Tephritis kutuki, Yaran & Görmez, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4838.2.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8450BE39-2D8B-49CA-9BE2-04C396A0D882 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4404455 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A6058939-FFEB-FF98-FF33-F431FD57FE20 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tephritis kutuki |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Tephritis kutuki sp. nov
( Figures 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 )
Type material: Holotype ♀: Turkey, Bayburt, Kop Mountain, Şehitlik Hill , 28.VI.2018, 40 00’ N, 40 31’ E, 2067 m. leg. M. Yaran & V. Görmez GoogleMaps . Paratypes 9 ♀♀, 18 ♂♂: labels as in the holotype ( GUGT) .
Diagnosis. Tephritis kutuki sp. nov. can be distinguished by the following combination of characters: wing with moderately developed pattern not extending into anal cell and anal lobe, brown spots at the end of vein R 4+5 and M joined to each other and widened as typical apical fork but separated from main dark area (as in Tephritis bimaculata Freidberg, 1981 and T. turkeri Kütük & Yaran, 2020 ); cell m with three large hyaline areas separated two narrow dark rays; abdomen shiny black (as in T. heringinella Korneyev, 2017 ), and with white setae; pointed and short aculeus.
The new species is similar to Tephritis dioscurea (Loew, 1856) in having wing with wide, subrectangular spots at the apices of R 4+5 and M either separated or narrowly fused to each other or remaining dark pattern, anal cell and anal lobe mostly or entirely hyaline, short oviscape, short and pointed aculeus, swollen spermathecae. It differs from T. dioscurea by the pterostigma completely brown without a hyaline spot (in T. dioscurea , pterostigma present one small hyaline spot); larger discal spot; larger three hyaline spots in cell r 2+3 (in T. dioscurea , smaller), two pale small dots surrounding upper part of crossvein r-m (in T. dioscurea , four small dots surrounding crossvein r-m separated); two small hyaline dots at the level of crossvein dm-cu (in T. dioscurea , usually having one small hyaline dot); completely black femora, shiny black abdomen, without gray microtrichose tergites 4–6.
The new species is very similar to T. turkeri with separated apical fork, anal cell and anal lobe mostly or entirely hyaline and cell m with three large hyaline areas separated two narrow dark rays. It is distinguished from T. turkeri with completely brown pterostigma, three cloven hyaline spots in cell r 2+3, completely black femora, shiny abdomen, shorter oviscape, slightly shorter than tergites 5 and 6 combined, (in T. turkeri longer than tergites 5–6 combined), shorter and pointed aculeus not incised (in T. turkeri aculeus incised on tip), shorter and swollen spermathecae (in T. turkeri moderately long spermathecae), basal part of phallus glans sclerotized (in T. turkeri fully membranous phallus glans)
The new species is similar to T. corolla Richter, 1975 , T. heringinella and T. sauterina Merz, 1994 with shiny abdominal tergites 4–6 and short oviscape. It is distinguished easily from them with its unique wing pattern and completely black femora. The new species is also similar to female of T. sahandi with shiny abdominal tergites 5–6 (in T. turkeri with abdominal tergites 4–6) and completely black femora; however, it easily distinguishes from T. sahandi with its unique wing pattern.
The new species is also similar to T. bimaculata , T. jabeliae Freidberg, 1981 , and T. spreta (Loew, 1862) , in having two hyaline spots in R 2+3 combined with the spots on the apices of veins R 4+5 and M separated from the remaining wing pattern, clearly differing from them by having completely black femora, shining abdominal tergites, shorter oviscape.
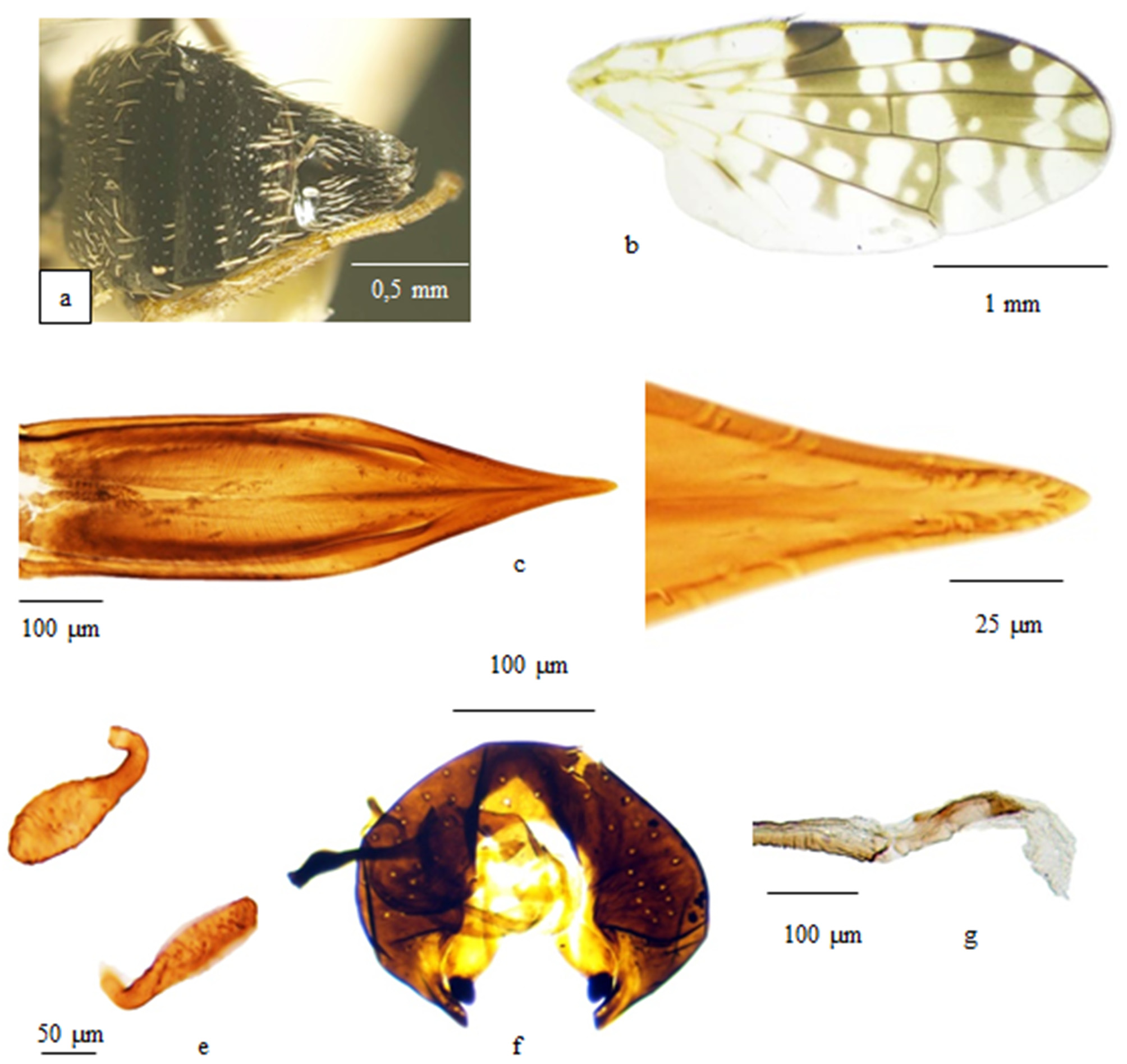
Description. Head: Dark yellow to brown, ocellar triangle black, occiput v-shaped and black; frons 1.1 times as long as wide; eye 1.15 times as long as wide; frontal, ocellar, inner vertical and anterior orbital setae dark brown and acuminate, rest of setae and setulae on head yellowish white; antenna yellow to brown, arista dark brown, pedicel with black setulae, third flagellomere of antenna 1.75 times as long as wide; gena yellow with whitish setulae; palpus yellow with white setulae ( Figure 1 View FIGURE 1 c–d).
Thorax: Ground color black, shining and gray microtrichose; setulae white and acuminate; all setae black and acuminate, except katepisternal setae whitish; apical scutellar setae 0,5 times as short as basal scutellar setae; halter yellow ( Figure 1e View FIGURE 1 ).
Wing: Pattern brown, apical fork developed and separated from main dark area. Basal cells bc, bm and bcu hyaline, cell c hyaline with narrow brown spot at middle; pterostigma brown without hyaline spot; cell r 1 brown from posterior to pterostigma with two trapeziform hyaline spots; hyaline spots of cell r 1 separated by narrow dark ray; apex of r 1 brown, without hyaline spot; cell r 2+3 hyaline at base, with dark area posterior to pterostigma; in cell r 2+3 three hyaline spots posterior to spots of r 1 separated by narrow dark rays or partly merged one small hyaline spot under the distal spot; apical half of cell br dark, usually with two small hyaline spots and tiny dot; crossvein r-m dark and two side of vein with two small pale gray spots at the level of vein R 2+3; vein R 4+5 bare; cell r 4+5 at the level of dm-cu with one large hyaline spot and one round small hyaline spot; having two hyaline spots in R 2+3 combined with the spots on the apices of veins R 4+5 and M; brown spots at the end of vein R 4+5 and M joined each other but separated from main dark area; basal half of cell dm hyaline, rest part of cell is brown, with two large hyaline spots and two smaller hyaline spots on the left side of crossvein dm-cu; cell m with three large hyaline areas separated by two narrow dark rays; apical dark ray of cell m reach hind margin of wing; basal dark rays of cell m short, not reaching hind margin of wing; cell cu with pale dark irregular pattern; rest of cell almost hyaline; vein A darkened at base, anal cell otherwise hyaline; anal lobe hyaline ( Figure 2b View FIGURE 2 ).
Legs: Brown; except black femora; with whitish and black mixed setulae ( Figure 1 View FIGURE 1 a–b).
Female abdomen: Ground color shining black; tergites 4–6 without microtrichia, sparsely white setulose, tergites 1–3 densely gray microtrichose and white setulose; tergite 6 with black marginal setae ( Figure 2a View FIGURE 2 ). Female terminalia: oviscape shining black, short, as long as tergite 6, sparsely white setulose on basal part, brown setulose and setose posteriorly; aculeus about 4 times as long as wide, moderately narrowed on apex; apex of aculeus pointed and not incised on tip; spermathecae papillose and slightly swollen in the middle part of bulb, about 2 times as long as wide ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 c-d-e).
Male abdomen: tergites shining, ground color gray, very sparsely microtrichose and white setulose, tergite 5 with black marginal setae. Male terminalia: Epandrium oval as in other Tephritis spp., phallus glans short and membranous at apex, sclerotized on basal part, preglans bare ( Figure 1 View FIGURE 1 f–g).
Measurements: Male: BL = 3.4–3.7 mm; WL = 2.9–3.2 m (n = 10). Female: BL = 3.8–4.1 mm; WL = 3.1–3.3 mm (n = 10); AL = 0,65 mm (n = 1)
Host plant: Unknown.
Etymology. The species named after Prof. Dr. Murat Kütük, who is an important expert of Tephritidae species and excellent supervisor of the authors.
Zoobank number. The ZooBank Life Science Identifier (LSID) for this publication is: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4E859FDE-9253-42F9-8892-215648B1343D
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |