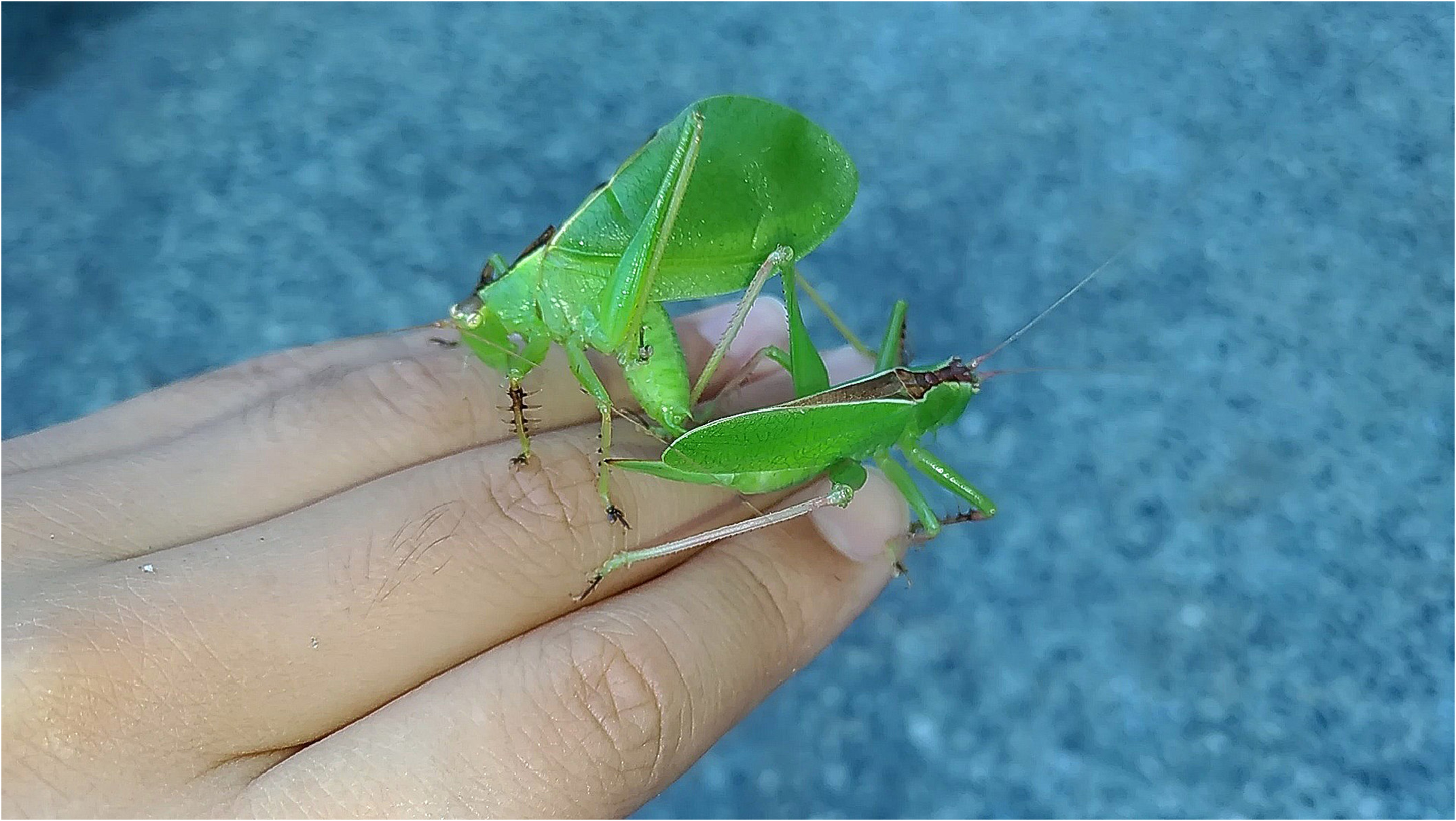
Hexacentrus formosanus Chen et He, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4933.4.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5664D12C-DBC4-4C48-A276-F2F0C5F16F65 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4556692 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AF8790-CB62-FFB1-FF2D-FA83FE4CFE0A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hexacentrus formosanus Chen et He |
| status |
sp. nov. |
2.1 Hexacentrus formosanus Chen et He View in CoL sp. nov.
Figs. 2–7 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7
Holotype: male, Kantoushan , Dongshan District, Tainan City, Taiwan, 17-viii-2019, coll. Po-Wei Chen.
Paratype: 2 males & 1 female, other data same as holotype .
Type specimens were deposited in National Museum of Natural Science, Taichung, Taiwan ( NMNS) .
Male: Body medium-sized. Antenna segments with alternate short dark bands apically. Fastigium of vertex compressed laterally, dorsally narrow, apex rounded from lateral view ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ), acute from dorsal view ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ). Fastigium of vertex separated from frons by a furrow. Eyes globular ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Pronotum saddle-shaped, longer than broad and extending posteriorly; dorsal anterior margin slightly concave ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ); disk dorsally depressed between second and third transversal sulcus, surface with a spoon-shaped mark, the margin smooth or constricted at transverse sulcus; posterior margin broadly rounded, very slightly concaved ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ), ventral margins of lateral lobes incline downwards, anterior angle obtuse, posterior angle rounded. Fore femora genicular lobes armed with a single spine on the inner side, outer side unarmed; middle femora genicular lobes armed with a single spine on both inner and outer side; hind femora genicular lobes armed with two spines on both inner and outer side. Fore and middle femora unarmed ventrally; hind femora ventrally armed with several small spins. Tegmina broad and long, reaching middle of middle tibiae, slightly inflated transversally (Fig. 3,4). MA veins curved upward, with 7 branches. Rs veins arised from 2/3 part of R vein. Hind wing shorter than tegmen. Stridulatory vein short, curved at the left side end, with about 30 teeth, two distinctly enlarged in the middle. Teeth distance subequal except for the two enlarged in the middle ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ). Cu2 vein of left tegmen curved and slender, spectrum slender and rectangular ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ). Ninth abdominal tergite with notch V-shaped; 10 th abdominal tergite with a shallow notch. Supra-anal plate triangular with medium groove at base. Cercus robust at base, inner middle with a slight projection; apical third finger-shaped and curved inwards; apex acute, slightly curved downward ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ). Subgenital plate long with a medium longitudinal groove, lateral ridge well developed, posterior margin with a rounded excision; styli long and slender, almost as long as subgenital plate ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ).
Female: Pronotum dorsally flat; tegmina reaching tip of meta femora, slightly suppassing or not reaching tip of ovipositor. Cerci conical, apex acute, slightly curved inward ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ). Subgenital plate wide, triangle, apex rounded, slightly concave. Ovipositor dagger shaped, nearly straight and robust, slightly decurved at base, apex acute ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ).
Coloration: Overall green when alive. Antennal scape pink or yellow. Dorsal band brown with dark brown and yellow margin. Female dorsal part of tegmina dark brown. Tibia color variable from pink to greenish yellow (Fig. 4,5). Base of tibia spines, pretarsus and apical tarsal pads dark brown in both sexes.
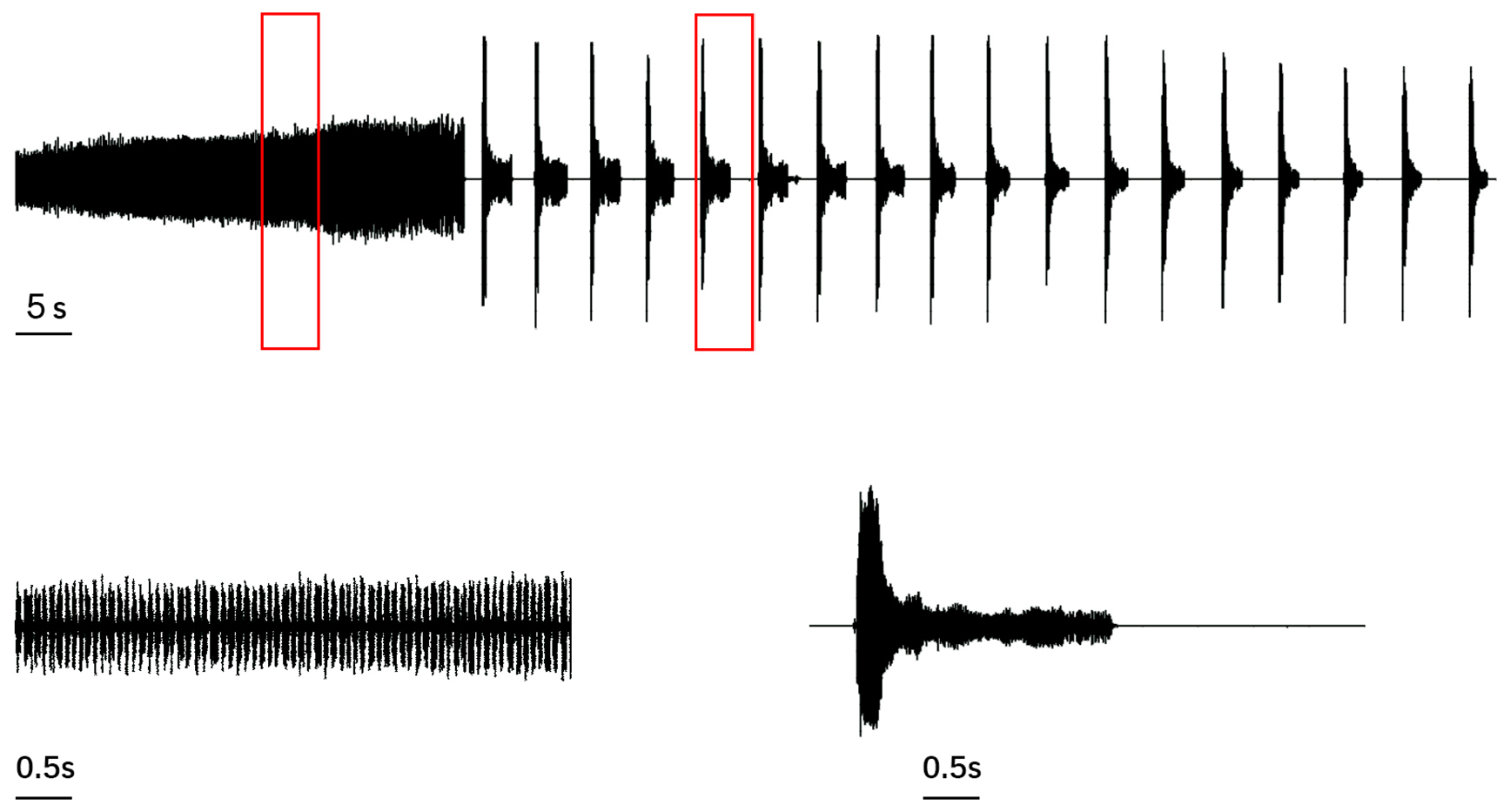
Song: Songs include two parts. The first part includes continually pulses without interval. The second part repeats with 12–13 cycles in one minute. It contains 1.635± 0.343s duration with first half loud and 3.158± 0.358s interval, but duration gradually decreased in the whole song.
Comparison: This species is similar to H. expansus Wang & Shi, 2005 and H. inflatissimus Gorochov & Warchalowska-Sliwa, 1999 , but differs from the former species by 1) male file of left tegmina shorter; 2) spectrum of male left tegmina slender and rectangular; 3) male Cu2 vein of left tegmina curved and slender; and differs from the latter species by 1) body smaller; 2) female tegmina narrow and shorter.
Measurements (in mm): Male: SZ 37.17–39.10, PR 8.50–9.29, FW 29.60–31.69, HF 19.96–20.80; Female: SZ 34.02–37.69, PR 6.50–6.55, FW 26.89–29.91, HF 22.47–22.58, OV 15.34–15.75.
Habitat: This species can be found in mountains areas under around 1000m above sea level in the west part of Taiwan, males can be heard stridulating in dense vegetations by the edge of laurel forest ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ).
Etymology: The name formosanus refers to the island of Formosa, a former name of Taiwan.
Note: This species was included in Matsumura (1931) and Kato (1932) but was misidentified as Hexacentrus munda Walker in both papers. In our field observations, calling males are usually ~10 meters away from each other, but additional males can sometimes be found near a calling male (Po-Wei Chen, personal experience). In an incident, a male with left front and middle legs missing were found within 30cm from a calling male. The remaining left front and middle coxae were darkened, indicating that the loss of limbs occurred some time previously. This male was possibly applying satellite behavior in attempt to intercept approaching females, as his fitness was obviously affected by the loss of limbs.
| NMNS |
National Museum of Natural Science |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |