Chironomus (Chironomus)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.280836 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6169915 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038B2C37-FF92-FFC3-FF72-99C5FC4D192C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chironomus (Chironomus) |
| status |
|
Chironomus (Chironomus) View in CoL f. fluviatilis
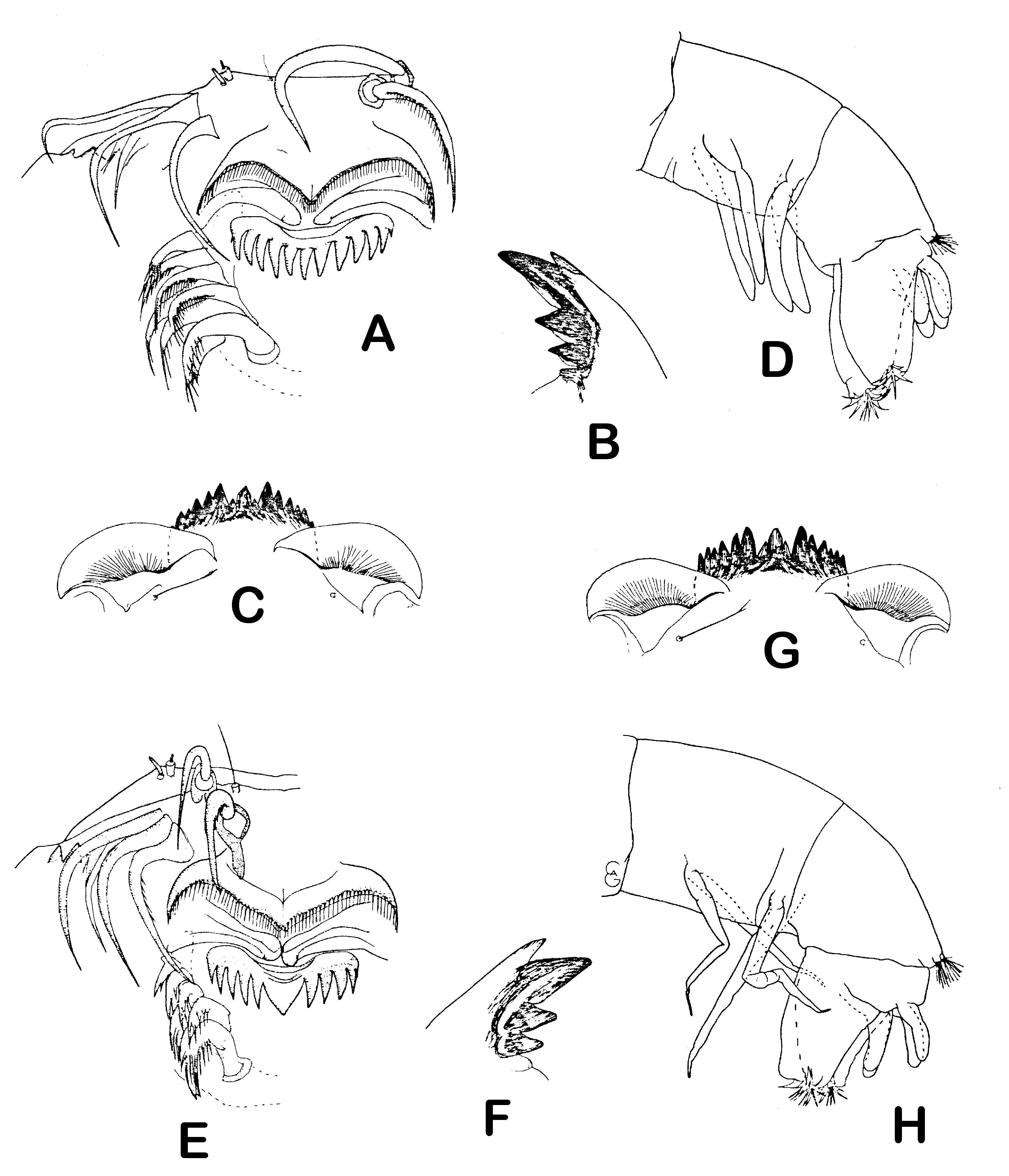
( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 E–H)
Material examined. North Basin, 2 larvae, 2.ix. –12.x. 1969.
Two larvae of this type ( Lenz 1954–62 fig. 73) were found near the outlet of the lake and illustrated in Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 E– H. Wülker (2007) describes two new species from the near-shore sediments of Lake Michigan, C. mozleyi Wûlker and C. winnelli Wülker. These larvae apparently belong to one of these species.
Distribution and ecology. Larvae of this type are known from large Russian rivers and from saline lakes in western Siberia ( Lenz 1954–62: 161) and have been reported from all of the Laurentian Great Lakes with the exception of Lake Superior ( Winnell & White 1984). Mozley (1975: 98) found the larvae commonly in Lake Michigan, and states that the imagines from these larvae are close to C. decorus .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.