Tigriopus namsaiensis, Chullasorn & Kangtia & Song & Khim, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5051.1.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:33238221-53F9-4842-8056-9536C09DD112 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5564017 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/094CF257-FF99-B53B-FF1D-F92DFDCFFBEE |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tigriopus namsaiensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Tigriopus namsaiensis sp. nov.
( Figs. 1–9 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 )
Type locality. Associated with green algae, Ulva clathrata attached to a small rock at the sandy Namsai Beach in Sattahip district, Chonburi Province, Thailand (12°36’12.7”N, 100°56’38.5”E) on 6 August, 2017: collected by S. Chullasorn. GoogleMaps
Type material. Adult female holotype (NIBRIV0000851927) dissected on six slides; male allotype (NIBRIV0000851928) dissected on three slides: three female and three male paratypes (NIBRIV0000851929) preserved in 95% alcohol.
Etymology. The species name refers to the type locality at Namsai Beach.
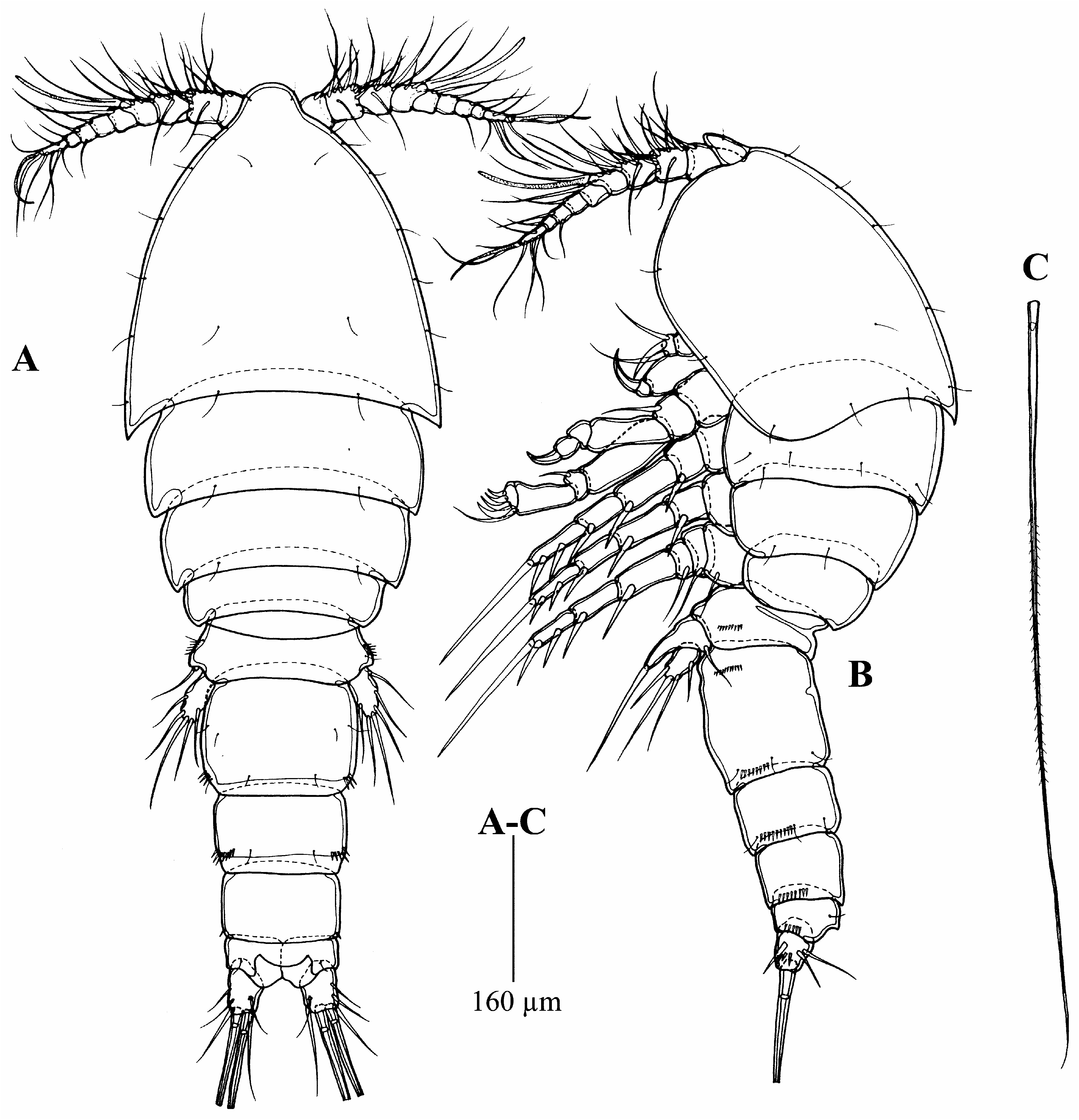
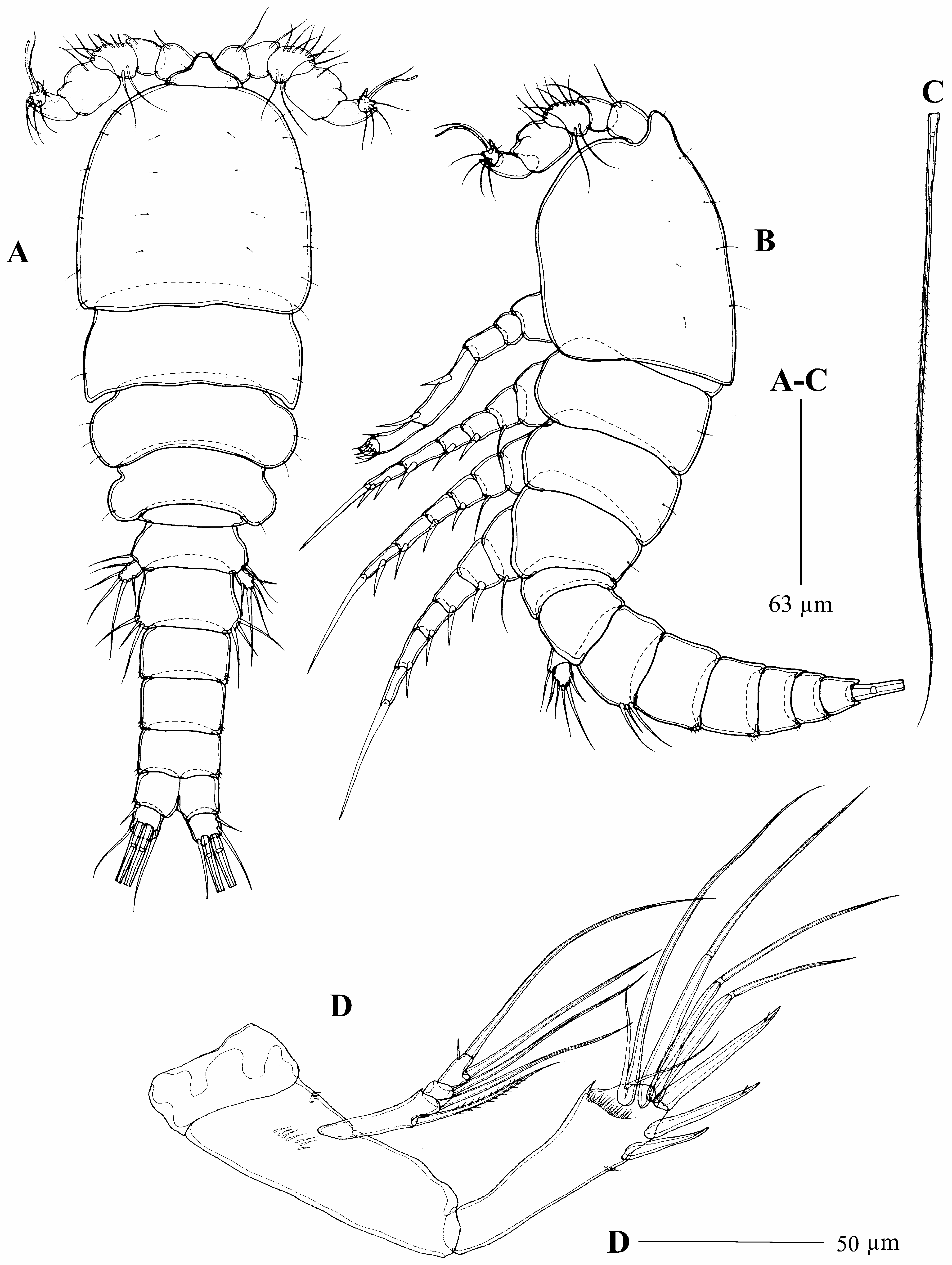
Description of female. Total body length of holotype 959 µm ( Fig. 1A–B View FIGURE 1 ), measured from tip of rostrum to posterior margin of caudal ramus. Total body length of paratypes 900–1,030 µm (n = 12, mean = 960 µm). Body compact, cyclopiform ornamented with few sensilla on surface. Nauplius eye not visible. Prosome 4-segmented, comprising cephalosome fused to first pedigerous somite, and three free pedigerous somites. Cephalothorax longer than three prosomites combined, posterior margin smooth. Rostrum ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ) large, slightly longer than first segment of antennule, with two pairs of sensilla; the first pair close to the rounded tip, and the second pair at halfway the rostrum length.
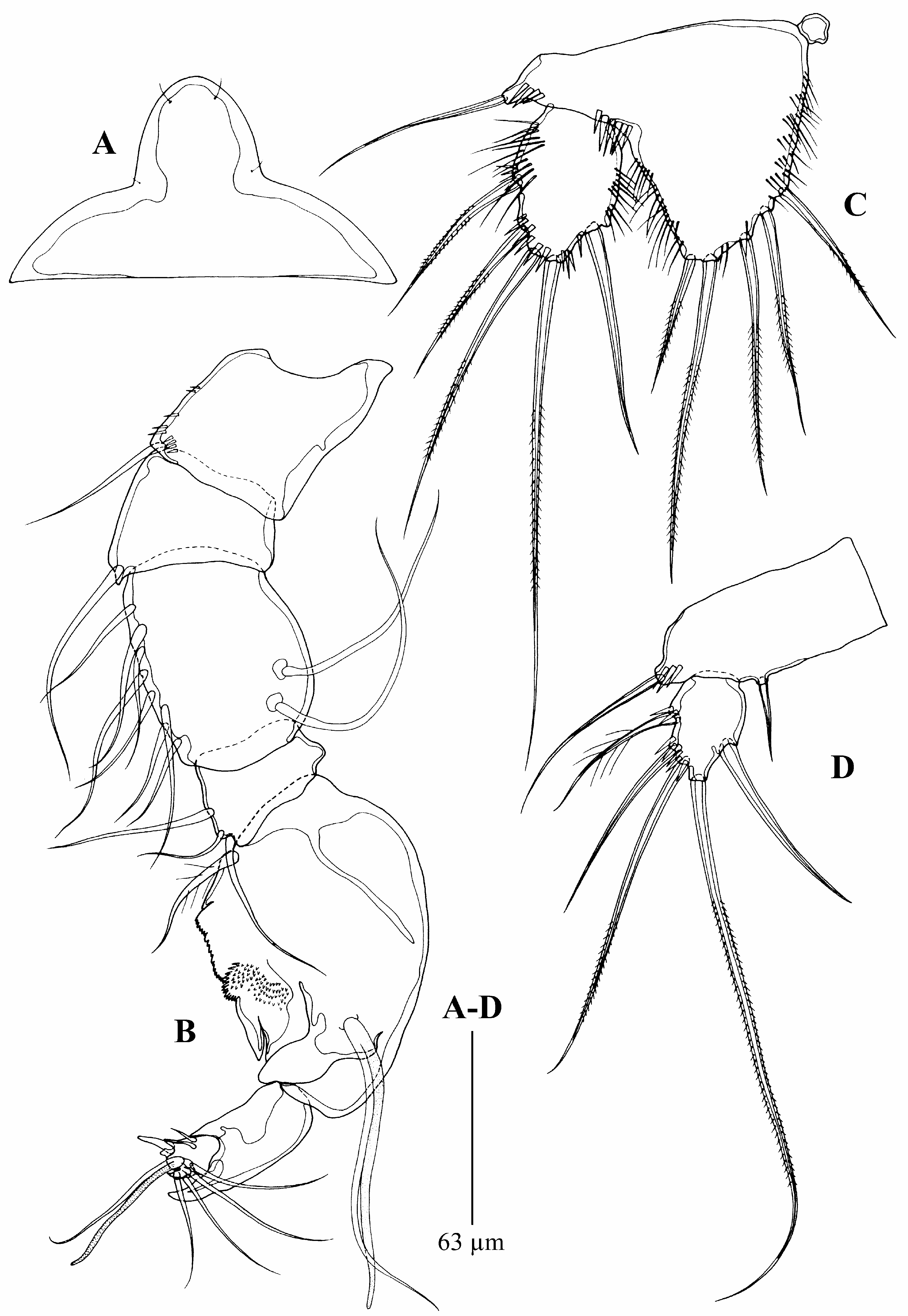
Urosome ( Fig. 2A–B View FIGURE 2 ) 5-segmented, comprising P5-bearing somite, genital double-somite, two free abdominal somites, and anal somite. Genital double-somite with P6, genital field indistinct, ventrally with two genital apertures. Third and fourth urosomites with rows of spinules ventrally. Anal operculum semicircular and smooth. Caudal rami slightly longer than wide, ornamented with small spinules dorsally and ventrally. Seta I arising laterally halfway the ramus length; seta II located between seta I and seta III; seta III twice longer than seta II; seta V ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ) longest, much longer than urosomal length; seta IV shorter than seta V; seta VI as long as seta III, located at inner distal corner; seta VII shortest located close to insertion point of seta V.
Antennule ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ) 9-segmented, first segment ornamented with row of spinules on surface, second segment largest, surface of segments 2–9 smooth. Length of segments 1–2 longer than five apical segments combined. Fourth and last segment with one large and one small aesthetasc, respectively. All setae slender and naked. Armature formula: 1-(1), 2-(10), 3-(9), 4-(3 + (1 + ae), 5-(2), 6-(2), 7-(2), 8-(2), 9-(5 + acrothek). Apical acrothek consisting of aesthetasc and two setae.
Antenna ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ) 3-segmented, comprising coxa, allobasis, and 1-segmented endopod. Coxa short, unarmed and unornamented. Allobasis bearing exopod, armed with one abexopodal smooth seta around middle of inner margin, furnished with rows of minute spinules on anterior surface. Exopod 3-segmented; first segment longest with two pinnate setae, second segment short with one pinnate seta, third segment short with one lateral pinnate and one apical pinnate seta. Free endopodal segment ornamented with row of minute spinules at outer distal corner, distal margin armed with smooth spines and setae: three spines, four small and short setae on anterior surface, and four geniculate setae.
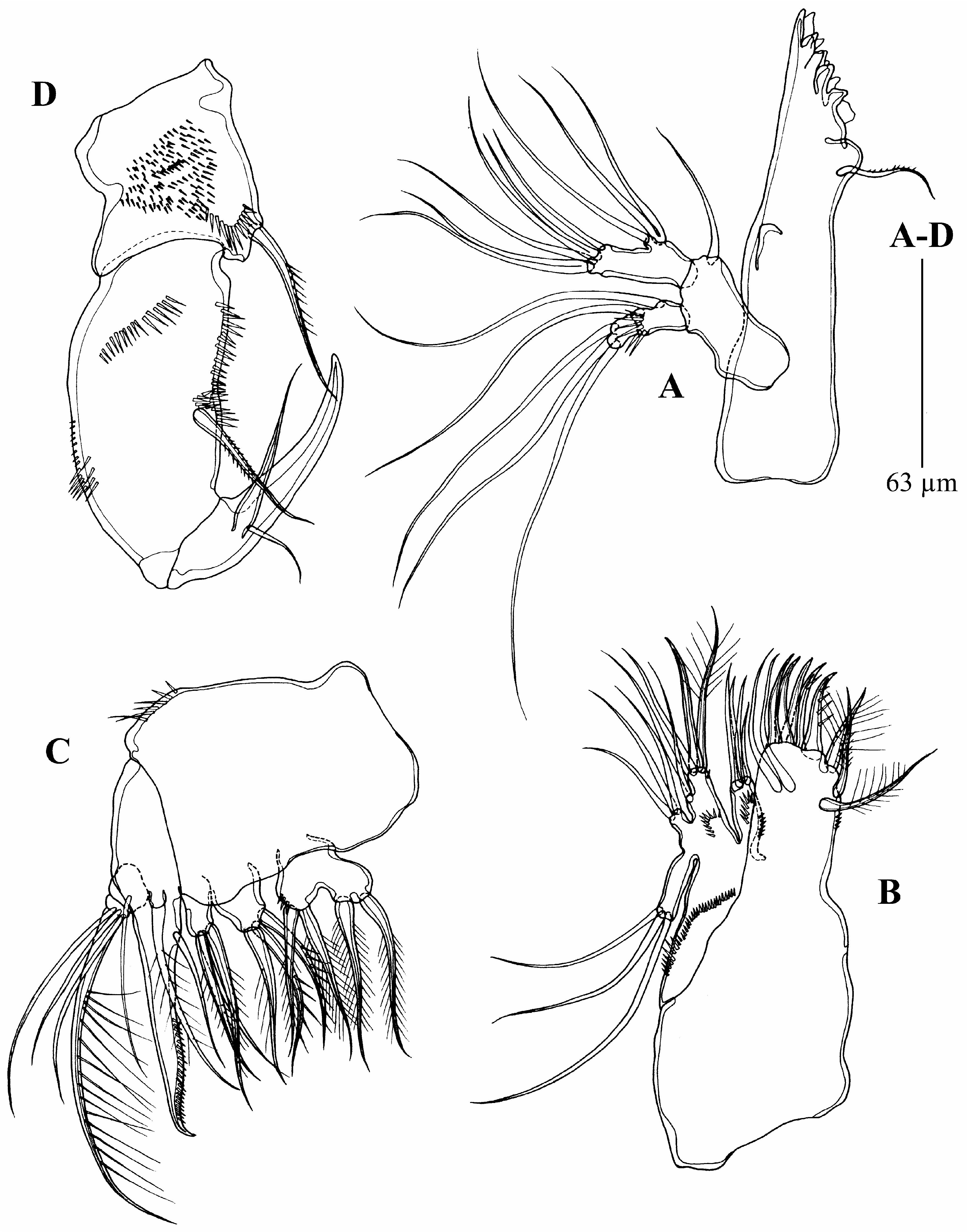
Mandible ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ) with large and elongate coxa, without surface ornamentation, bearing well-developed gnathobase, cutting edge with nine strong teeth overlapping each other, and one pinnate seta. Basis with apical smooth seta; exopod 3-segmented, first segment with two setae and some spinules at distal edge, second segment with one seta, third segment with three setae basally; endopod 1-segmented, with three lateral inner setae (two of them fused basally), and six apical setae (two of them fused basally).
Maxillule ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ). Praecoxa without surface ornamentation, arthrite with two slender setae on surface, two plumose, spine-like, outer elements, and with five apical spines. Coxa with cylindrical endite furnished with spinules on anterior surface, with four smooth setae. Basis ornamented with spinules on anterior surface, one naked spine and four setae distally. Endopod 1-segmented with three smooth setae. Exopod 1-segmented, three times longer than wide, with three smooth setae.
Maxilla ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ) with row of spinules distally on outer margin of syncoxa. Syncoxa with three endites (one praecoxal and two coxal); praecoxal endite bilobed, each lobe with two plumose distal setae; both coxal endites with three plumose distal setae. Basis with one smooth inner seta on a unipinnate strong claw and one plumose seta. Endopod 1-segmented with four slender setae and one plumose seta near base of the claw.
Maxilliped ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ) comprising syncoxa, basis, and 1-segmented endopod. Syncoxa short and stout, with one unipinnate seta at inner distal corner, and many spinular rows of unequal length on anterior surface. Basis with rows of spinules on anterior surface and along outer margin, with some minute spinules at outer margin, and with median, pinnate, inner seta halfway its length. Endopod represented by smooth curved claw, about as long as basis, and with one conical process bearing one lateral and one apical seta.
All swimming legs ( Figs. 5A–B View FIGURE 5 ; 6A–B View FIGURE 6 ) biramous; P1–P4 with 3-segmented exopods and endopods. Members of each leg pair connected by simple narrow intercoxal sclerite.
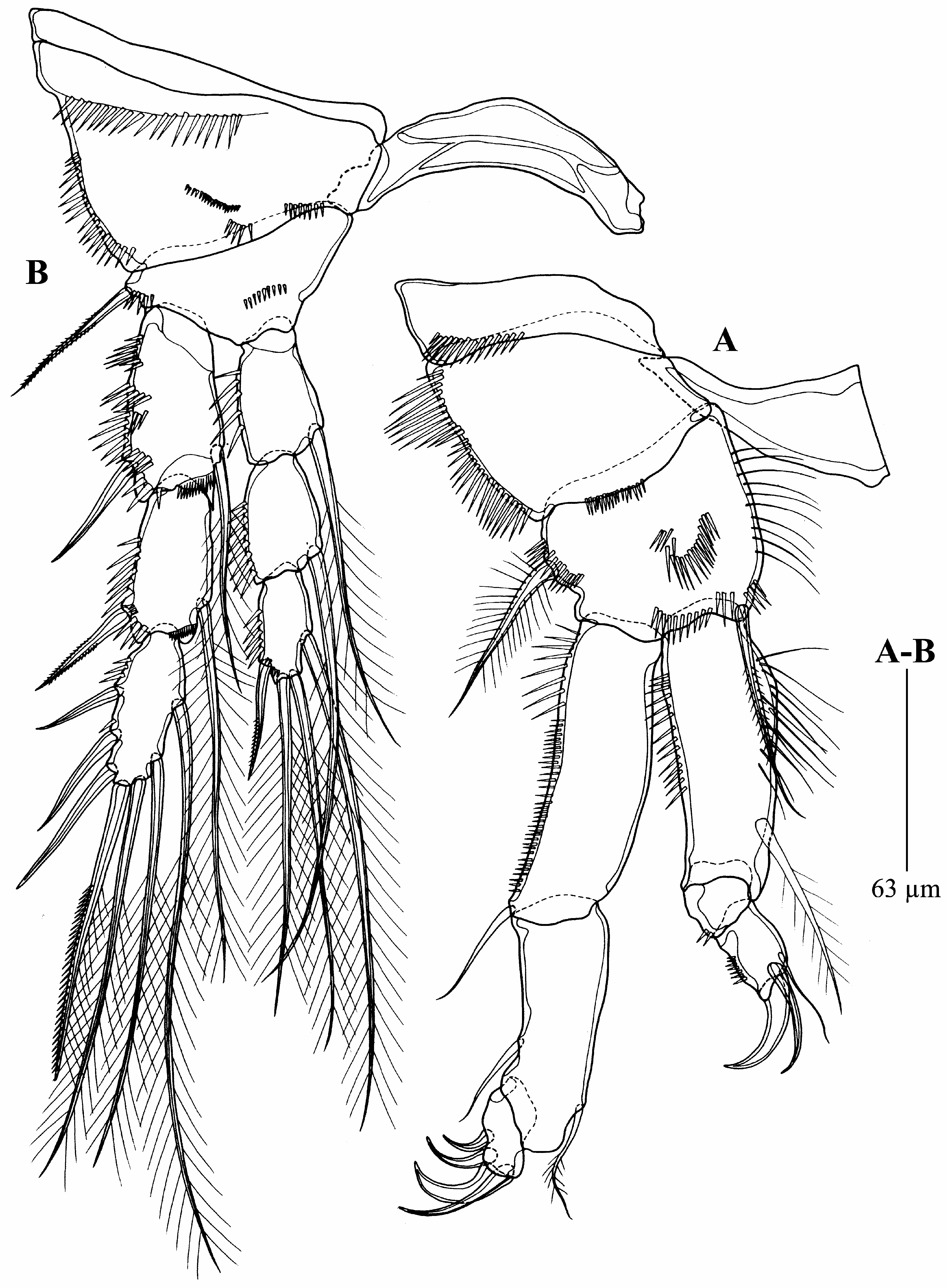
P1 ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Praecoxa with row of spinules on anterior surface along distal margin. Coxa rectangular, ornamented with row of spinules along outer margin. Basis with one pinnate inner spine and one plumose outer spine, with three rows of spinules on anterior surface, and row of setules along inner margin. Endopod much shorter than exopod, both three-segmented. Enp-1 much longer than enp-2 and enp-3 combined, with one plumose inner seta; enp-2 shorter than last segment, unarmed; enp-3 with one strong smooth curved claw, one slender spine and one slender inner seta. Both exp-1 and exp-2 long, exp-3 short. Exp-1 with one smooth outer seta; exp-2 with one small smooth outer seta at two-thirds of outer margin, and one pinnate inner seta; exp-3 with one outwardly curved outer spine, two smooth, curved distal claws, and one smooth inner spine.
P2 ( Fig. 5B View FIGURE 5 ). Praecoxa small and naked. Coxa ornamented with spinular rows of unequal length on anterior surface, and row of spinules along outer margin. Basis with one bipinnate outer spine, and small spinules on anterior surface. Endopod 3-segmented; enp-1 and enp-2 each with one plumose inner seta; enp-3 with one unipinnate outer spine, and three plumose setae (two distal and one inner). Exopod 3-segmented; exp-1 with one smooth outer spine and one plumose inner seta; exp-2 with one bipinnate outer spine and one plumose inner seta; exp-3 with three smooth outer spines, two plumose distal setae, and two plumose inner setae.
P3 ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6 ). Coxa ornamented with spinular rows of unequal length on anterior surface, and row of spinules along outer margin. Basis smooth, with some spinules at base of slender outer seta. Endopod 3-segmented; enp-1 with one small pore on anterior surface, and one plumose inner seta; enp-2 with one plumose inner seta; enp-3 with one smooth outer spine, and three plumose setae (two median distal and one inner). Exopod 3-segmented; exp-1 and exp-2 each with one smooth outer spine and one plumose inner seta; exp-3 with three outer spines (two smooth and one unipennate), two plumose distal setae, and two plumose inner setae.
P4 ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ). Praecoxa small and naked. Coxa with row of spinules along distal outer margin. Basis with one slender outer seta, and small spinules on anterior surface. Endopod 3-segmented; enp-1 with one plumose inner seta; enp-2 unarmed; enp-3 with one unipinnate outer spine and three plumose setae (two distal and one inner). Exopod 3- segmented; exp-1 and exp-2 each with one bipinnate outer spine and one plumose inner seta; exp-3 with one smooth outer spine, two unipinnate outer spines, two distal plumose setae, and two plumose inner setae. Exp-2 and exp-3 each with a pore on anterior surface.
Armature formula of swimming legs as follows (Arabic numbers represent setae, Roman numbers represent spines):
| Basis | Exopod | Endopod | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | I-I | I-0; I-1; I,II,I | 0-1; 0-0; I,I,1 |
| P2 | I-0 | I-1; I-1; III,2,2 | 0-1; 0-1; I,2,1 |
| P3 | 1-0 | I-1; I-1: III,2,2 | 0-1; 0-1; I,2,1 |
| P4 | 1-0 | I-1; I-1: III,2,2 | 0-1; 0-0; I,2,1 |
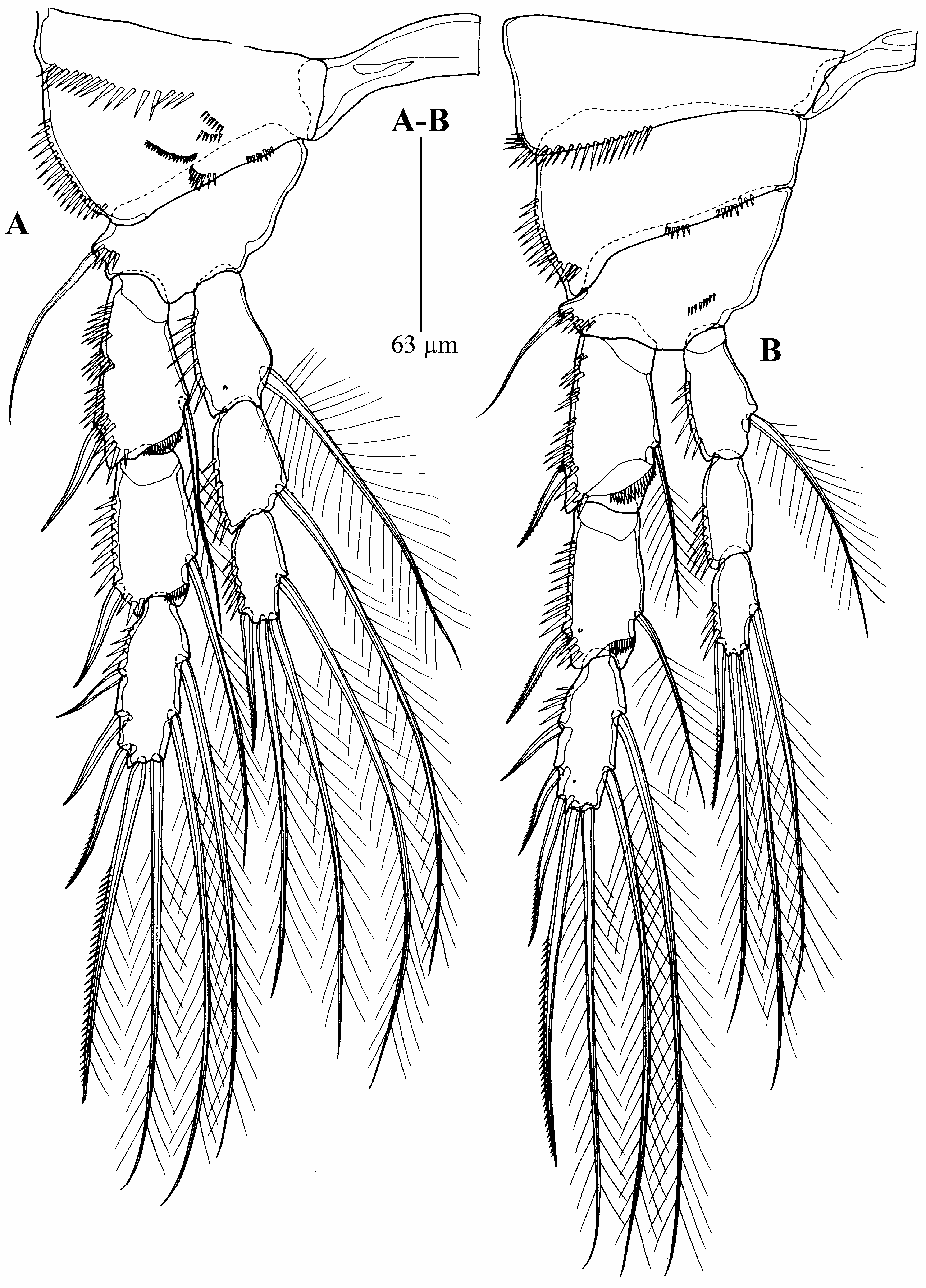
P5 ( Fig. 8C View FIGURE 8 ) with separate exopod and baseoendopod (fused basis and endopod); with spinular row along outer margin; without intercoxal sclerite and not fused medially. Exopod ovoid and small with five bipinnate setae of unequal length, second outermost longest. Baseoendopod with long smooth outer basal seta, and with five setae (innermost smooth, and four bipinnate outer elements), the second innermost longest.
Description of male. Total body length of allotype ( Fig. 7A–B View FIGURE 7 ) 902 µm. Total body length of paratypes 796– 929 µm (n = 12, mean = 874 µm). Rostrum ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ), general body shape and size similar to those of female. Sexual dimorphism expressed in antennule, antenna, P2, P5, P6, and urosomal segmentation.
Urosome ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9 ) 6-segmented, comprising P5-bearing somite, genital somite, three abdominal somites and anal somite. Third to sixth urosomites with small spinules along ventral posterior margin. Ornamentation as in female.
Antennule ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ) subchirocer, 7-segmented, with smooth setae. First segment with small spinules on anterior surface, fourth segment shortest, fifth segment largest and globularly expanded with one plumose seta and long aesthetasc, sixth segment forming claw-like outer process, seventh segment with six setae (two short and four long) and acrothek. Armature formula: 1-(1), 2-(1), 3-(10), 4-(3), 5-(1 + (1 + ae)), 6-(0), 7-(7 + acrothek).
Antenna ( Fig. 7D View FIGURE 7 ) similar to female condition, except for anterior edge of allobasis without abexopodal seta, and fewer spinules on anterior surface. Except for bipinnate proximal seta on exp-1 all other exopodal setae naked.
P2 ( Fig. 9B View FIGURE 9 ). Basis with one smooth outer seta. Endopod 3-segmented and modified; enp-2 with curved spinulose inner seta almost twice as long as enp-3, and distinct spiniform outer apophysis; enp-3 small, with one unipinnate outer spine and two distal setae (one spinulose outer and one smooth inner) and one plumose outer seta. Exopod 3-segmented, as in female.
P3 and P4 as in female.
P5 ( Fig. 8D View FIGURE 8 ) baseoendopod bearing one smooth basal outer seta, and one smooth (endopodal) inner seta. Exopod armed with five setae of unequal length: innermost one smooth; second inner one bipinnate and longest; apical bipinnate; outermost plumose; second outer smooth.
P6 ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9 ) represented by three smooth setae, innermost longest, and middle one shortest.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |