Gigantochloa maneensis Q. M. Qin, N. H. Xia & J. B. Ni, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.616.1.6 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8389449 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DDAC67-E712-DB46-FF0C-FD88FC48FA1A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Gigantochloa maneensis Q. M. Qin, N. H. Xia & J. B. Ni |
| status |
sp. nov. |
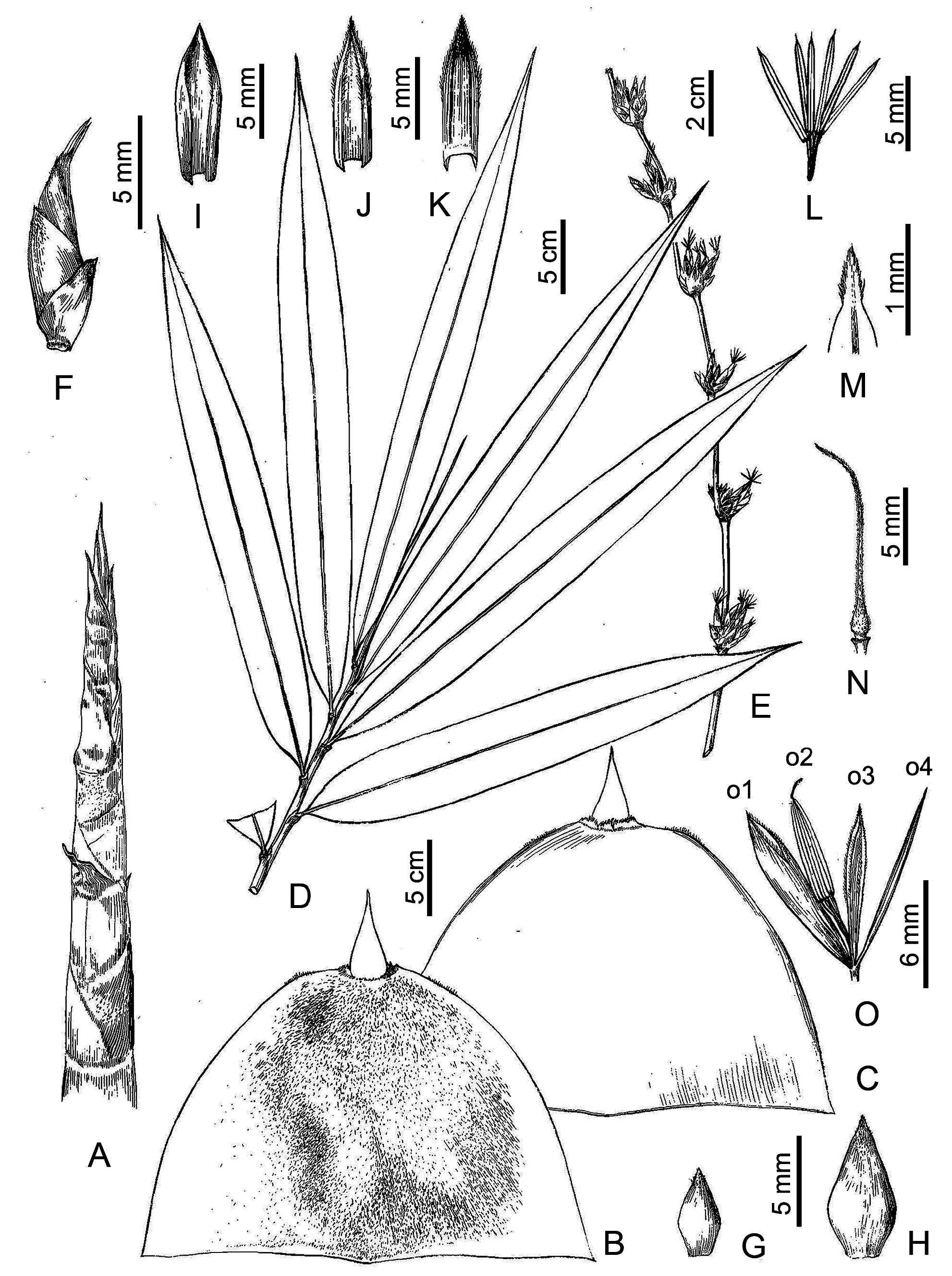
Gigantochloa maneensis Q. M. Qin, N. H. Xia & J. B. Ni , sp. nov., Figs. 1−2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2
Type:— CHINA. Yunnan, Mengla County, Menglun , cultivated in Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden , introduced from Man’e Village , 8 August 2017, Qiao-Mei Qin, Juan Chen & Su Li QQM-319 (holotype IBSC!) .
Diagnosis: — Gigantochloa maneensis is similar to G. callosa , but differs in the intranodes with a ring of white hairs (vs. glabrous), infranodal regions with a ring of white (vs. brown) hairs, culm leaf sheath without stripe (vs. with yellow stripes initially) and densely black- (vs. brown- and gray-) hispid abaxially, erect (vs. reflexed) culm sheath blades, oblong (vs. rhombic) culm sheath auricles, 6–7 mm (vs. ca. 10 mm) wide, and sparsely brown-hispid (vs. white-pubescent) foliage leaf sheaths ( Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
Description:— Rhizomes pachymorph. Culms erect, ca. 10 m tall, 5–7 cm in diam., walls ca. 2.5 cm thick, lower nodes with a few verticillate aerial roots; internodes 20–30 cm long, terete, greyish-green with yellow stripes, white-pubescent; nodes slightly prominent, intranode ca. 1 cm tall, with a ring of white hairs, infranodal region with a ring of white hairs. Branches 0.5–1.5 m long, developing from the 5 th –8 th node above the ground, numerous, dominant branches inconspicuous. Culm leaf sheath deciduous, leathery, nearly as long as internodes, densely brown-hispid abaxial surface with deciduous trichomes; blade erect, lanceolate, 1/3–1/2 as long as culm leaf sheath; auricles oblong, 6–7 mm wide and ca. 3 mm tall; ligule 2–3 mm tall, dentate. Foliage leaves 7–9 per ultimate branch; sheath sparsely brown-hispid, with deciduous trichomes; auricles absent; ligule ca. 2 mm tall; outer ligules ca. 2 mm high; petiole ca. 2 mm long; blades 13–30 cm × 1.5–3.0 cm, lanceolate, apex acuminate, glabrous, longitudinal veins 6–8 pairs. Pseudospikelets densely clustered at nodes of flowering branches, 8.5–11.0 mm long, with 3–4 glumes, 2 perfect florets and a terminal sterile floret consisting of only an empty; rachilla very short; lemma 7–8 mm long, apex mucronate, margins ciliate; palea 6.0– 7.5 mm long and ca. 1 mm wide, apex bifid, 2-keeled, keels and margins ciliate, 2 veins between keels, 1 vein on each side; stamens 6, filaments united into a tube, translucent; anthers yellow, 4–5 mm long, with an apical hairy mucro ca. 0.5 mm long; ovary subcylindrical with a slightly expanded, thickened and hairy apex, ca. 0.7 mm long; style terminating in a single hairy stigma, 7–8 mm long. Caryopsis ca. 6 mm long.
Distribution and Habitat: —This species is cultivated in Man’e Village, Menglun Town, Mengla County, Yunnan Province, and then introduced to Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden. Wild population has not been found so far.
Phenology: —New shoots October to November, flowering August to September.
Etymology: —The specific epithet is derived from the type locality, Man’e Village.
Additional specimens examined (paratypes): — CHINA. Yunnan: Mengla, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden , 21°41’N, 101°26’E, elev. 570 m, 18 November, 2010, Ping-Yuan Wang C130036 ( HITBC) GoogleMaps ; ibid., 12 October 2011, Ping-Yuan Wang C130092 ( HITBC). GoogleMaps
Chinese vernacular names:—AENJfflfi (pinyin: màn é jù zhú).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |