Cheumatopsyche meghalayaensis, Pandher & Malicky & Parey, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4379.3.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4D3AC077-3F94-42B8-BF67-3063B453C40C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5997013 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E287C4-8317-FFA0-FF55-0492FC7D6F0A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cheumatopsyche meghalayaensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cheumatopsyche meghalayaensis sp. nov.
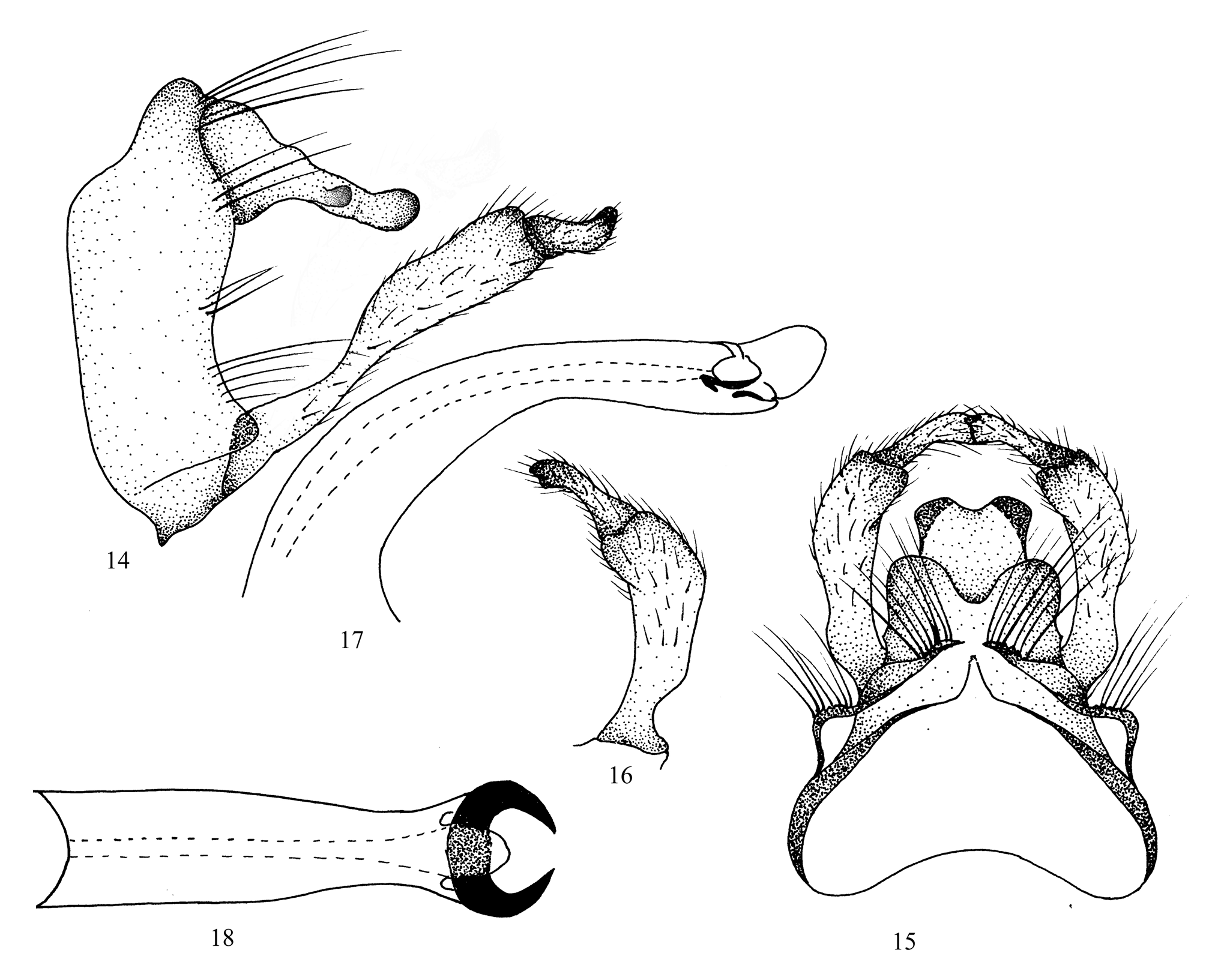
( Figs. 14–18 View FIGURES14–18 )
Material examined. Holotype, male, India: Meghalaya; Bhagmara , 200 m, 12-iv-2009, Pandher & Parey ( NPC) . Paratypes. 2 males, 1 female, collection data same as of holotype.
Diagnosis. Due to the presence of unilobed segment X, Cheumatopsyche meghalayensis sp. nov. belongs to the Cheumatopsyche concava Species Group as defined by Oláh & Johanson (2008). Based on the similarity in the overall male genitalic structure, it is closer to Cheumatopsyche chryseis Malicky & Chantaramongkol 1997 and Cheumatopsyche chrysothmis Malicky & Chantaramongkol 1997 (both reported from Thailand), especially Ch. chryseis . Cheumatopsyche meghalayaensis resembles Ch. chryseis in the lateral view of the male genitalia (similar shape of segment IX and of the harpago (apical segment) of each inferior appendage), but segment X is narrow in lateral view and the mesocaudal lobe is blunt and slightly invaginated apically in dorsal view in Ch. meghalayaensis , whereas segment X is broad in lateral view and the mesocaudal lobe is rounded apically and is produced medially in dorsal view in Ch. chryseis , strongly supporting Ch. meghalayensis as a distinct species.
Description. Adult male; color in alcohol fuscous, sparsely covered with golden yellow pubescence, dorsum of head dark brown. Length from tip of head to apices of folded forewings about 8.25 mm; maxillary palps each 1.75 mm, segment II almost equal to III; V as long as I–IV combined; labial palps each 0.50 mm long, short. Length of each forewing 7 mm; venation typical for genus; crossveins m-cu and cu parallel and separated; veins Sc and R, Cu and A running separately to wing margin. Hind wings each about 6 mm long; fork I present; veins Sc and R meeting at crossvein r before apex; stem of M and Cu1 running close together; median cell closed.
Male genitalia ( Figs. 14–18 View FIGURES14–18 ). Abdominal segment IX longitudinally short, each side anterolaterally almost straight in lateral view; apicodorsal median keel small, acute, triangular, and granulose; apical lobe on each posterolateral margin slightly indicated, setose, its posterior spine row aligned in continuity with setae on posterolateral slope of keel. Small depression visible dorsally between segments IX and X. Lateral setose areas (preanal appendages) indicated by small lobes. Body of segment X slender, lobe-like in lateral view, quadrate in dorsal view; Apicoventral setal lobes fused into single lobe, collectively quadrate apically, smooth mesocaudal lobe medially invaginated in dorsal view, forming shallow dorsal interlobular gap. Inferior appendages each with coxopodite long, slightly dilated medially and broad subapically in lateral view and in ventral view slightly curved mesad; harpago (apical segment) small, broad basally, slightly notched preapically, apically with outer edge pointed, inner protrusion small. Phallic apparatus broad basally, slender and curved caudoventrad in lateral view; phallotheca slender, slightly constricted preapically in ventral view and apically with pair of broad, sclerotized endothecal processes.
Distribution. India: Meghalaya.
Etymology. This species is named after the type state Meghalaya.
| NPC |
National Pusa Collection |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |