Dactylogyrus djimensis Fankoua, Bassock Bayiha & Rahmouni, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1590/S1984-4689.v39.e21009 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D016DD4F-A78A-4FE8-B6C0-34575FAA9AF1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8229768 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D703D538-7418-4FE5-843F-95D37AF0DA94 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:D703D538-7418-4FE5-843F-95D37AF0DA94 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Dactylogyrus djimensis Fankoua, Bassock Bayiha & Rahmouni |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Dactylogyrus djimensis Fankoua, Bassock Bayiha & Rahmouni View in CoL , sp. nov.
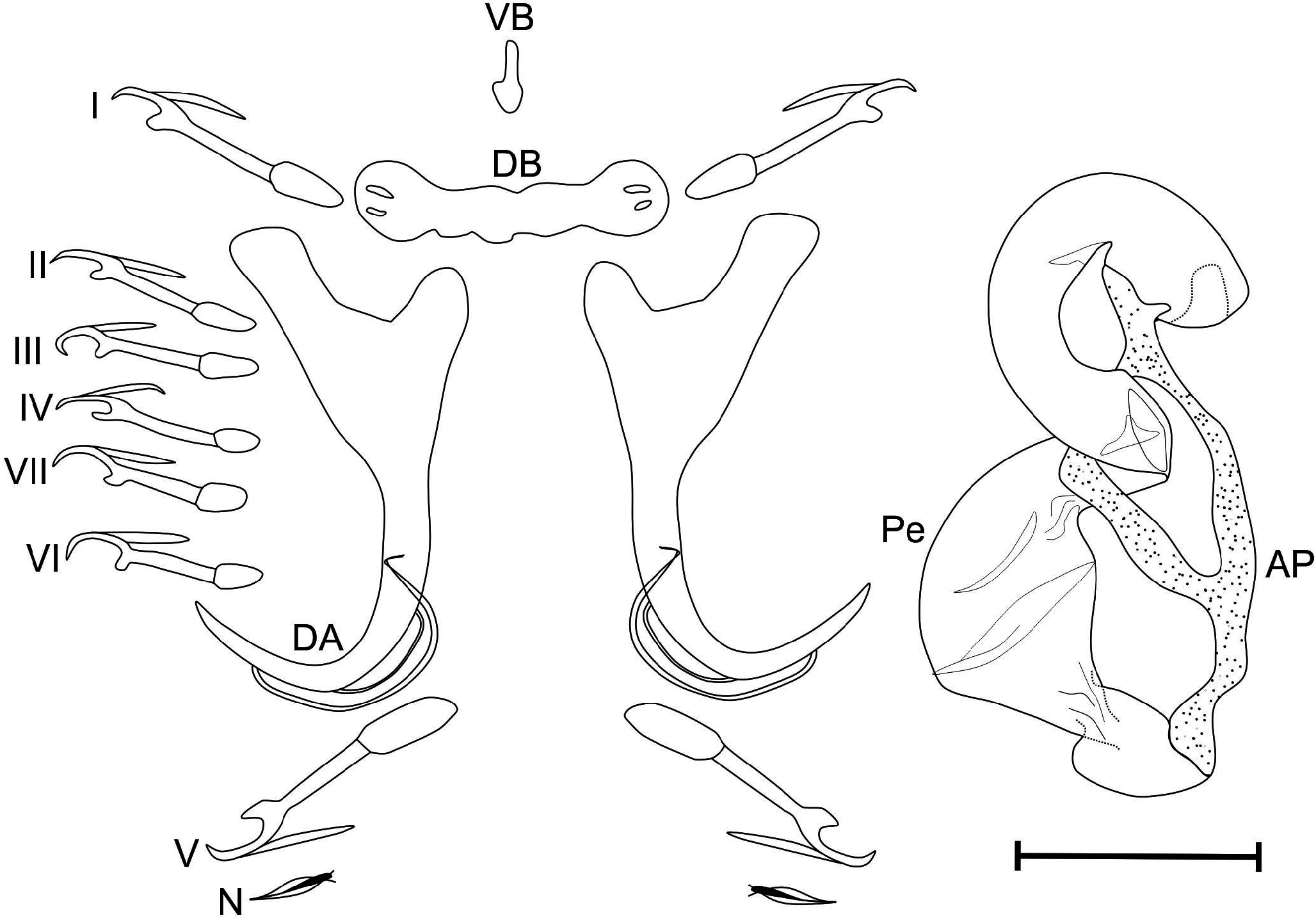
Fig. 5 View Figure 5
http://zoobank.org/ D703D538-7418-4FE5-843F-95D37AF0DA94
Type host. Labeo camerunensis Trewavas, 1974 .
Infection site. Gill lamellae.
Type locality. Djim river : 04°20’50, 1”N; 011°38’00, 3”E GoogleMaps ; alt. 441 m.
Prevalence. 50 %.
Mean intensity. 3.5.
Material studied. 16 whole mounted specimens in GAP.
Type specimens. Holotype RMCA _VERMES_43358 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43359 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43360 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43361 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43362 , Paratype RMCA _VERMES_43363 .
Etymology. Epithet djimensis refers to the River Djim in which specimens of the type host were sampled.
Description. Body length 612 (455–822, n = 16) and 141 (14–245, n = 16) width at the level of ovary. Cephalic glands present, two pairs of eye-spots of variable sizes, anterior to pharynx. Haptor well separated from the rest of the body by a narrow constriction. Dorsal anchors strong with arched point, guard longer than shaft. Dorsal bar (DB) straight with spherical and fenestrated extremities. Ventral bar (VB) vestigial shovel-shaped. Presence of seven pairs of hooks morphologically similar with larval form, approximately same length except hooks pairs I and V longer than others. One pair of needles (N) located near hooks pair V. Male copulatory organ (MCO) with: tubular coiled penis starts from a bulb with large base, lacks flange, winds around the accessory piece at its middle and ends in a rounded part; accessory piece slightly sclerotized, forms an asymmetrical triangular frame with a shaft. No sclerotized vagina observed.
New measurements of haptoral and reproductive sclerites are given in Table 1 View Table 1 .
Remarks. By the morphology of the haptoral sclerites and the MCO, this species is close to D. yassensis Musilová, Řehulková & Gelnar, 2009 from L. coubie , D. cyclocirrus Paperna, 1973 from Labeo coubie , L. cylindricus Peters, 1852 , L. victorianus and L. senegalensis Valenciennes, 1842 , D. digitalis Paperna, 1969 from L. coubie , D. nathaliae Guégan & Lambert, 1988 from Labeo sp. from Mali, and D. omega Guégan & Lambert, 1991 from L. parvus and L. rouaneti . It differs from D. yassensis by the length of anchor inner root 9.6–12.9 µm and outer root 3.1–6.6 µm vs 12–14 µm and 5–7 µm, dorsal bar 21.1–26.4 µm vs 26–27µm, penis 74.8–90.4 µm vs 74–79 µm; from D. cyclocirrus by the length of anchor inner root 9.6–12.9 µm vs 24–28 µm, dorsal bar 21.1–26.4 µm vs 23–27 µm, penis 74.8–90.4 µm vs 62–69 µm; from D. digitalis by the length of dorsal bar 21.1–26.4 µm vs 28–34 µm, and its coiled penis 74.8–90.4 µm vs simple penis 70 µm; from D. nathaliae by the size of anchor inner length 32.7–36.3 µm vs 26–30 µm, its coiled penis 74.8–90.4 µm vs curved penis 37–45 µm; from D. omega by the length of anchor inner root 9.6–12.9 µm and outer root 3.1–6.6 µm vs 10–14 µm and 3–6 µm, dorsal bar 21.1–26.4µm vs 24–28µm, though hooks length and diameter of penis 10.7–16.7 µm vs 2–3.
| RMCA |
Royal Museum for Central Africa |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |