Simulium ( Gomphostilbia ) hiroyukii
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3911.3.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CC0AAA02-C395-4E29-93E9-62B02B966541 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6119268 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B9398785-1C12-FFC6-AAAA-FF5A8FEA1859 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Simulium ( Gomphostilbia ) hiroyukii |
| status |
|
Simulium ( Gomphostilbia) hiroyukii View in CoL Ya’cob and Sofian-Azirun, sp. nov.
Female (n=8). Body length 2.8–3.0 mm. Head. Nearly as wide as thorax. Frons black, shiny, moderately covered with yellowish-white scale-like recumbent short hairs interspersed with several dark simple longer hairs along each lateral margin; frontal ratio; 1.9:1.0:3.4–3.7; head ratio 1.0:5.3–5.9. Fronto-ocular area well developed, narrow, directed dorsolaterally. Clypeus black, shiny, gray pruinose, densely covered with yellowish-white short hairs interspersed with several dark longer hairs on each side. Labrum 0.6–0.7 times length of clypeus. Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and nine flagellomeres, medium to dark brown except scape, pedicel and base of first flagellomere yellow. Maxillary palp composed of five segments, dark brown, proportional length of third, fourth, and fifth segments 1.0:1.0–1.1:2.4–2.5; third segment of moderate size ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, B); sensory vesicle ellipsoidal, medium long, 0.36–0.46 times length of third segment and with medium–sized opening. Maxillary lacinia with 12–14 inner and 16–18 outer teeth. Mandible with 21 inner and 8 or 9 outer teeth. Cibarium ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C) medially forming sclerotized plate folded forward from posterior margin, with strongly sclerotized medial longitudinal ridge bearing deep notch apically. Thorax. Scutum black, shiny when illuminated at certain angles, densely covered with white or yellowish-white scale-like recumbent short hairs. Scutellum brownish-black, slightly shiny when illuminated at certain angles, covered with yellowish-white short hairs and dark-brown long upright hairs along posterior margin. Postnotum brownish-black and bare. Pleural membrane bare. Katepisternum brownish-black to black, longer than deep, shiny when illuminated at certain angles, moderately covered with short hairs. Legs. Foreleg: coxa medium brown; trochanter light brown except base yellow; femur light to medium brown with apical cap dark brown; tibia medium brown with extreme base yellow and apical cap dark brown, and median portion largely light brown, moderately covered with white (shiny in light) short hairs on outer surface; tarsus black, with moderate dorsal hair crest; basitarsus somewhat dilated, 6.2–6.3 times as long as its greatest width. Midleg: coxa medium brown except posterolateral surface brownish-black; trochanter light brown except base yellow; femur medium to dark brown except base yellow and apical cap dark brown; tibia medium brown except basal tip yellow and apical cap dark brown, and with white (shiny in light) short hairs on outer and posterior surfaces of basal twothirds; tarsus dark brown except basal half of basitarsus dark yellow. Hind leg: coxa medium brown; trochanter yellow; tibia ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D) medium to dark brown except base yellow and apical cap brownish-black, moderately covered with white (shiny in light) short hairs on outer and posterior surfaces of basal two-thirds; tarsus darkbrown to brownish-black except basal two-thirds of basitarsus (though base light brown) and basal half of second tarsomere yellowish-white ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 E); basitarsus narrow ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 E), nearly parallel-sided, 7.40 times as long as wide, and 0.53–0.56 and 0.47–0.53 times as wide as greatest width of tibia and femur, respectively; calcipala ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 E) well developed, as long as wide, and 0.63 times as wide as greatest width of basitarsus; pedisulcus well developed; claw ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 F) with large basal tooth 0.46 times length of claw. Wing. Length 2.3–2.4 mm. Costa with dark brown spinules and light brown hairs. Hair tuft on base of radial vein dark brown. Basal portion of radius fully haired. Basal cell absent. Halter . Clear white except basal stem partially darkened. Abdomen. Basal scale medium brown, with fringe of yellowish-white hairs. Dorsal surface of abdomen medium to dark brown except base of segment 2 yellow, moderately covered with dark short to long hairs; tergites 2 and 6–9 shiny when illuminated at certain angles. Ventral surface of abdomen light to medium brown except base of segment 2 yellow; sternal palte on segment 7 undeveloped. Genitalia. Sternite 8 ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 G) bare medially, with 20–22 medium-long to long hairs and three slender short hairs on each side. Ovipositor valves triangular (though medioposterior corners rounded), tapered laterally, thin, membranous, moderately covered with microsetae interspersed with two short hairs; inner margin slightly sinuous, moderately sclerotized, and somewhat separated from each other. Genital fork ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 H) of usual inverted Y-form, with slender stem; arms of moderate width, moderately folded medially, with short posteromedial lobe. Paraproct in ventral view ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 I) with anterolateral tip unsclerotized and anteromedian margin darkened, with four or five sensilla on anteromedial surface; paraproct in lateral view ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 J) somewhat produced ventrally, 0.44 times as long as wide, with 20 or 21 medium-long to long hairs on ventral and lateral surfaces. Cercus in lateral view ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 J) short, rounded posteriorly, 0.44 times as long as wide. Spermatheca ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 K) oblong, 1.4 times as long as greatest width, well sclerotized except duct and small area near juncture with duct sclerotized, and with many fissures on surface; internal setae absent; both accessory ducts slender, subequal in diameter to major one.
Male (n=8). Body length 2.8–3.0 mm. Head. Slightly wider than thorax. Upper eye consisting of 14 or 15 vertical columns and 16 or 17 horizontal rows of large facets. Clypeus as in female, but densely covered with dark hairs. Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and nine flagellomeres, brownish black; first flagellomere somewhat elongate, 1.56 times as long as second flagellomere. Maxillary palp with five segments; proportional lengths of third, fourth, and fifth segments 1.00:1.05–1.06:2.68–2.74. Sensory vesicle ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A) small, 0.23 times as long as third segment, with medium-sized opening medially. Thorax. Scutum dark brown, with whitish pruinose (silvery shining in light) pattern composed of anterior pair of triangular patches on shoulders (often fused when illuminated from dorsally and viewed from front), longitudinal band along each lateral margin and large patch on prescutellar area; scutum densely covered with bright brassy recumbent short hairs. Scutellum brown, with bright brassy short hairs and several dark long marginal hairs. Postnotum brown, whitish pruinose (silvery shiny when illuminated at certain angles), and bare. Pleural membrane and katepisternum as in female. Legs. Nearly medium brown to brownish black except hind trochanter pale brown, basal half of both hind basitarsus and second tarsomere whitishyellow. Fore basitarsus slender, 6.1–6.4 times as long as its greatest width. Hind basitarsus ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C) somewhat enlarged, spindle-shaped, 4.6 times as long as wide, 0.8 and 1.2 times as wide as greatest width of tibia ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B) and femur respectively. Calcipala ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C) well-developed, nearly as long as wide. Pedisulcus well developed. Wing. Length 2.2 mm. Other features as in female except subcosta bare. Abdomen. Basal scale dark brown, with fringe of dark hairs. Dorsal surface of abdomen brownish black, covered with dark hairs; segments 2 and 5–7 each with dorsolateral pair of shiny, whitish pruinose patches. Genitalia. Coxite in ventral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D) nearly rectangular, 1.8 times as long as wide. Style in ventrolateral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 E) 0.7 times length of coxite, tapered toward apical tip; style in medial view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 H) gently curved inward. Ventral plate in ventral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D) tranverse, subquadrate, 0.55 times as long as wide, with lateral margin depressed basally, somewhat divergent posteriorly and anterior margin produced anteriomedially, with posterior margin concave and with microsetae almost entirely on ventral surface; basal arm divergent, then slightly convergent apically; ventral plate in lateral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 H) produced ventrally along posterior margin; ventral plate in caudal view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 G) rounded ventrally. Paramere ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 I) with three long parameral hooks and several small ones. Median sclerite weakly sclerotized, plate-like, widened toward tip, with round and unpigmented tip.
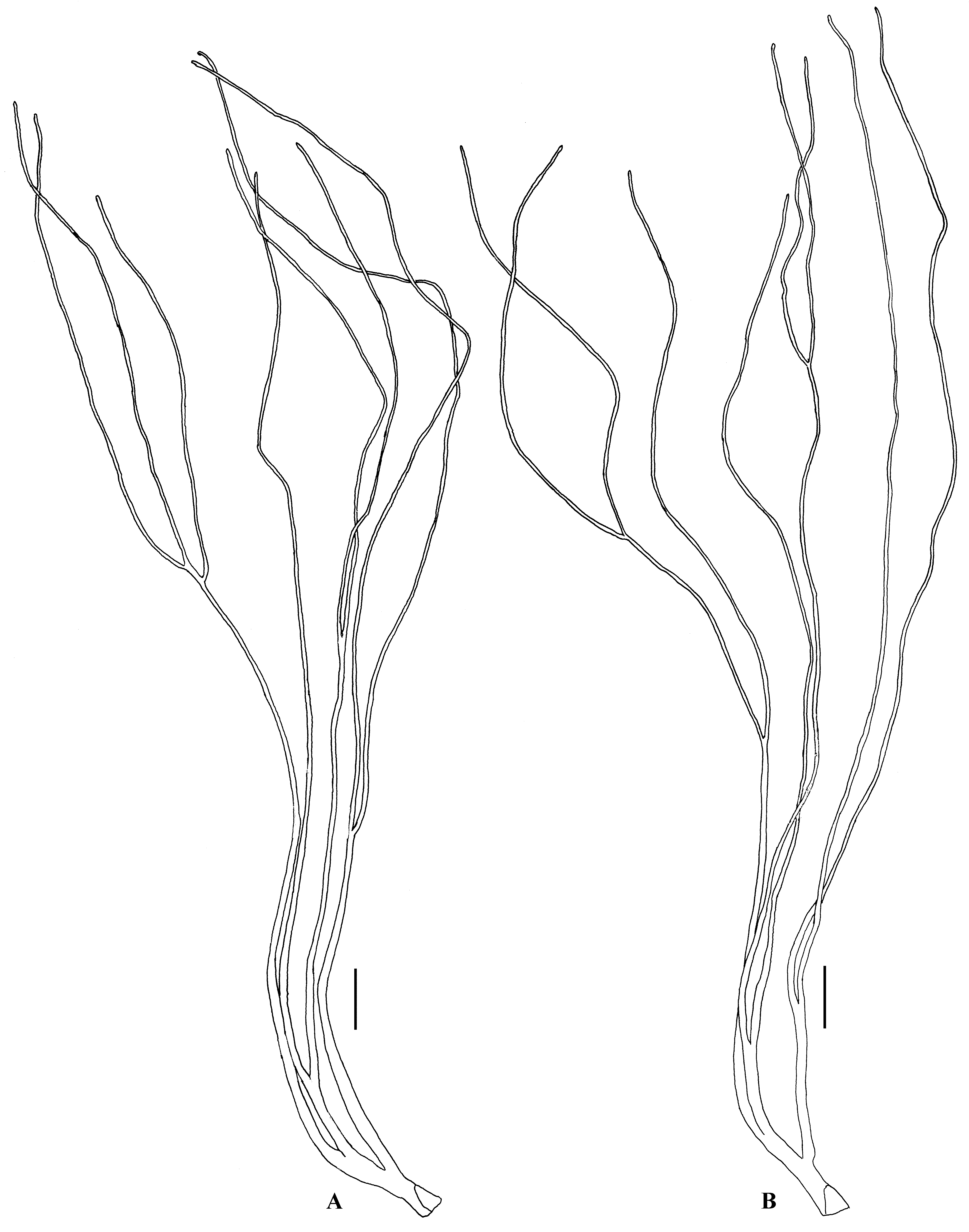
Pupa (n=11). Body length 3.0– 3.2 mm. Head. Integument yellow, moderately covered with round tubercles; antennal sheath without tubercles; frons with three pairs of unbranched long trichomes with coiled or uncoiled apices; face with pair of unbranched long trichomes with coiled apices; three frontal trichomes on each side arising close together, subequal in length to one another and somewhat longer than facial one. Thorax. Integument yellow, moderately covered with small round tubercles, with three unbranched long mediodorsal trichomes with coiled or uncoiled apices, two unbranched long anterolateral trichomes (one with coiled apex, one with uncoiled apex), one unbranched long mediolateral trichome with uncoiled apex, and three unbranched ventrolateral trichomes with uncoiled apices (one long, two short) on each side. Gill ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A, B and Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A, B) composed of eight slender thread-like filaments arranged as [(2+1)+(1+2)]+2 filaments from dorsal to ventral, with somewhat swollen basal fenestra at base; common basal stalk short ( 0.2 mm), 0.74 times length of interspiracular trunk; dorsal triplets with medium to long primary stalk ( 1.1–1.5 mm) with the longest one almost two-thirds of total gill length; secondary stalk short to medium-long ( 0.1–0.8 mm); middle triplets with primary stalk of moderate length ( 0.2–0.3 mm) and secondary stalk long ( 1.4–2.2 mm), 5.4–7.7 times length of primary stalk, with longest stalk almost two–thirds of total gill length; ventral paired filaments with medium to long stalk ( 0.5–1.1 mm), 1.7–4.2 times length of primary stalk of middle triplets; all filaments yellowish-brown, lying close together, gradually tapered toward apex; entire length of filaments (measured from base of gill to tips of filaments) based on one pupa, 3.5–3.6 mm for dorsal triplet, 3.4–3.7 mm for middle triplet and 3.8 mm for ventral paired filaments; cuticle of all filaments with welldefined annular ridges and furrows though gradually becoming indistinct from middle to apex, densely covered with minute tubercles. Abdomen. Dorsally all segments light yellow; segment 1 without tubercles and with one unbranched slender long hair-like seta on each side; segment 2 with one unbranched slender long hair-like seta and five short somewhat spinous setae submedially near posterior margin on each side; segments 3 and 4 each with four hooked spines and one short somewhat spinous seta near posterior margin on each side; segments 6–9 each with spine-combs in tranverse row, comb-like groups of minute spines near anterior margin and two unbranched short setae near posterior margin on each side; segment 9 with pair of broad plate-like terminal hooks, of which outer margin crenulated ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 C). Ventrally, segment 4 with one unbranched hook and few unbranched short setae on each side; segment 5 with pair of bifid hooks submedially and few unbranched short slender setae on each side; segments 6 and 7 each with pair of bifid inner and unbranched outer hooks somewhat spaced from each other and few unbranched short slender setae on each side; segments 4–8 each with comb-like group of minute spines. Each side of segment 9 with three grapnel-shaped hooklets. Cocoon. Wall pocket-shaped, moderately woven, somewhat extended ventrolaterally; anterior margin thickly woven, with dorsal portion not produced anteriorly when viewed dorsally; posterior half with floor roughly or moderately woven; individual threads visible; 3.2–3.6 mm long by 1.7–2.0 mm wide.
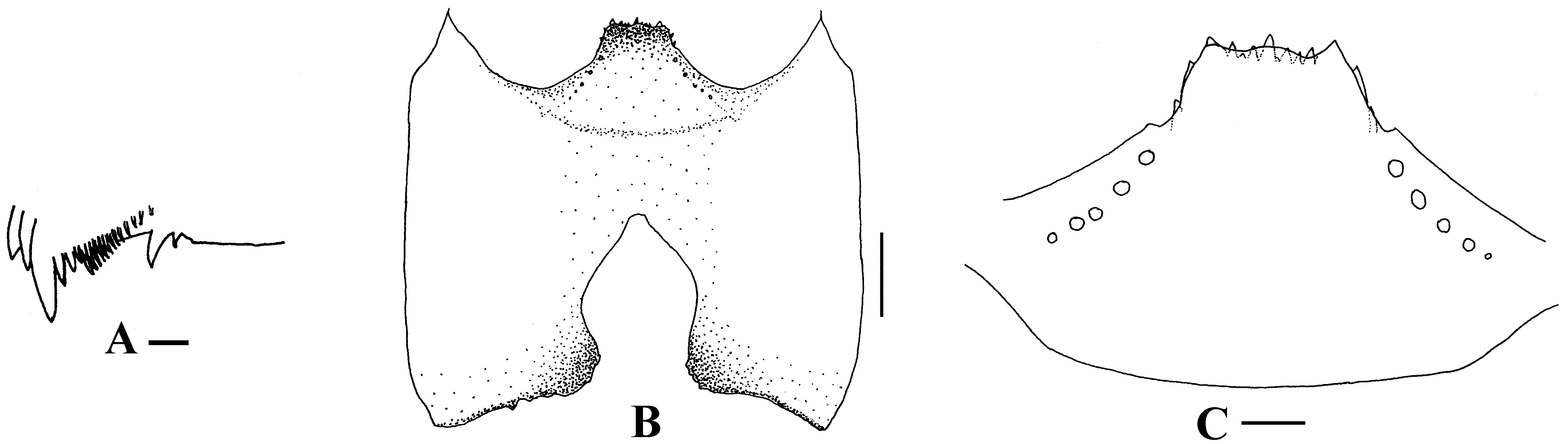
Mature larva (n = 2). Body length 5.7 mm. Body ochreous on thorax, brown on dorsal and dorsolateral surfaces of abdomen though intersegmental from segment 1 to segment 5, pale. Cephalic apotome whitish-yellow to yellow; head spots positive. Lateral surface of head capsule yellow except eye-spot region white; eyebrow indistinct though one dark sport present medially; two large spots and one small spot near posterior margin and two small spots below eye-spot region faintly to moderately positive. Mandible ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A) with serrations consisting of two teeth (one large and one small); large tooth at acute angle with mandible on apical side; comb-teeth composed of three teeth shortened from first to third; supernumerary serration absent. Ventral surface of head capsule ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 B) yellow except medial large portion darkened, and basal area on each side of postgenal cleft dark brown; one elongate and one round spot on each side of postgenal cleft markedly positive. Cervical sclerite composed of two faint small elliptical pieces, not fused to occiput, widely separated medially from each other. Antenna consisting of three articles and apical sensillum, much longer than stem of labran fan; proportional lengths of first, second, and third articles 1.00:0.76:1.04. Labran fan with 42 main rays. Hypostoma ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 C) with nine apical teeth in row; median and corner teeth well developed; lateral margin nearly smooth; five or six hypostomal bristles lying slightly divergent posteriorly from lateral margin on each side. Postgenal cleft medium-long, 2.2 times length of postgenal bridge. Thoracic cuticle bare. Histoblast of pharate pupal gill with eight slender thread-like filaments. Abdominal cuticle bare except both sides of anal sclerite moderately covered with unbranched colorless setae and each lateral surface just above ventral papilla also sparsely covered with unbranched colorless setae. Rectal scales minute and colorless. Rectal organ compound, with 14 or 15 secondary lobules per lobe. Anal sclerite of usual X-form, with anterior arms nearly as long as posterior ones, broadly sclerotized at basal juncture; sensilla absent on basal juncture and just posterior to basal juncture area; accessory sclerite absent. Last abdominal segment much expanded ventrolaterally forming large ventral papilla on each side. Posterior circlet with 82 rows of up to 14 hooklets per row.
Type specimens. Holotype female, reared from pupa (preserved with associated pupal exuviae and cocoon in 80% ethanol) collected at Church Camp, Mount Murud, Sarawak at altitude 2,115 m (03°55′36.5″N, 115°30´50.6”E), 13. VI. 2013 by Z. Ya’cob. Paratypes: eight males, seven females (with associated pupal exuviae and cocoons), all reared from pupae, and two mature larvae, same data as holotype.
Ecological notes. Pupae and larvae were collected from grasses and slender tree sticks in water of a small, slow and clean stream flowing on blackish muddy streambed (width 0.5 ̶ 0.6 m, depth 10 cm), partially shaded by montane plants, with water temperature 14.4°C. This species was collected together with S. ( G.) sp. and S. ( S.) sp. The biting habit of the female remains unknown.
Etymology. The species name hiroyukii is in honour of Professor Hiroyuki Takaoka, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, who is currently a supervisor of Zubaidah Ya’cob.
Discussion. According to the key to species-groups of the subgenus Gomphostilbia (Takaoka 2012) , this new species is placed in the Simulium darjeelingense species-group (five species included) based on the darkened fore coxa of the female and male adults, and the enlarged male hind basitarsus ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C). This new species is readily distinguished from the related species of the group by the very long primary stalk of the dorsal triplet, and a similarly very long secondary stalk of the middle triplet ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A, B and Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A, B), a character very rarely occurring in species of the subgenus Gomphostilbia .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Gomphostilbia |