Divergita macinnisii Lobban, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.508.3.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/35288784-6A23-EC00-8084-172AFE8485EC |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Divergita macinnisii Lobban |
| status |
sp. nov. |
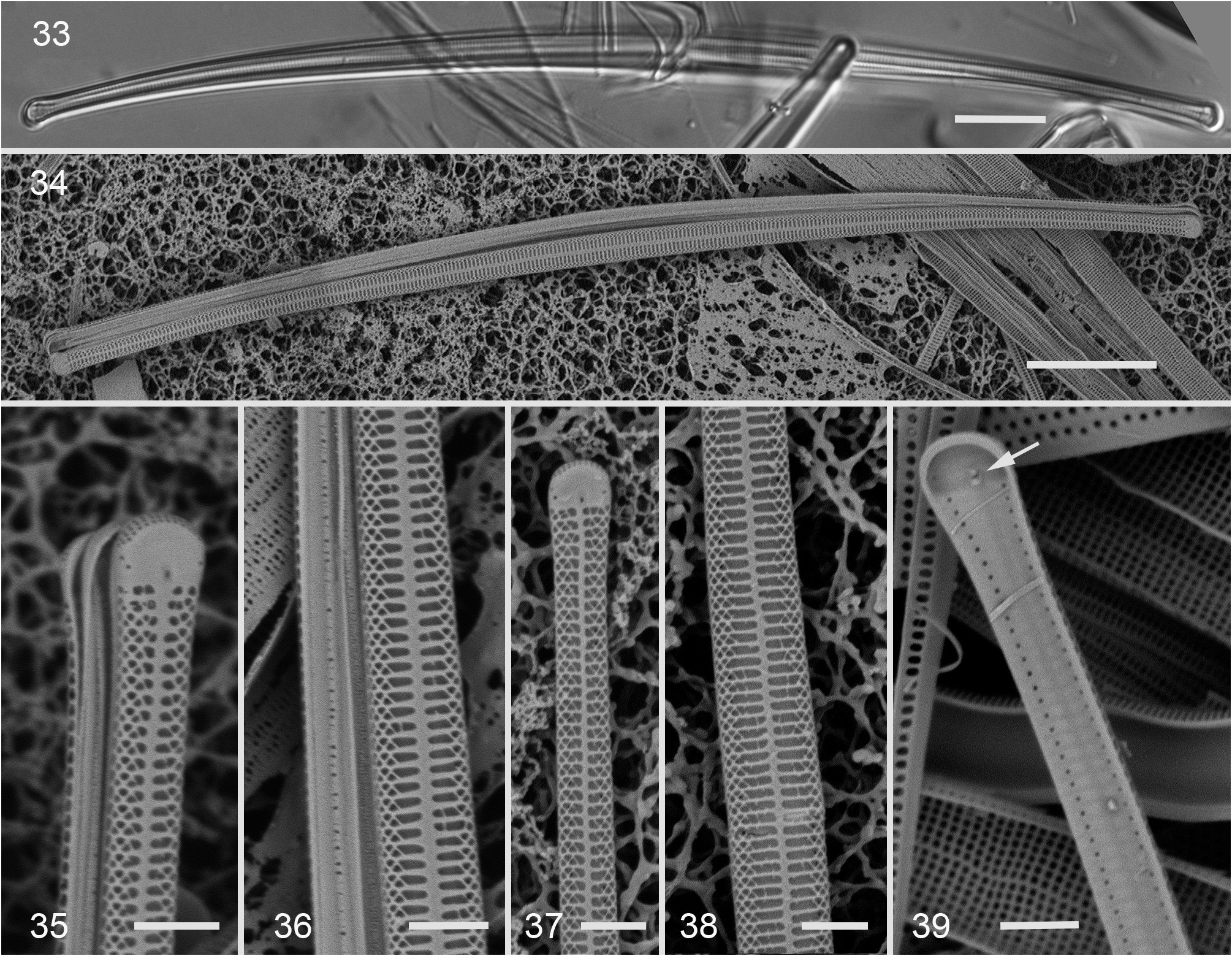
Divergita macinnisii Lobban , sp. nov. Figs 33–39 View FIGURES 33–39 .
Diagnosis:— Valves curved, lanceolate with weakly capitate apices. Striae biseriate and decussate only on the mantle, striae on valve face comprising a single elongated areola; sternum linear.
Description:— Valves curved, 96–140 µm long, 3 µm wide, lanceolate with weakly capitate apices ( Figs 33–36 View FIGURES 33–39 ). Striae 25–27 in 10 µm, biseriate and forming a decussate pattern of triangular areolae on the margin, this pattern extending to the sternum near the apices; changing on the valve face to a row of extended, almost alveola-like areolae along each side of the sternum ( Figs 34–38 View FIGURES 33–39 ). Occasional vimen crossing these long areolae, sometimes diagonally ( Figs 36–38 View FIGURES 33–39 ). Sternum linear. A hyaline area at each apex with a rimoportula in each ( Figs 35, 37, 39 View FIGURES 33–39 ). Apical pore field with three rows of pores and not sunken ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 33–39 ). Internal view ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 33–39 ) showed asymmetrical rimoportula and a row of foramina in the inner wall along each mantle–valve-face boundary; sternum and adjacent rows of areolae discernable through the inner wall.
Holotype hic designatus:— Specimen at 22.7 mm E and 13.4 mm S of the mark on slide 2922, deposited at ANSP, accession # ANSP-GC20097 . Fig. 33 View FIGURES 33–39 . Registration: http://phycobank.org/102758.
Type locality: — MARSHALL ISLANDS. Jaluit Atoll: reef NW of Kabbenbock I., 5.933 N, 169.636 E, in farmer fish turf, ca. 1 m deep, sample J5. C.S. Lobban and M. Schefter, 9 June 1991 GoogleMaps .
Etymology:— Named for Andrew McInnis, graduate student at U. Guam Marine Laboratory, who kindly made the collections at Bikar Atoll in October 2019.
Additional Records:— MARSHALL ISLANDS. Bikar Atoll: BA-3!.
Comments:— Sabir et al. (2018) defined the genus with two characters that we see here at variance: the decussate areola pattern, and the lanceolate sternum. In the new material we see that the pattern of areolae is not entirely decussate—a phenomenon that was also documented by Montgomery (1978, pl. 203, figs A, B) in a specimen identified as “ Synedra laevigata var. hyalina Grunow. ” (It has an areola pattern like D. macinnisii but is straight.) The sterna in two of the new species were linear. However, it is clear from the similarities that these species must be included in Divergita . Another curved species, originally described as Synedra toxoneides Castracane 1880: 105 , transferred to Hyalosynedra toxoneides Pérez Coca, YT Chang, WL Wang & MY Wang in Pérez Coca & al. 2016: 514 and to Divergita toxoneides (Castracane) Theriot in Sabir et al. 2018: 21 (and see Belando et al. 2018), has markedly different areolae from D. macinnisii .
Thalassionema Grunow ex Mereschkowsky 1902: 78 emend. Hallegraeff 1986: 75
Thalassionema is a small genus of usually colonial, planktonic diatoms that has been intensively studied in the last 40 years ( Hasle & Mendiola 1967, Moreno-Ruiz & Licea 1994, Hallegraeff 1986, Hasle & Semina 1988, Round et al. 1990, Hasle 2001, Sar et al. 2007, Tanimura et al. 2007, and Sugie & Suzuki 2015). The genus name has a convoluted taxonomic history in the transfer of the type species from Synedra , described by Fourtanier & Kociolek (1999) and Hasle (2001). Thalassionema is similar to Thalassiothrix Cleve & Grunow 1880: 108 , from which it is distinguished by areolae that open freely to the outside “surmounted by one to three simple silica branches” as opposed to being covered with a velum ( Hallegraeff 1986); Hasle (2001) keyed the differences in genera as the presence of marginal spines in Thalassiothrix . Both Hasle (2001) and Sugie & Suzuki (2015) gave keys to the species, of which there are currently six, and Sugie & Suzuki (2015) include a table of morphological characters. Thalassionema is characterized ( Hasle 2001) by colonies attached at one pole (the foot pole) by mucilage pads, forming stellate or zigzag or fan-shaped arrangements, except for a few species that are solitary. Those that are colonial are usually somewhat heteropolar, and isopolarity may indicate a solitary habit ( Sugie & Suzuki 2015). Valves have one marginal row of loculate areolae with a circular foramen on the inside, while the outside has no velum but is partially covered by simple or crossing bars. Tubular or spine-like processes are usually at both ends but differing in size and shape. Rimoportulae open to the exterior on the mantle beneath the process, or in an apical pit. The following small species does not match any of the known taxa.
| ANSP |
Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Divergita macinnisii Lobban
| Lobban, Christopher S. 2021 |
Thalassionema Grunow ex Mereschkowsky 1902: 78 emend. Hallegraeff 1986: 75
| Hallegraeff, G. M. 1902: 78 |