some morphological characters typical of the family Tripylidae de Man, 1876 and others of the family Tobrilidae de Coninck, 1965 (Tsalolikhin, 1983). The presence of three lips, a narrow stoma lacking sclerotized walls and teeth, and the arrangement of outer labial and cephalic setae are characteristic of the family Tripylidae , while the presence, in males, of vesiculate precloacal supplements and the absence of a muscular pouch for spicular apparatus are characteristic of the family Tobrilidae . For correction of these contradictions the new family Neotripylidae fam. n. is established for the new genus.
Neotripyla vulgaris sp. n. ( Figs 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 ; Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Type material. Holotype male, slide reference number 102/18, deposited in the helminthological museum of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), Institute of Ecology and Evolution, Center for Parasitology, RAS (Moscow, Russia).
Paratypes. Three males and five females deposited in the helminthological museum of RAS, Institute of Ecology and Evolution, Center for Parasitology RAS (Moscow, Russia). One male and three females deposited in nematode collection in the Institute for Biology of Inland Waters, RAS (Borok, Russia).
Measurements. Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Type locality. Vietnam, Đồng Nai Province, Cát Tiển National Park, a small, shallow forest lake, Nai Cạp (N 11°27.354, E 107°20.072), altitude 136 m, depth 0.2 m, water temperature 27.0 °С, dissolved oxygen 1.6 mg /l, рН 6.1, conductivity 42 ΜS/sm, white clay with plant residues, 12 May 2012 (leg. V.A. Gusakov).
Additional locality. Besides the type locality, Neotripyla vulgaris sp. n. has been found in other water bodies in Cát Tiển National Park: 1) a forest stream, Bển Cự (N 11°25.873, E 107°25.767), altitude 126 m, depth 0.2 m, water temperature 29.9 °С, рН 7.6, conductivity 355 ΜS/sm, gray clay with plant residues, 8 September 2010; 2) a temporary flood-plain lake, Bàu Chim (N 11°28.826, E 107°22.641), altitude 132 m, depth 0.1 m, water temperature 31.3 °С, рН 6.3, conductivity 105 ΜS/sm, gray clay with plant residues and roots, 9 September 2010; 3) another small, shallow forest lake, Đâu Châ (N 11°27.282, E 107°20.360), altitude 138 m, depth 0.05 m, water temperature 24.9 °С, dissolved oxygen 1.0 mg/l, рН 6.6, conductivity 112 ΜS/sm, white clay with plant residues, 12 May 2012; 4) a nameless small, shallow forest lake (N 11°27.311, E 107°20.121), altitude 131 m, depth 0.25 m, water temperature 27.0 °С, dissolved oxygen 2.0 mg/l, рН 6.2, conductivity 40 ΜS/sm, white clay with plant residues, 12 May 2012. In other regions of Vietnam, the species has been recorded from only one habitat: Đắk Lắk Province, Lake Lắk, a plant-filled (aero-aquatic macrophytes), shallow area in the lake center (N 12°25.393, E 108°11.305), altitude 416 m, depth 1.1 m, water temperature 29.7 °С, рН 6.8, conductivity 53 ΜS/sm, silty gray clay with plant residues, 30 July 2010.
Etymology. The specific epithet means “common, usual”.
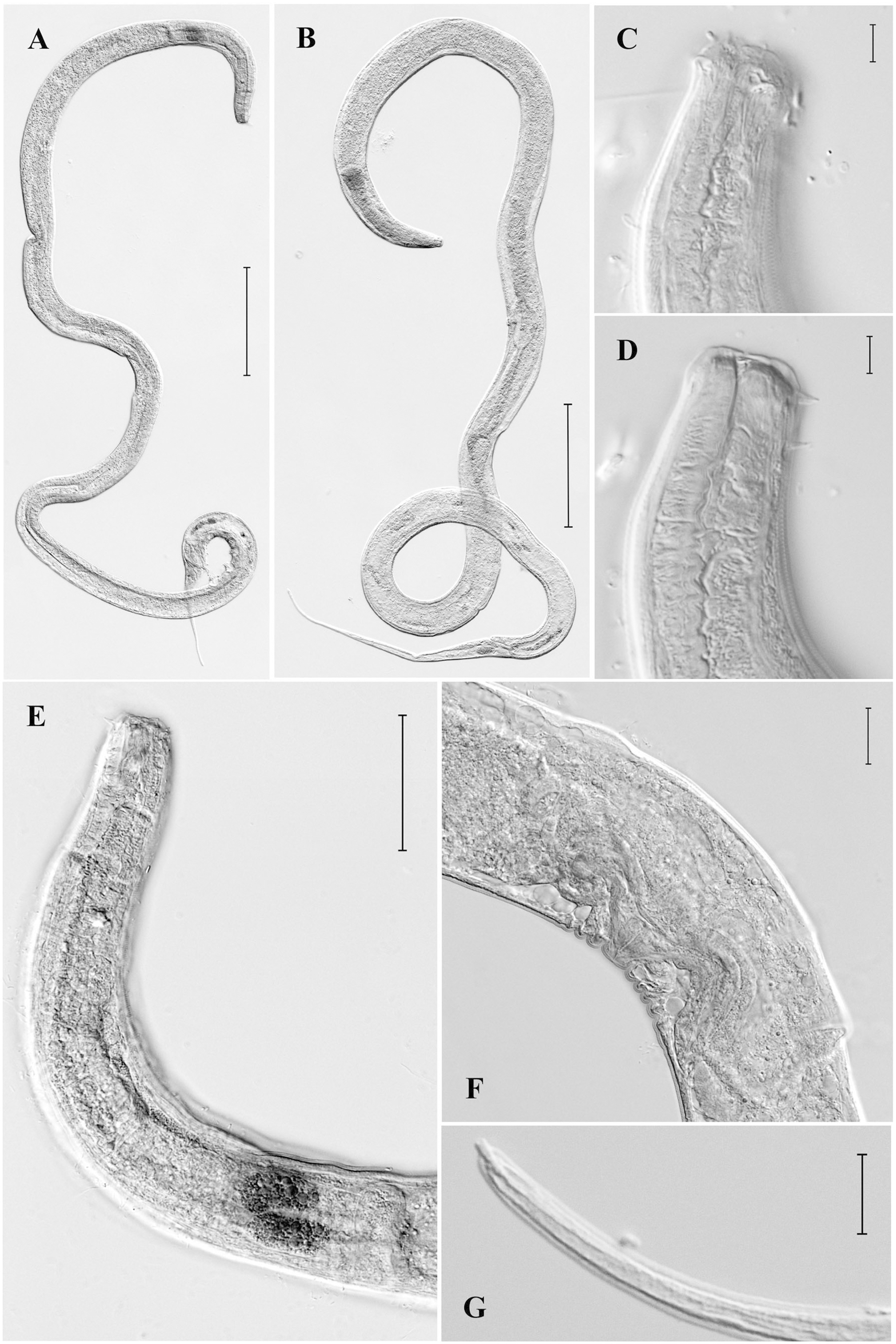
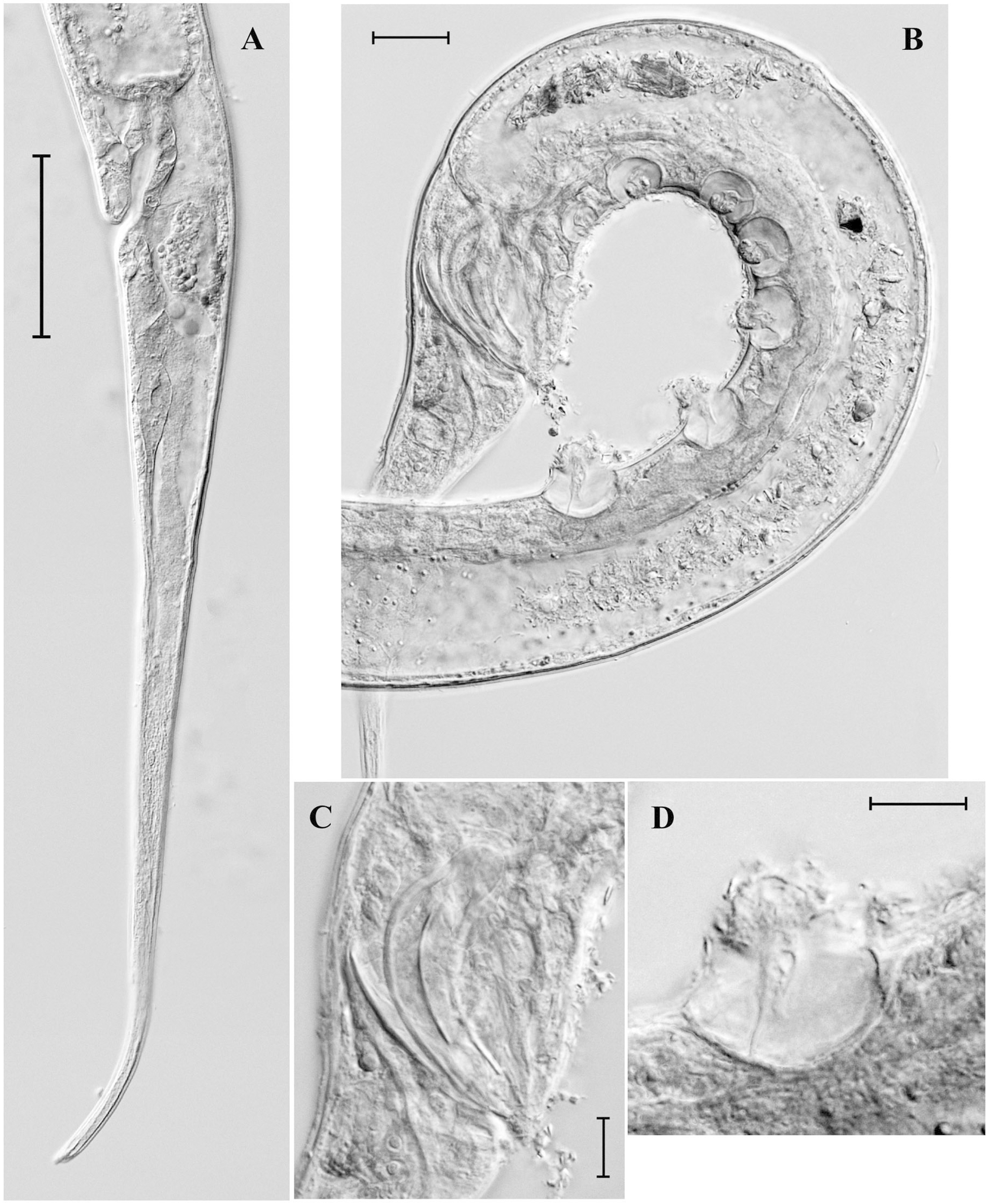
Description. Male. Body comparatively long and thin. Cuticle finely annulated, 1.0–1.5 µm thick at mid-body. Cuticular rings narrow, poorly visible. Crystalloids and somatic setae absent. Lips three. Labial region narrow, not off set. Inner labial sensillae papilliform. Six outer labial sensillae in the shape of stout and short setae 2.5–3.2 µm long, 17–18 % of labial region width. Four cephalic sensillae in the shape of thin setae the same length as outer labial setae or slightly shorter. Both rings of setae are arranged on considerable distance (6.0–6.7 µm) from each other. Stoma narrow, walls not sclerotized, 12–18 µm long, 0.8–1.0 times labial region width. Teeth in stoma absent. Amphidial fovea cup-shaped, 5.0-6.5 µm wide, located slightly behind labial region. Pharynx muscular, expanding gradually towards its base. Cardia small, surrounded by 3 oval glands 18–21 µm diameter. Renette, renette canal, ampulla and excretory pore not observed. Testes paired, opposed, situated to the left of intestine; anterior testis outstretched, posterior testis reflexed. Vas deferens well developed. Spicules comparatively short and stout, 1.3–1.4 times as long as the cloacal body diameter, slightly ventrally curved, with central longitudinal seam. Apical end of spicules with small ventral concavity. Gubernaculum in the shape of a thin plate, 23–25 µm long. Precloacal supplements vesiculate, echinate, 8 in number and arranged in three groups (2+3+3). Supplement ampulla spacious, spherical, contents concentrated in the upper portion of ampulla. Supplement pads armed with small thorns and one longer and thicker thorn. The three supplements nearest to cloaca are smallest, the two supplements more distant from cloaca are largest, 14–16 µm long, 35–45 % of the corresponding body diameter. Length of supplements row is 210–263 µm. Tail long, with conical proximal and cylindrical distal portions. Caudal glands well visible. Spinneret in the shape of a thin tube.
Character Holotype Paratype males (n = 4) Paratype females (n = 8)
male
range mean range mean Female. General morphology is similar to that of males in structure of cuticle and anterior body end. Cuticle finely annulated. Lips three. Labial region narrow, not set off. Inner labial sensillae papilliform. Outer labial sensillae in the shape of stout and short setae. Cephalic sensillae in the shape of thin and short setae. Both rings of setae are arranged on considerable distance from each other. Stoma narrow, its walls not sclerotized, 14-20 µm long, teeth absent. Pharynx muscular, expanding gradually towards base. Cardia small, surrounded by 3 oval glands. Prerectum not observed. Rectum length equal to or slightly greater than anal body diameter. Reproductive system didelphic, amphidelphic. Ovaries situated to the left of intestine, reflexed and comparatively short. Oocytes numerous. Vulva a transverse slit and situated anterior to mid-body. Vulval lips not sclerotized and not protruding outside the body contour. Cuticular wrinkles round vulva present. Vulval glands not seen. Vagina with thick, muscular walls. Uterus containing one or two eggs, measuring 76– 98 x 67–73 µm. Tail long, with conical proximal and cylindrical distal portions. Three caudal glands present, opening through a short, tube-like spinneret.
Distribution and ecology. So far Neotripyla vulgaris gen. n., sp. n. is known only from the freshwater sites of Central and South Vietnam described above, but presumably has a wider distribution (at least in Southeast Asia). As can be seen, the species is mainly common in shallow and temporary forest water bodies. So it is probably amphibiotic or soil-dwelling representative of free-living nematodes.
TABLE 1. Morphometrics of Neotripyla vulgaris gen. n., sp. n. (all measurements are given in µm, except for the ratios a, b, c, c’, V).
| L a b | 2210 39 9.8 | 2012–2543 36–40 9.3–11.7 | 2171 38 10.4 | 2322–3153 34–44 9.6–13.5 | 2866 41 10.8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c c’ V, % | 10.8 6.0 – | 10.8–12.4 4.9–5.8 – | 11.4 5.3 – | 7.5–9.7 7.9–11.7 35.8–43.3 | 8.3 9.8 40.0 |
| diam.c.s. diam.midb. a.d. | 18.0 56 38 | 14.5–18.0 54–61 34–38 | 16.5 56 36 | 15.0–19.2 62–86 34–38 | 17.6 71 36 |
| o.l.s c.s. ph.l. | 2.7 2.5 225 | 2.5–3.2 2.4–3.0 189–225 | 2.8 2.7 210 | 2.7–3.5 2.5–3.5 214–308 | 3.0 3.0 269 |
| dis.ph.cl. dis.ph. v. dis .v.a. | 1780 – – | 1643–2125 – – | 1773 – – | – 776–934 1069–1535 | – 875 1369 |
| spic. | 46 | 46–50 | 48 | – | – |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.