Inocellia tibetana, Shen & He & Pan & Liu, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4712.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:81C67066-56E8-424D-BF49-10B37116B6F4 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5C5C8049-F625-FF8D-FF60-1405FED7358D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Inocellia tibetana |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Inocellia tibetana sp. nov.
( Figs. 1–20 View FIGURES 1–2 View FIGURES 3–7 View FIGURES 8–18 View FIGURES 19–20 )
Diagnosis. In appearance, the new species is generally blackish brown with a pair of anterolaterally curved, hooklike, pale reddish brown markings on the middle of pronotum, and a transverse yellowish stripe posteriorly on each tergum of the pregenital segments. The pro- and mesofemora are brown on distal 1/3, while the metafemur is brown on its distal half. The male is characterized in the genitalia by the presence of a membranous, short and digitiform gonostylus 9, the gonarcus (fused gonocoxites 11) subtriangular in caudal view with a pair of short dorsal tubercular processes, and the reduction of bristle tuft on the endophallus. The female is characterized by the subgenitale (fused gonocoxites 8) anteroposteriorly separated into an anteriorly trilobed sclerite and a small transverse sclerite.
Description. Male. Body length 7.0–10.5 mm; forewing length 8.0–10.0 mm, hindwing length 7.0–8.0 mm.
Head ( Figs. 1 View FIGURES 1–2 , 3 View FIGURES 3–7 ) subquadrate, blackish brown, clypeus brown; vertex with two pairs of indistinct reddish brown stripes on lateral margins and with a pair of reddish brown vittae medially. Antennal sclerite (torulus), scape, and pedicel yellow; flagellum dark brown, but gradually becoming pale on distal half (from 22nd flagellomere). Mouthparts brown, except for clypeusand maxillary palps yellowish brown.
Thorax ( Figs. 1 View FIGURES 1–2 , 4 View FIGURES 3–7 ) blackish brown, pronotum brown on anterior margin, medially with a pair of anterolaterally curved, hook-like, pale reddish brown markings; meso- and metanota each with a brown transverse marking on the posterior of the scutellum. Legs ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 3–7 ) yellow with yellowish setae; pro- and mesofemora brown on distal 1/3; metafemur brown on distal half; tibiae and tarsi pale brown. Wings hyaline, pterostigma blackish brown, veins also blackish brown. RP with one forked vein and one simple vein running to wing margin ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–2 ).
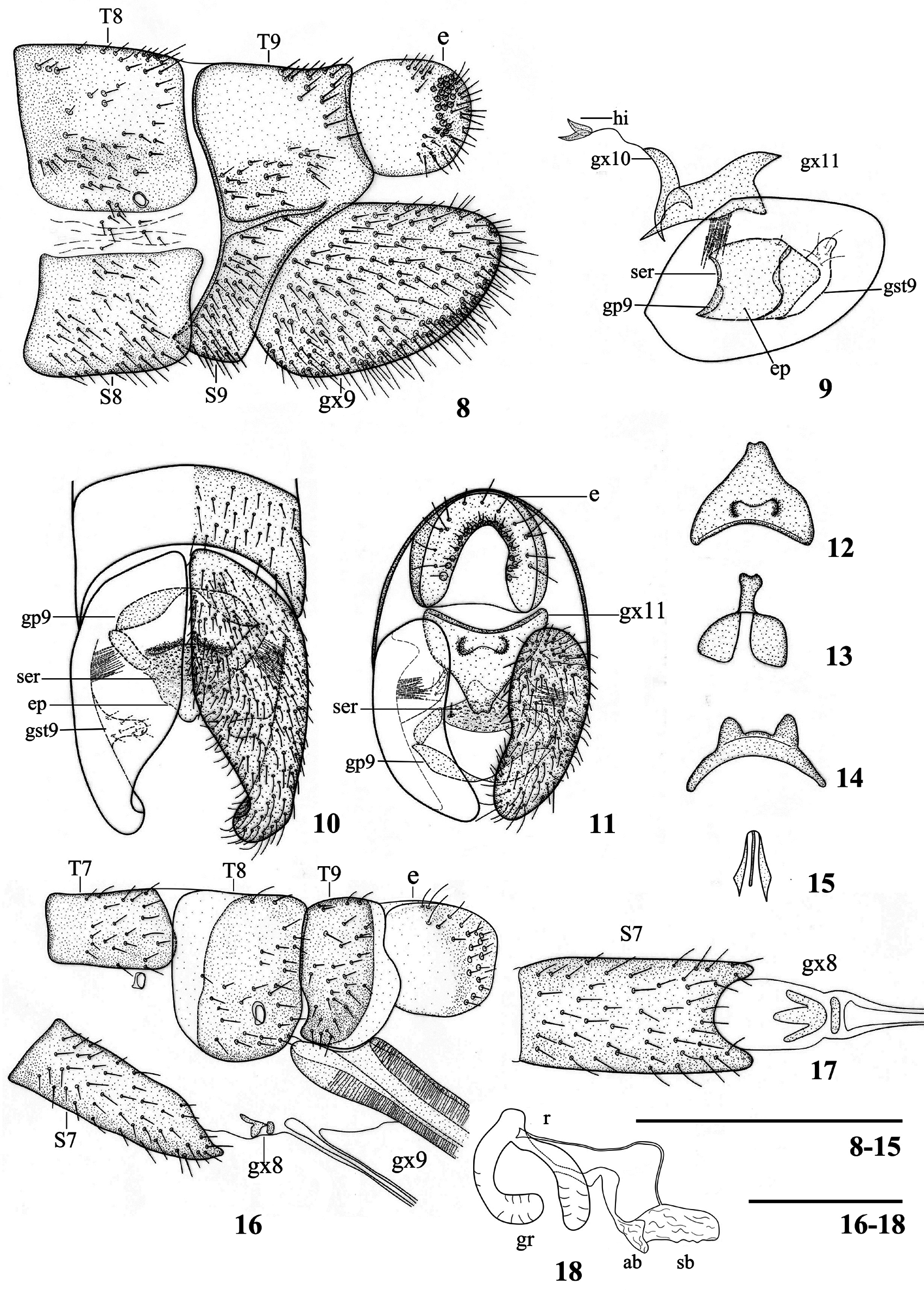
Abdomen ( Figs. 1, 2 View FIGURES 1–2 , 6–7 View FIGURES 3–7 ) blackish brown; each tergum of pregenital segments posteriorly with a transverse yellowish stripe; each sternum of pregenital segments much paler than tergum, joints between sterna transversely yellowish. Genital segments yellowish brown, ectoproct yellow. Tergum 9 ( Figs. 8, 10 View FIGURES 8–18 ) approximately twice as long as sternum 9, anterior margin slightly incised medially, posterior margin feebly incised in dorsal view. Sternum 9 ( Figs. 8, 11 View FIGURES 8–18 ) broadly concaved posteriad in ventral view. Gonocoxite 9 ( Figs. 8–11 View FIGURES 8–18 ) shell-like, slightly longer than wide of its proximal portion, with apex rounded in lateral view; a bristle tuft present near anterior margin on inner side of gonocoxite 9. Gonostylus 9 ( Figs. 9–10 View FIGURES 8–18 ) slightly distad midpoint of gonocoxite 9 on its inner side, entirely membranous, short and digitiform with sparse setae, directed dorsad. Gonapophyses 9 (pseudostyli) ( Figs. 9, 11 View FIGURES 8–18 ) feebly sclerotized, foliate, anteriorly curved in ventral view. Complex of fused gonocoxites, gonapophyses, gonostyli 10 (fused parameres) ( Figs. 9, 13 View FIGURES 8–18 ) small, flattened and broadly bilobed on proximal portion, ventrally bearing a slender distal projection, which is slightly curved dorsad and concaved at apex. Fused gonocoxites 11 (gonarcus) ( Figs. 9, 11–12 View FIGURES 8–18 ) shield-like, in caudal view subtriangular with arcuately concaved dorsal margin, medially with a pair of small tubercular processes. Endophallus ( Figs. 9, 11 View FIGURES 8–18 ) short, laterally with only a pair of bristles. A scabrous membranous structure (serratulum) ( Figs. 9–11 View FIGURES 8–18 ) present near dorsoproximal portion of endophallus. Ectoproct ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8–18 ) ovoid in lateral view. Hypandrium internum ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 8–18 ) small with lateral lobes rather narrow and foliate.
Female. Body length 10.0–12.5 mm (without ovipositor)/18.0–20.5 mm; forewing length 10.0–12.5 mm, hindwing length 8.0–11.0 mm.
Coloration similar to male ( Figs. 2 View FIGURES 1–2 , 7 View FIGURES 3–7 ). Ectoproct entirely yellow; ovipositor blackish brown. Sternum 7 ( Figs. 16–17 View FIGURES 8–18 ) in lateral view subtrapezoidal, posteriorly produced; in ventral view posterior margin with deep arcuate incision, forming a pair of short processes. Fused gonocoxites 8 (subgenital plate) ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 8–18 ) composed of a small transverse sclerite and a separated anteriorly trilobed sclerite. Ectoproct ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 8–18 ) in lateral view subquadrate. Atrium bursae ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 8–18 ) membranous, rugous; sacculus bursae rugous and outspread; receptaculum seminis short, with a pair of ovoid glandulae receptaculi.
Type material. Holotype ♂, CHINA: Xizang, Zayü , near county town [28°67’W, 97°47’E], 2362 m, 2019. VI.12, Shen Rongrong ( CAU) . Paratypes: 1♂ 1♀, CHINA: Xizang, Zayü , near county town [28°67’W, 97°47’E], 2362 m, 2019.VI .12, light trap, Yang Qicheng ( CAU) ; 2♂ 1♀, CHINA: Xizang, Zayü, Lower Zayü, Cibagou Na- tional Nature Reserve [28°56’W, 97°08’E], 1592 m, 2019. VI .14, Yang Qicheng ( CAU); 1♂, CHINA: Xizang, Zayü, Lower Zayü [28°50’W, 97°02’E], 1578 m, 2019. VI .15, He Yingnan ( CAU); 1♂ 2♀, CHINA: Xizang, Zayü, Upper Zayü, Gonggu [28°71’W, 96°79’E], 1911 m, 2019. VI .16, Shen Rongrong ( CAU); 2♂, CHINA: Xizang, Zayü , near county town [28°62’W, 97°41’E], 2254 m, 2019.VI .18, Shen Rongrong ( CAU); 1♂, CHINA: Xizang, Zayü, Lower Zayü [28°62’W, 97°41’E], 2254 m, 2019.VI .18, light trap, He Yingnan ( CAU) .
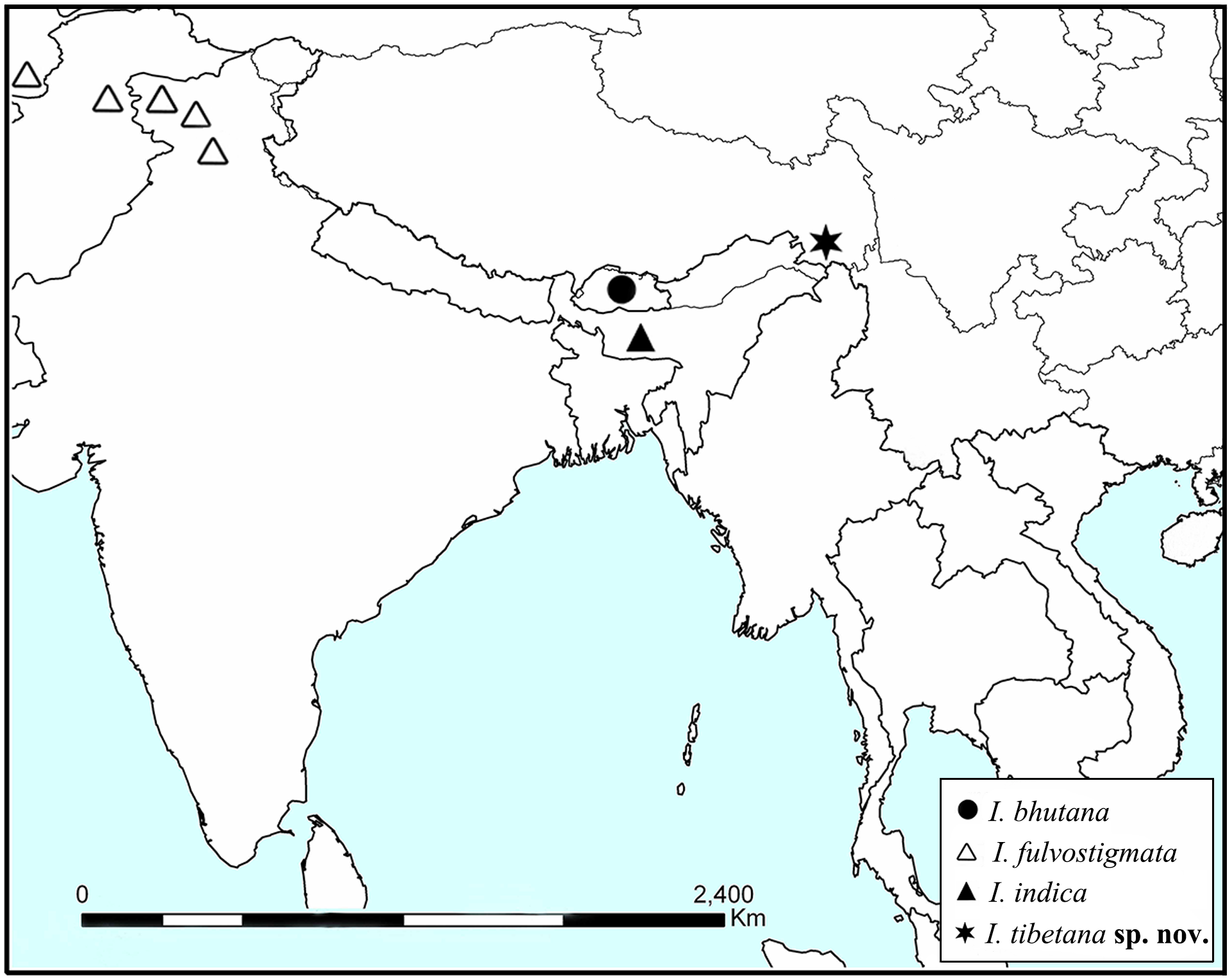
Distribution. China (Xizang: Zayü) ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 ).
Etymology. The specific epithet ‘ tibetana ’ refers to the geographic distribution of the new species in Xizang Autonomous Region (= Tibet) of China.
Remarks. Based on the male gonocoxite 9 that is longer than wide on its base, the new species belongs to the I. fulvostigmata species-group. The new species appears to be closely related to I. fulvostigmata U. Aspöck, Rausch & H. Aspöck, 1968 , which includes two subspecies ( I. fulvostigmata fulvostigmata U. Aspöck & H. Aspöck, 1968 and I. fulvostigmata nigrostigmata H. Aspöck, U. Aspöck & Rausch, 1982 ), because of generally similar male genital characters, e.g. the gonostylus 9 ( Figs. 9–11 View FIGURES 8–18 ) membranous, the gonarcus medially prominent posteriad with a pair of processes, and the endophallus laterally with only one or two bristles on each side. However, the new species differs from I. fulvostigmata in the male genitalia by the digitiform gonostylus 9 and the gonarcus ( Figs. 9, 11–12 View FIGURES 8–18 ) subtriangular in caudal view. In I. fulvostigmata the gonostylus 9 presents a broadly domed process, and the gonarcus is subquadrate in caudal view.
All specimens of the new species were collected from the areas with mixed forests of coniferous and broadleaved trees. Some specimens were collected by using a sweeping net mainly from pine trees, while a few of them were also found on lower vegetations ( Figs. 19–20 View FIGURES 19–20 ). In addition, some specimens were collected by using Mercury- Vapor light trap.
| CAU |
China Agricultural University |
| VI |
Mykotektet, National Veterinary Institute |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |