Dactylogyrus sanagaensis Fankoua, Bassock Bayiha & Rahmouni, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1590/S1984-4689.v39.e21009 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D016DD4F-A78A-4FE8-B6C0-34575FAA9AF1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8229756 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2D8AE8F9-05D1-4ABC-8734-AB1E3E43FA2A |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:2D8AE8F9-05D1-4ABC-8734-AB1E3E43FA2A |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Dactylogyrus sanagaensis Fankoua, Bassock Bayiha & Rahmouni |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Dactylogyrus sanagaensis Fankoua, Bassock Bayiha & Rahmouni View in CoL , sp. nov.
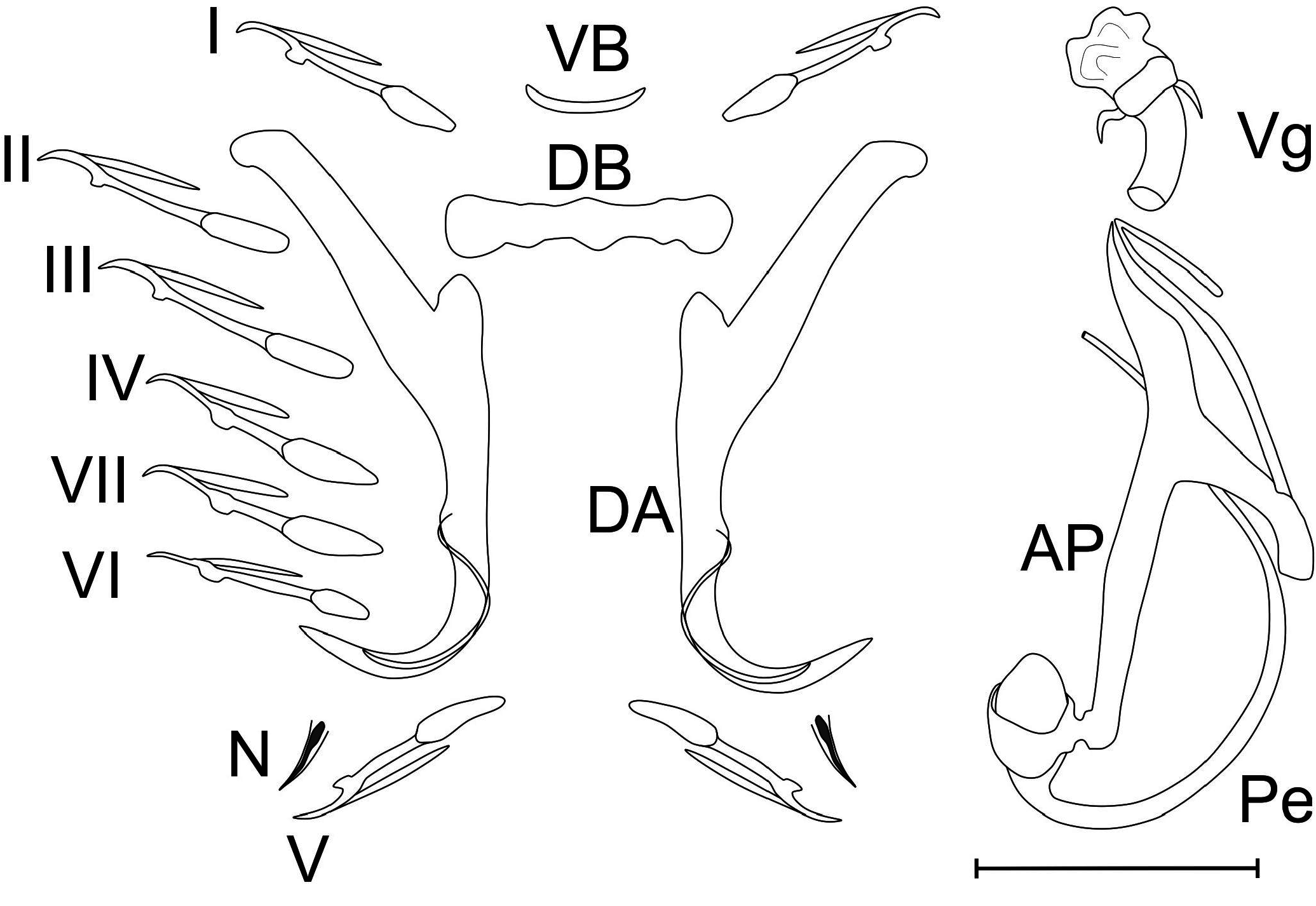
Fig. 3 View Figure 3
http://zoobank.org/ 73C94FE9-77F5-4999-95CB-6A3F1F8B75C5
Type host. Labeo sanagaensis Tshibwabwa, 1974 .
Other hosts. Labeo nunensis Pellegrin, 1929 ; Labeo camerunensis Trewavas, 1974 ; Labeo annectens Boulenger, 1903 .
Infection site. Gill lamellae.
Type locality. Nachtigal (04°20’50.1”N; 011°38’00.3”E). GoogleMaps
Other localities. Ndokoa (04°23’56.64”N; 011°44’14.52”E), National Park of Mpem GoogleMaps and Djim (05°6’37.23”N; 11°33’28.91”E).
Prevalence. 69.2% in Labeo sanagaensis , 60% in L. nunensis , 67.7% in L. camerunensis , 33.3% in L. annectens .
Mean intensity. 7.9 in L. sanagaensis , 15.5 in L. nunensis , 8.5 in L. camerunensis , 01 in L. annectens .
Material studied. 18 whole-mounted specimens in GAP.
Type specimens. Holotype RMCA _VERMES_43352 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43353 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43354 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43355 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43356 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43357 .
Etymology. Epithet sanagaensis refers to the River Sanaga in which specimens of the type host were sampled.
Description. The anatomy is that of the Dactylogyrus . Body length 335.8 (271.9–483.8; n = 18); width 68.3 (48.5–86.4; n = 18) at level of ovary. Cephalic glands present. Two pairs of eye-spots of variable size, anterior to pharynx. Haptor not well separated from rest of the body. Dorsal anchor (DA) with arched point, guard distinctively longer than shaft, and arched at the distal extremity. Ventral bar (VB) reduced, crescent moon-shaped. Dorsal bar (DB) straight and enlarged at the middle and at the two extremities. All the 14 hooks (07 pairs) with similar morphology but different sizes. One pair of needles (N) located near hooks pair V.Male copulatory organ (MCO) complex, J-shaped, tubular penis starting by a basal bulb (one ovoid lobe). Accessory piece (AP) is T-shaped with two branch of equal size, one with a sharp extremity, the other with a rounded extremity; a thinner part attached to this extremity folded back near the sharp extremity. Vagina (Vg) is a short thick tube with a flame shaped structure at its distal extremity; the distal third of vagina is wrapped by a large ring with two short filaments on either side.
The measurements of haptoral and copulatory sclerites are similar in both hosts and given in Table 1 View Table 1 .
Remarks. Dactylogyrus sanagaensis sp. nov. resembles D. leonis Musilová, Řehulková & Gelnar, 2009 from Labeo coubie Rüppell, 1832 , D. longiphallus Paperna, 1973 from L. victorianus Boulenger, 1901 , D. longiphalloides Guégan & Lambert, 1991 from Labeo allauadi, Pellegrin, 1933 , and D. marocanus El-Gharbi, Birgi & Lambert, 1994 from Carasobarbus fritschii Günther, 1901 and D. dembae Musilová, Řehulková & Gelnar, 2009 from L. coubie by the similar shaped haptoral sclerites, the conspicuous subterminal notch on the outer root of the dorsal anchor, the same ‘pseudanchoratus’ type of the male copulatory organ (J-shaped), accessory piece T-shaped, tubular vagina with a distal flame shaped structure, and a large ring with two short distal filaments. The main difference is the size of MCO: AP = 29–41µm vs 28–32 µm; 31–40 µm; 45–52 µm; 38–57 µm and 26–30 µm respectively for D. leonis , D. longiphallus , D. longiphalloides , D. marocanus and D. dembae ; Pe = 27–34 µm vs 28–34 µm; 38–45 µm; 40–45 µm; 41–61 µm and 27–34 µm respectively for D. leonis , D. longiphallus , D. longiphalloides , D. marocanus and D. dembae .
| RMCA |
Royal Museum for Central Africa |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |