Eunice shihmenensis, Hsueh, Pan-Wen & Li, Yan-Huei, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3802.2.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:20400951-A62C-49FD-9D70-3FE54557E5D8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6141566 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AF67D207-FFCE-FFA0-FF14-FCC4FE55A0B0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Eunice shihmenensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Eunice shihmenensis View in CoL sp. nov.
Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7
Material examined. Taiwan: Holotype ( NMNS 6696-1), Shihmen (25°17´50˝N, 121°34´11˝E), New Taipei, intertidal algal reef, October 31, 2003; paratypes: one specimen ( NMNS 6696-2), Shihmen, New Taipei, intertidal algal reef, October 31, 2003; three specimens ( NMNS 6696-3), Jihuei (23°06´53˝N, 121°24´11˝E), Taitung County, intertidal algal and coral mixed reefs, October 7, 2010.
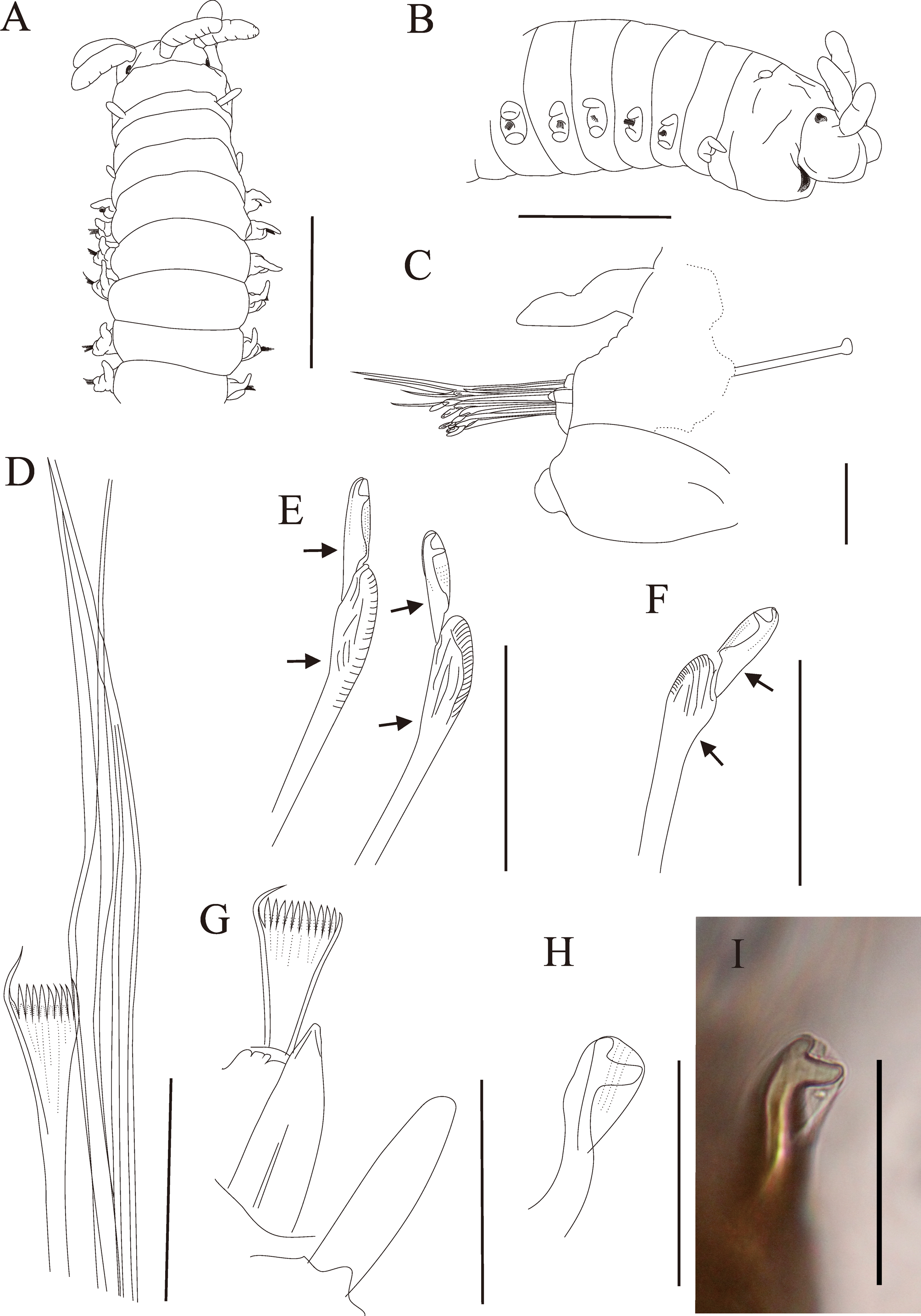
Description. Holotype, incomplete specimen, sex unknown, 12 mm in length for 53 chaetigers; maximum width 0.9 mm at chaetiger 15; length through chaetiger 10 about 3.0 mm, width at chaetiger 10 about 0. 8 mm; paratype, complete specimen but distorted, 37 mm in length for 131 chaetigers; maximum width 0.9 mm at chaetiger 15; length through chaetiger 10 about 2.4 mm, width at chaetiger 10 about 0.9 mm. Paired anal cirri present, short and slender, without articulations.
Prostomium equals in length and width to peristomium, about 1/2 as deep as peristomium, prostomial lobes frontally rounded, dorsally flattened, median sulcus shallow ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 A–B). Eyes present, posterior to base of palps, triangle and brick red. Prostomial appendages arranged in semicircle, median antennae isolated by gap, all similar in thickness; palpophores and ceratophores bases ring-shaped, not articulated; palpostyles and ceratostyles rodlike, with evenly spaced surface wrinkles but without articulations; A-II reaching chaetiger 1, A-I and II to middle of posterior peristomial ring, and palps to anterior margin of posterior peristomial ring. Peristomium anterior inflated, lower lip muscular; separation between rings distinct dorsally and ventrally, indistinct for a short distance laterally; anterior ring about 2/3 of total peristomial length. Peristomial cirri ovate, reaching middle of anterior peristomial ring, without articulations ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 A).
Maxillary formula: 1+1, 5+5, 7+0, 5+8, 1+ 1 in paratype; mandibles flat.
Branchiae absent.
Anterior neuropodial acicular lobes rounded; aciculae emerge above midline; prechaetal lobes truncate, postchaetal lobes rounded ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 C). First 5 ventral cirri short, digitiform, basally inflated from chaetiger 6 to chaetiger 29, posterior ventral cirri short button-shaped. Dorsal cirri slender, distally tapering, without articulations, shorter on median segments.
Limbate chaetae elongate, longer than all other chaetae, marginally smooth ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 D). Pectinate chaetae flat, flaring, with one elongate marginal tooth, about 8–12 inner teeth ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 D, G). Shafts of compound falcigers subdistally bent, distal inflated, marginally serrated; appendages wide at base, large bidentate head; proximal tooth isosceles triangle, larger than distal tooth, nearly at right angle to the axis of appendage, distal tooth directed obliquely; guards bullet-shaped, distally blunt, cutting edge serrated, without mucros, internal striations present ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E–F); pseudo-compound falcigers absent. Aciculae light brown at anterior segments, amber at posterior segments; thick and straight, tapering, distally blunt, cross-sections rounded, single per segment; separation between core and sheath indistinct at anterior segments, distinct on posterior segments. Subacicular hooks brown, with large bidentate head, present from chaetiger 28 to last chaetiger, single per chaetiger; shafts of hooks Sshaped; proximal tooth twice as large as distal tooth; proximal tooth triangle, forming a right angle to axis of shaft, distal tooth directed obliquely; separation between core and sheath distinct; guards large, distally truncate, covering distal head entirely, internal striations present ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 H–I).
Etymology. The name is derived from the name of village where the species was first collected.
Type locality. Shihmen, New Taipei, Taiwan.
Habitat. Intertidal areas of algal reefs or algal and coral mixed reefs.
Distribution. Known only from Taiwan, occurs on northwestern and eastern coasts of Taiwan.
Remarks. Of known abranchiate eunicids, a recently transferred Eunice (= Nicidion ) cariboea (Grube, 1856) ( Zanol et al. 2014) is most similar to Eunice shihmenensis sp. nov. However, differences in the shape of compound falciger and subacicular hook, and the form of aciculae separate these two species. Fauchald (1992) noted that: 1) shafts of compound falcigers in E. (= Nicidion ) cariboea are straight and distally inflated, with very small bidentate head appendages; proximal tooth is shorter than distal tooth, and proximal tooth is directed obliquely and distal tooth points upright ( Fauchald 1992: 97, Fig. 29 j, p), 2) aciculae of E. (= Nicidion ) cariboea are bluntly pointed and with mucronate guard ( Fauchald 1992: 97, Fig. 29 i), and 3) subacicular hooks of E. (= Nicidion ) cariboea are distally curved with large bidentate head, with both teeth strongly curved and directed laterally with proximal tooth about twice as large as distal tooth ( Fauchald 1992: 97, Fig. 29 m, o). In comparison, shafts of compound falcigers on E. shihmenensis sp. nov., are subdistally curved and strongly inflated distally with large bidentate head; proximal tooth is slightly larger than distal tooth, and proximal tooth directs perpendicular to the axis of the appendage and distal tooth directs obliquely ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E–F). Moreover, aciculae and shafts of subacicular hooks in E. shihmenensis sp. nov., are distally blunt but without mucronate guards and S-shaped, respectively ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 H–I).
| NMNS |
National Museum of Natural Science |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.