Rhytidaspis variata brevis, Ingrisch, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4661.2.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:71122FBE-0022-4D1F-B200-3946D770CAE8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5935385 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CEF84A-FFA7-FFFE-FF67-531F31263939 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhytidaspis variata brevis |
| status |
subsp. nov. |
Rhytidaspis variata brevis View in CoL ssp. n.
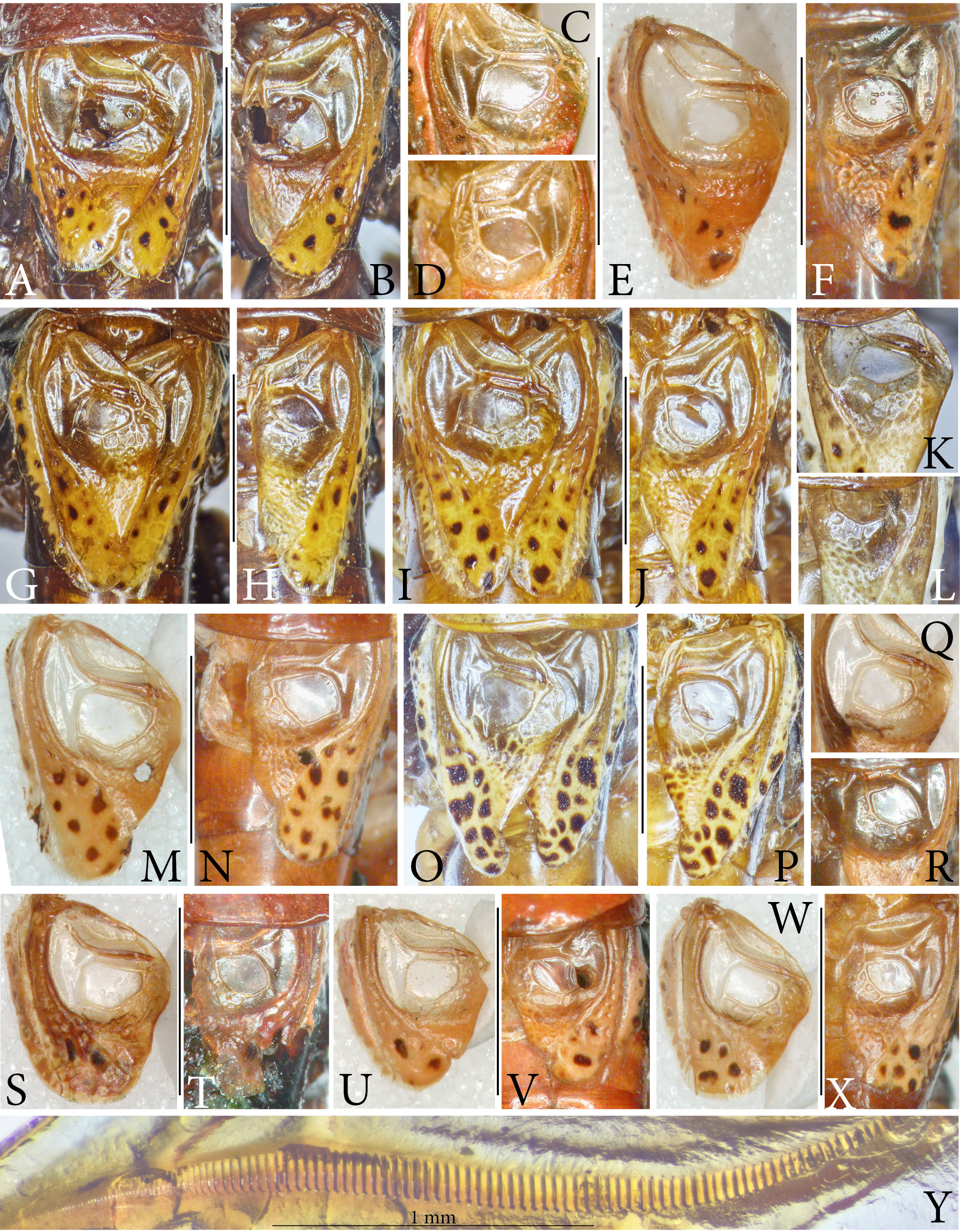
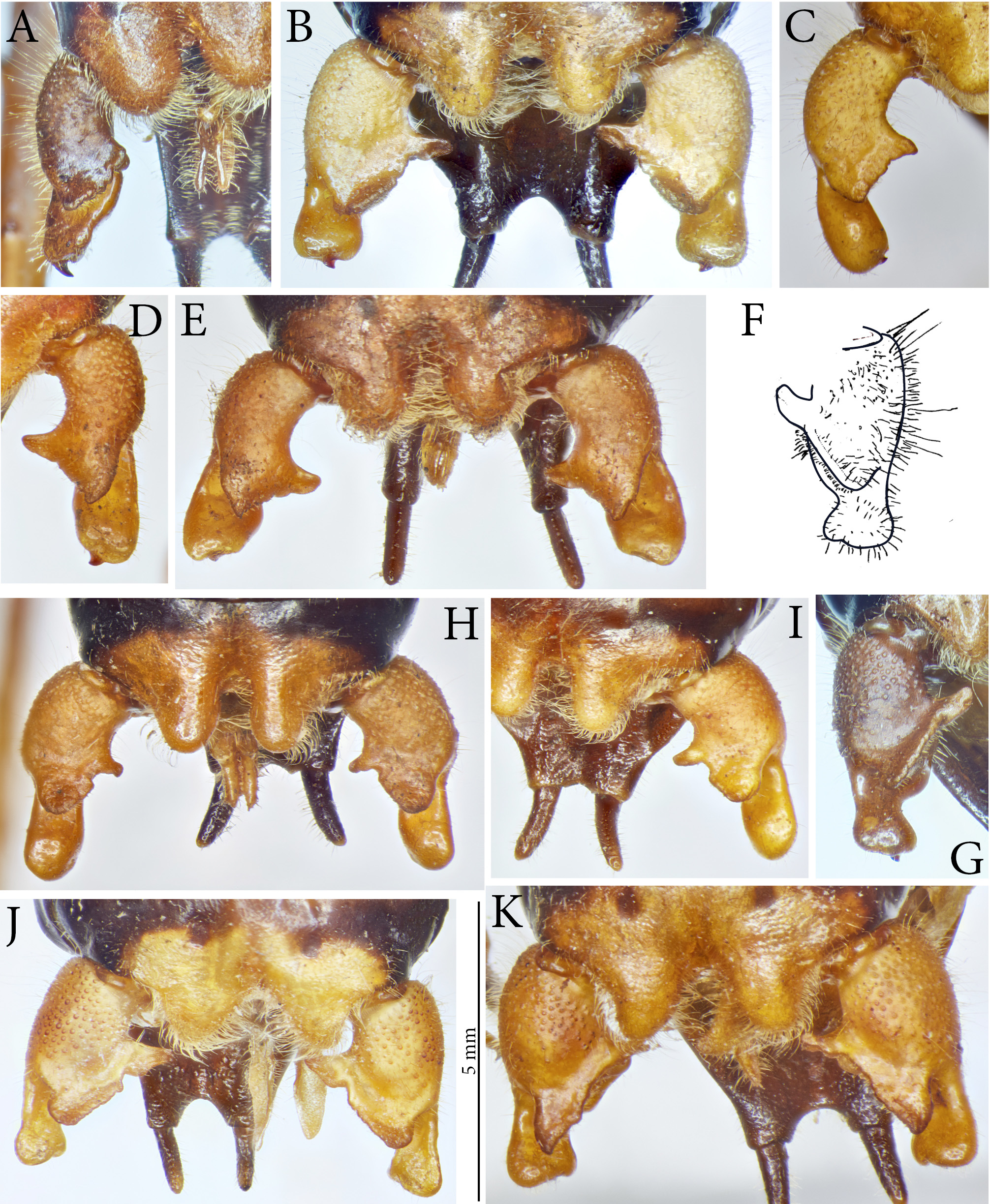
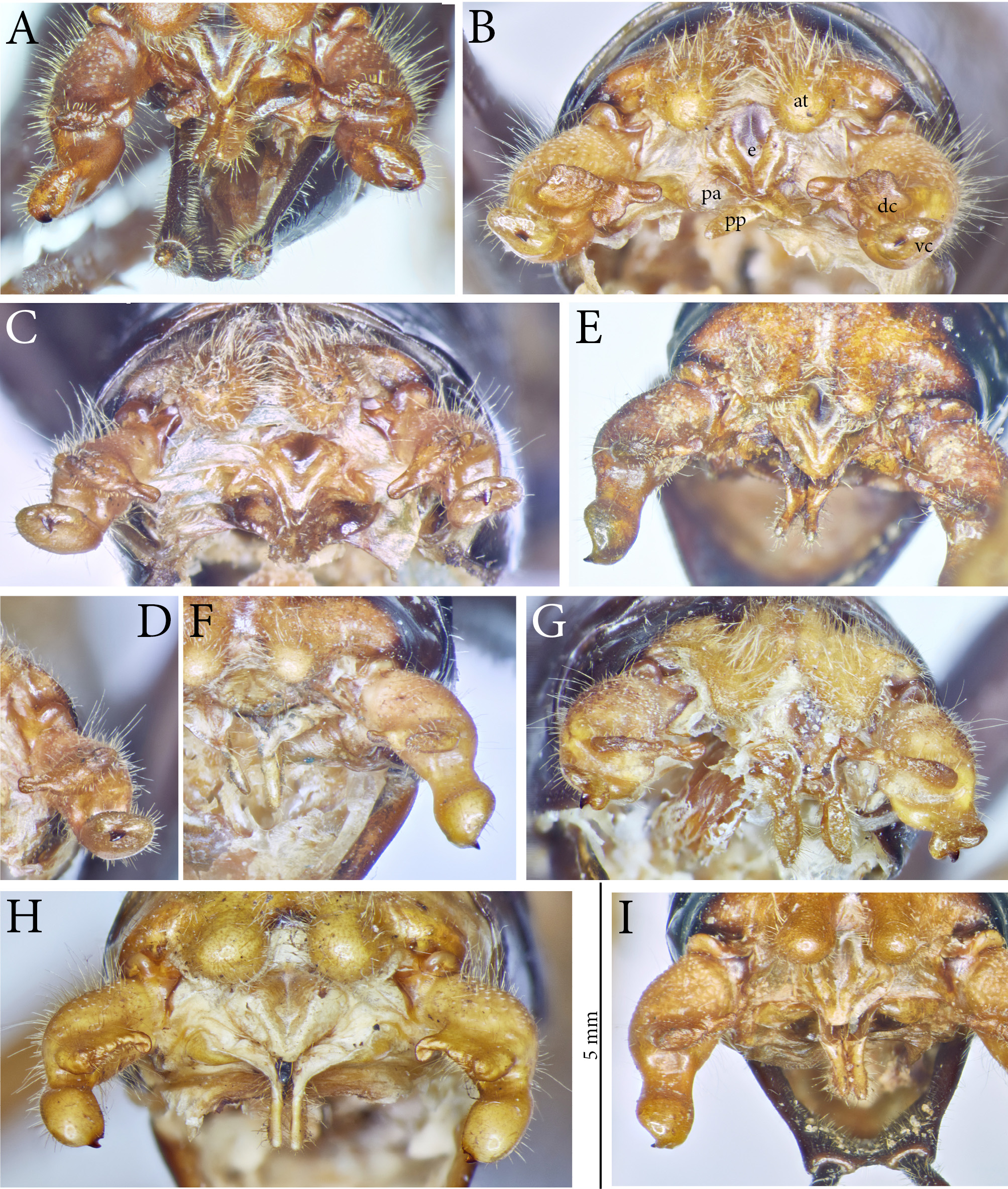
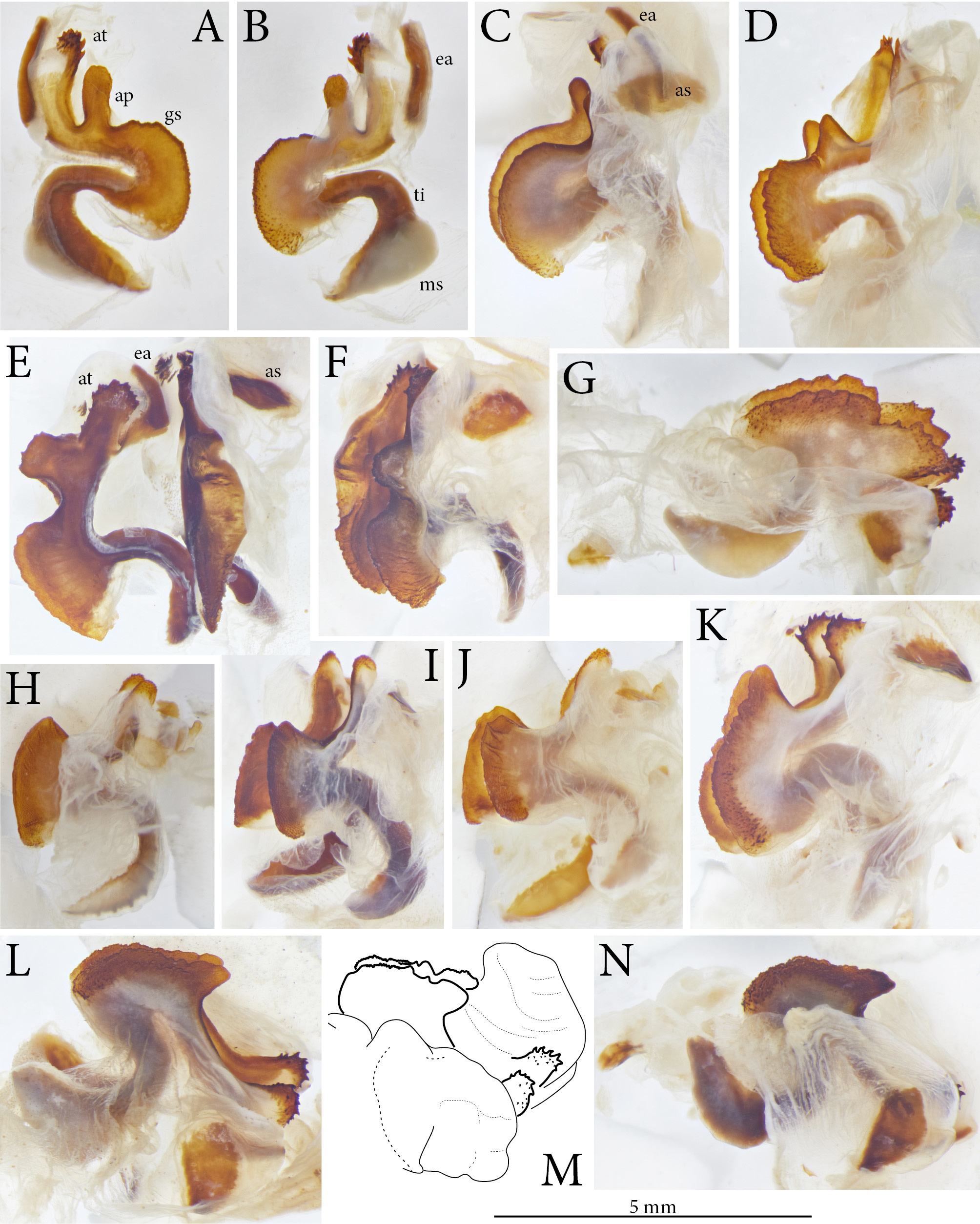
Figs. 1M View FIGURE 1 , 2F View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 K–L, 4F, 5J, 6G, 7R–S, 8N, 9D
Holotype (male): Indonesia, Papua: Freeport [4°5’S, 137°7’E], 26–28.iii. (year not recorded, label reads /174), leg. Xavier Miçonne—(Brussels, ISNB). GoogleMaps
Diagnosis. R. v. brevis ssp. n. differs from both other subspecies of R. variata by the dorsal apical lobe of the male cercus that has the proximal angle prolonged into a compressed triangular lobe and the distal end terminating into a narrowly rounded lobe while the proximal end is finger-shaped and the distal end about angularly projecting in both other subspecies. Moreover, the stridulatory file on the underside of the left tegmen is with 2.4 mm markedly shorter in R. v. brevis than in R. v. meja (2.6 mm) and R. v. variata (2.8 mm), while the density of teeth in the middle of the stridulatory file is nearly identical with that in R. v. variata but less dense than in R. v. meja .
Description of male. Tegmen behind stridulatory area with converging lateral margins, apex rounded. Stridulatory file on underside of left tegmen 2.4 mm long, with about 82 teeth, in middle with 27.5 teeth per 1 mm, toward end teeth become very small and dense ( Fig. 4F View FIGURE 4 ). Mirror on right tegmen with nearly parallel fore and hind margins, internal margin strongly oblique, 1.61 mm wide, 1.05 mm long ( Fig. 3L View FIGURE 3 ).
Cerci with dorsal apical lobe running oblique and parallel along inner margin of cercus trunk to nearly basal third of cercus; on apical side surpassing cercus trunk by a rounded lobe; margin of lobe very faintly wavy, the basal most area is separated by a v-shaped incision from the remainder, is dorsoventrally widened and terminates into a compressed-rounded lobe ( Fig. 5J View FIGURE 5 ); the ventral apical lobe is dorsoventrally compressed with dorsal side convex and ventral side concave; on ventral side it is separated from the cercus trunk by a transverse bulge; apical margin down-curved, sub-truncate but little concave in middle; a strong curved acute tooth inserted at inner half of apical margin pointing ventrad ( Fig. 6G View FIGURE 6 ).
Titillators with granular extension above the U-shaped curvature with margin in middle sub-straight to slightly concave, at proximal end rounded, and distally prolonged into a short, in lateral view triangular projection; separated by a long arm from little curved tip of titillator, which is only in apical area covered by spinules and a few larger teeth ( Figs. 8N View FIGURE 8 , 9D View FIGURE 9 ).
Coloration: Light to medium brown; pronotum and abdominal tergites of somewhat darker color ( Fig. 1M View FIGURE 1 ). Antennal scrobae, scapus and pedicellus black, flagellum yellowish ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ). Meso- and metapleura and lateral areas of abdominal tergites black. Apical cones of tenth abdominal tergites and cerci yellow. Tegmen bright yellow with black dots, stridulatory area semi-transparent. Legs yellow; femora with black transverse strokes; hind femur in basal area medium to dark red brown. Thoracic sternites and parts of coxae of all legs dark brown or black. Male subgenital plate black.
Measurements (1 male).—Body: 32; pronotum: 11; tegmen: 8; hind femur: 22.5; anterior femur: 11 mm.
Etymology. The name of the new subspecies refers to the short stridulatory file compared to both other subspecies; from Latin brevis short (Maskulinum and Femininum).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Conocephalinae |
|
Genus |