Manota geniculata, Hippa & Søli & Kurina, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4652.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2BE983B6-FDD2-4175-A7EB-295FFB4FE6DB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5940791 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/9CEE6B19-440B-46DD-91C5-AC615210ABBD |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:9CEE6B19-440B-46DD-91C5-AC615210ABBD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Manota geniculata |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Manota geniculata View in CoL sp. n.
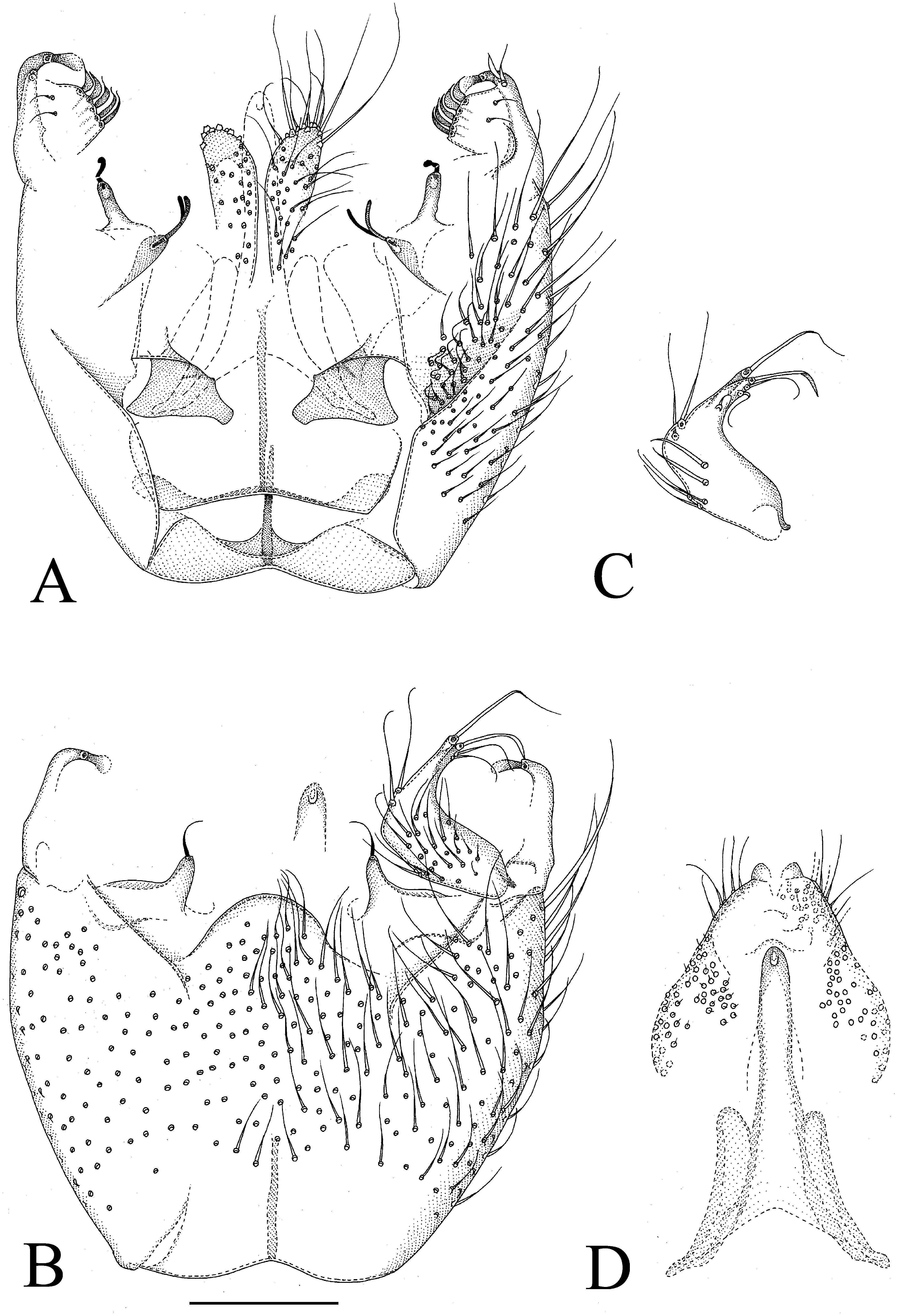
Figs 4 View FIGURE 4 A–D
Male. Colour. Head brown, face somewhat paler. Antenna light brown, including scape and pedicel. Clypeus and mouthparts pale yellowish. Thorax light brown to brown. Legs yellowish, apical fourth of hind femur slightly infuscated. Wing with light brownish tinge because of microtrichia; halter yellowish with dark brown knob. Abdomen brown, tergites laterally and sternites lighter. All vestiture pale, yellowish or brownish, thicker setae and trichia seeming darker than finer ones. Head. Antennal flagellomere 4 ca. 1.7 times as long as wide. Palpomere 3 of maxillary palpus with apicomesial thumb-like extension, with 4 apically curved sensilla; palpomere 4 with parasegment; palpomere 5 not measurable in holotype. Ten strong postocular setae. Thorax. Anepisternum with 43 setae; anterior basalare with 5 setae, laterotergite with 21 setae, preepisternum 2 non-setose; metepisternum with 15 setae. Legs. Mid and hind tibial organs absent. Wing. R 1 meeting C within basal half of costal margin; sclerotized part of M 2 extending to level of tip of R 1; wing length 1.9 mm. Hypopygium ( Figs 4 View FIGURE 4 A–D). Sternite 9 laterally fused to gonocoxa, posterior margin semicircular, tongue-like, extending to base gonostylus, anterior margin with a shallow concavity, anterior 1/3 non-setose, posterior 2/3 setose, setae similar to those on ventral side of gonocoxa but arranged more densely. Ventral medial margin of gonocoxa oblique. Parastylar lobe plate-like, medially drawn out to a finger-like lobe that has an apical seta. No paraapodemal lobe identifiable. Dorsal medial margin of gonocoxa complex, posteriorly with a row of five flattened and apically pointed megasetae at medial margin and a single equal megaseta at posterolateral corner. At the dorsal medial margin of gonocoxa, on more ventral level a plate-lake submembranous lobe with two medially directed simple and blunt megasetae at anteromedial corner, and a posteriorly directed geniculate megasetae arising from a finger-like basal body. Gonocoxal apodeme large, polygonal. One juxtagonostylar seta present as a flattened and apically expanded megaseta arising from a curved basal body which is about five times longer than the megaseta. Gonostylus slightly less than half of the ventral length of gonocoxa, medially geniculate, basal half twice as wide as apical half, basal half ventrally setose, dorsally non-setose except for two strong setae, apical half with two strong setae at basal portion of medial margin and 4–5 apical setae, 2–3 of them stronger, deviating from others. Aedeagus elongated subtriangular, without lateral shoulders, apex curved ventrad. In holotype, aedeagal apodemes turned upward, pressed against the basal part of aedeagus. Hypoproct large, extending posteriorly near to apex of gonostylus, number of ventral setae (sternite 10) ca. 50 on each half, the setae indistinctly divided into an anterior and posterior groups with ca. 45 and 5 setae, respectively. Cerci medially separated, setae scattered over the surface, apical 4–5 setae about twice as long as the rest of cercal setae.
Female. Unknown.
Etymology. The name is Latin, geniculata, ‘like the bent knee’, referring to the geniculate gonostylus.
Comments. Manota geniculata sp. n. belongs to a group of six Afrotropical species that have (1) setose laterotergite and anterior basalare, (2) the ventral setae of the hypoproct scattered over the whole ventral surface, (3) nonsetose preepisternum 2, and (4) the dorsal medial margin of gonocoxa posteriorly with a row of scale- or leaf-like megasetae. The other species being M. bracteata, M. foliolata , M. peltigera , M. pinnata and M. pinnulata . Manota geniculata , M. peltigera and M. pinnulata all have 3 flattened megasetae at the dorsal medial margin of gonocoxa posteriorly and a tongue-like posterior part of sternite 9. The latter character is shared also with M. foliolata , but that species has only two flattened megasetae posteriorly at the dorsal medial margin of gonocoxa. Of these three species, M. geniculata is most similar to M. pinnulata (cf. Hippa & Kurina 2012: fig. 18) but differs in having the gonostylus geniculate (subtriangular, widening from base to apex in M. pinnulata ), and in having the megasetae posteriorly at the dorsal medial margin of gonocoxa comma-like, apically pointed, and becoming medially wider towards posterior end of the row (megasetae scale-like, apically widening and enlarging in size towards posterior end of the row in M. pinnulata ).
Types. Holotype. Male , GABON, Makoku M’Passa Bale affl., 200 m, J. Legrand rec., 28.05– 5.06. 1979, Piège de Malaise (slide mounted, MNHN).
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |