Mannheimsia conica, Ament, Danilo César, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.212710 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5672333 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/306CBA7B-3F34-FFBA-2DA2-F9C2BD93F9F5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mannheimsia conica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mannheimsia conica View in CoL , sp. nov.
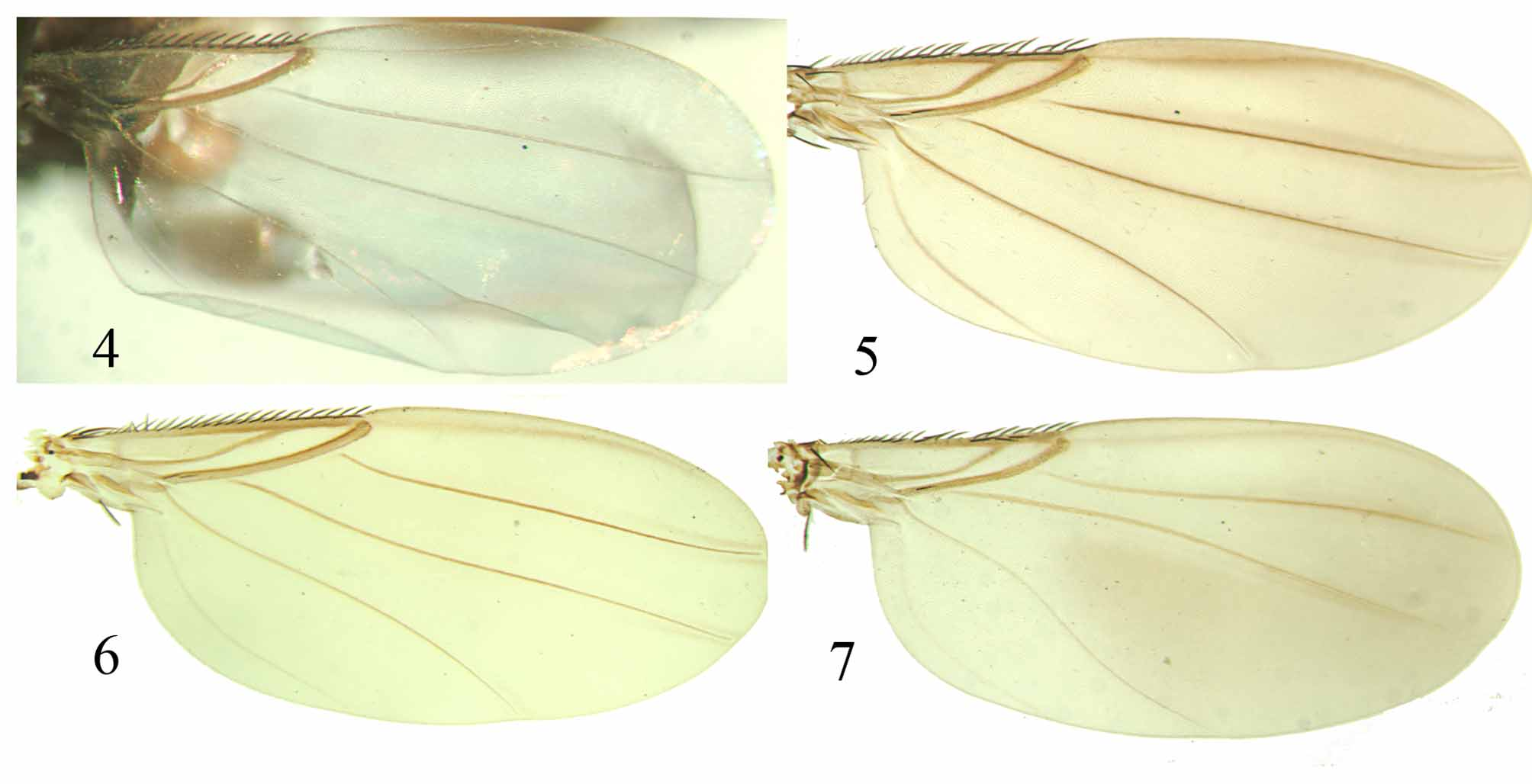
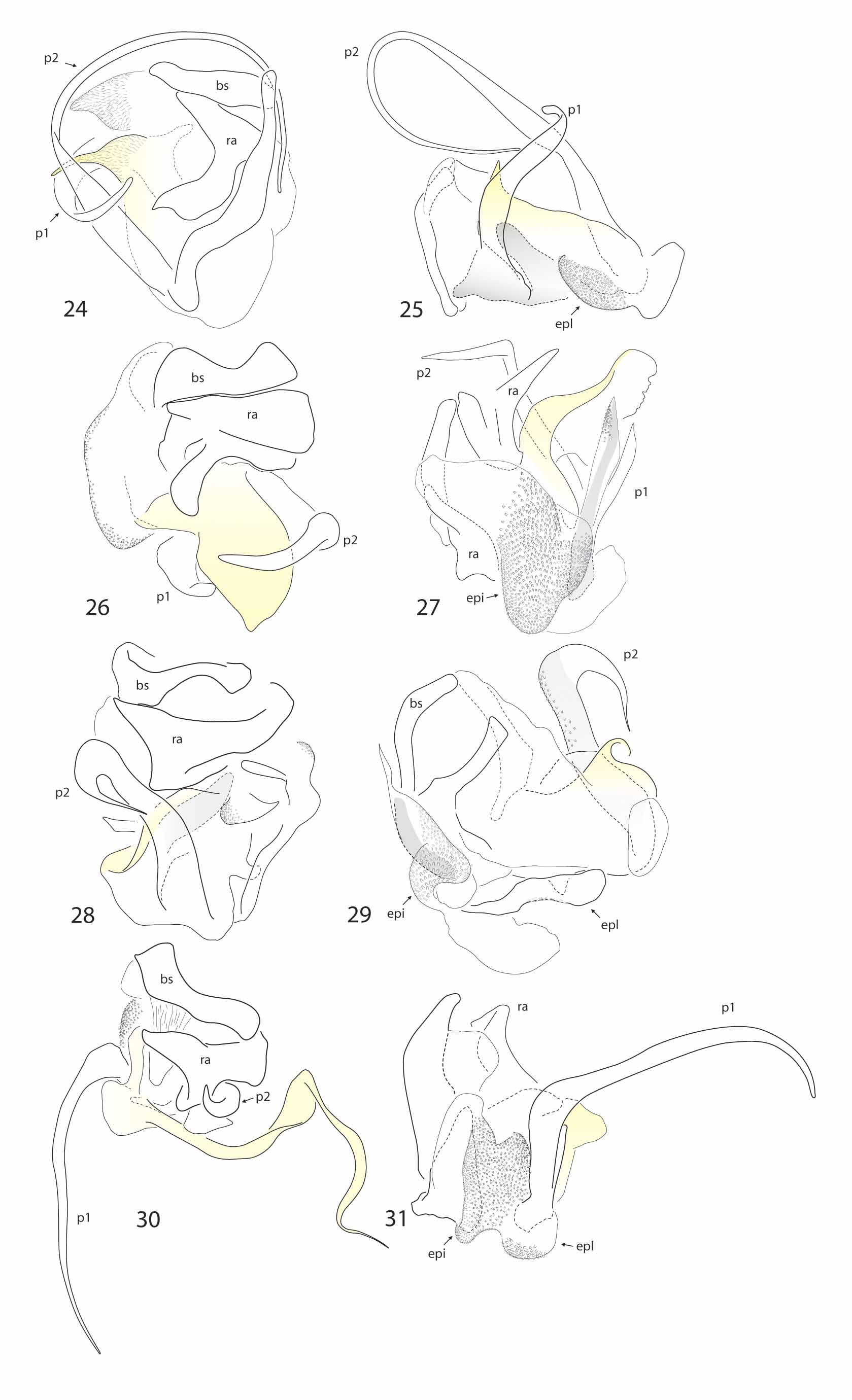
( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 3 , 4 View FIGURES 4 – 7 , 8–11 View FIGURES 8 – 23 , 24–25 View FIGURES 24 – 31 )
Diagnosis (male). Flagellomere 1 elongate-conical. Two setae on hindtibia. Right lobe of hypandrium clearly bifurcated.
Material examined. Holotype: ɗ, THAILAND: Chiang Mai, 18.70ºN 98.80ºE, 1–31.xii.1997, Malaise trap, S. Sonthichai col.
Description. Male. Body length, 1.9 mm. Head. Frons brown, pubescent, without median furrow. Flagellomere 1 light brown, pubescent, conical-elongated. Arista apical, pubescent. Palpus light brown; four medium size genal setae ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 3 ). Thorax. Scutum, scutellum and pleural regions brown; anepisternum setulose. Legs light brown. Foretibia with one dorsal seta at basal third and anterodorsal row of strong setae. Midtibia with one anterodorsal and one posterodorsal setae. Hind femur not swollen. Hind tibia with one anterodorsal and one posterodorsal setae near midlength. Wing. ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 – 7 ) Costa 0.36 of the wing length, M2 sinuous. Halter gray with apical black circle. Abdomen. Tergites brown. Hypopygium yellowish-brown ( Figs. 8–11 View FIGURES 8 – 23 ). Left epandrial process (fused surstyli) with a medially-directed tooth-like projection near apex. Right epandrial margin narrowing ventrally, with subepandrial right process bearing setae. Hypandrium left lobe bifurcated in ventral bare extension and dorsal microtrichose extension; right lobe apically microtrichose, with medially-directed elongated process. Hypoproct with two setae. Cerci large. Phallus ( Figs. 24–25 View FIGURES 24 – 31 ). Right arm with dorsal projection. Epiphallus mostly absent, just posterior lobe present. Core plate hairy, with three dorsally curved processes. Female. Unknown.
Geographic distribution. Known from only one site in Thailand.
Etymology. Mannheimsia conica was named after its characteristic conical first flagellomere.
Comments. In Brown’s key for Mannheimsia species ( Brown 2005) M. conica , sp. nov. keys in couplet 2, together with M. stricta . Mannheimsia conica sp. nov. can be differentiated from this species by its elongate-conical flagellomere 1, two setae on the hindtibia, and many differences in the hypopygium and phallus.
Mannheimsia stricta Beyer, 1965 View in CoL ( Figs. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 3 , 5 View FIGURES 4 – 7 , 12–15 View FIGURES 8 – 23 , 26–27 View FIGURES 24 – 31 )
Mannheimsia stricta Beyer, 1965: 29 View in CoL ; Brown, 2005: 136 View Cited Treatment .
Material examined. 1ɗ, KENYA: Kakamega: Isecheno Nature Reserve, 0.24ºN 34.86ºE, 19–30.iv.2001, Malaise trap, 1800m, R. Snelling col; 2ɗ, same data but 1–10.ii.2002; 1ɗ, same data but 11–20.v.2002, W. Okeka col; 1ɗ, NIGERIA: Onde Idanre Hills, 7.09ºN 5.40ºE, 16–19.vii.2008, Malaise trap, 440m, J. Heraty col.
Redescription. Male. Body length, 1.9–2.1 mm. Head. Frons brown, pubescent, without median furrow. Flagellomere 1 light brown, pubescent, globose. Arista dorsal, pubescent. Palpus light brown; 4–6 medium size genal setae. Thorax. Scutum, scutellum and pleural regions yellowish-brown; anepisternum setulose. Legs light brown, midcoxa brown. Foretibia with one dorsal seta at basal third and anterodorsal row of strong setae. Midtibia with one anterodorsal and one posterodorsal setae. Hind femur not swollen. Hind tibia with one anterodorsal seta near midlength. Wing. ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 4 – 7 ) Costa 0.37 of the wing length; M2 proximal half slightly concave, distal half almost straight. Halter yellowish-brown with apical black circle. Abdomen. Tergites brown. Ventral pair of gland-like projections near the hypopygium, connected to the internal wall of abdomen ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 3 ). Venter of abdomen with two pairs of rounded elevations near hypopygium bearing few strong setae. Hypopygium yellowish-brown ( Figs. 12– 15 View FIGURES 8 – 23 ). Left epandrial process (fused surstyli) with median finger-like extension. Right epandrial posterior margin narrowing ventrally, with subepandrial right process bearing setae. Hypandrium with two similar lobes; left lobe sometimes with a suture, with a medially-directed process. Hypoproct with two setae. Cerci small. Phallus ( Figs. 26–27 View FIGURES 24 – 31 ). Right arm with dorsal projection. Epiphallus large, almost reaching the posterior part of the phallus. Core plate large, bare and flattened, with three dorsally curved processes.
Female. Unknown.
Geographic distribution. Kenya, Congo and Nigeria.
Comments. The recognition of gland-like structures and the rounded setose elevations in the venter of the abdomen of M. stricta are the main complements to the original description ( Beyer 1965) and Brown’s revision of this species ( Brown 2005). Mannheimsia stricta is the only species in the genus with relatively small cerci, a condition present in some outgroups.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Mannheimsia conica
| Ament, Danilo César 2012 |