Chaudhripalpus costacola Beard and Seeman
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3778.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:20D5DCD9-17F5-4863-B627-42B7C349B9A7 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6137205 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/194C87D0-FFE8-FFCB-F387-FF3EFAB6F829 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chaudhripalpus costacola Beard and Seeman |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chaudhripalpus costacola Beard and Seeman sp. nov.
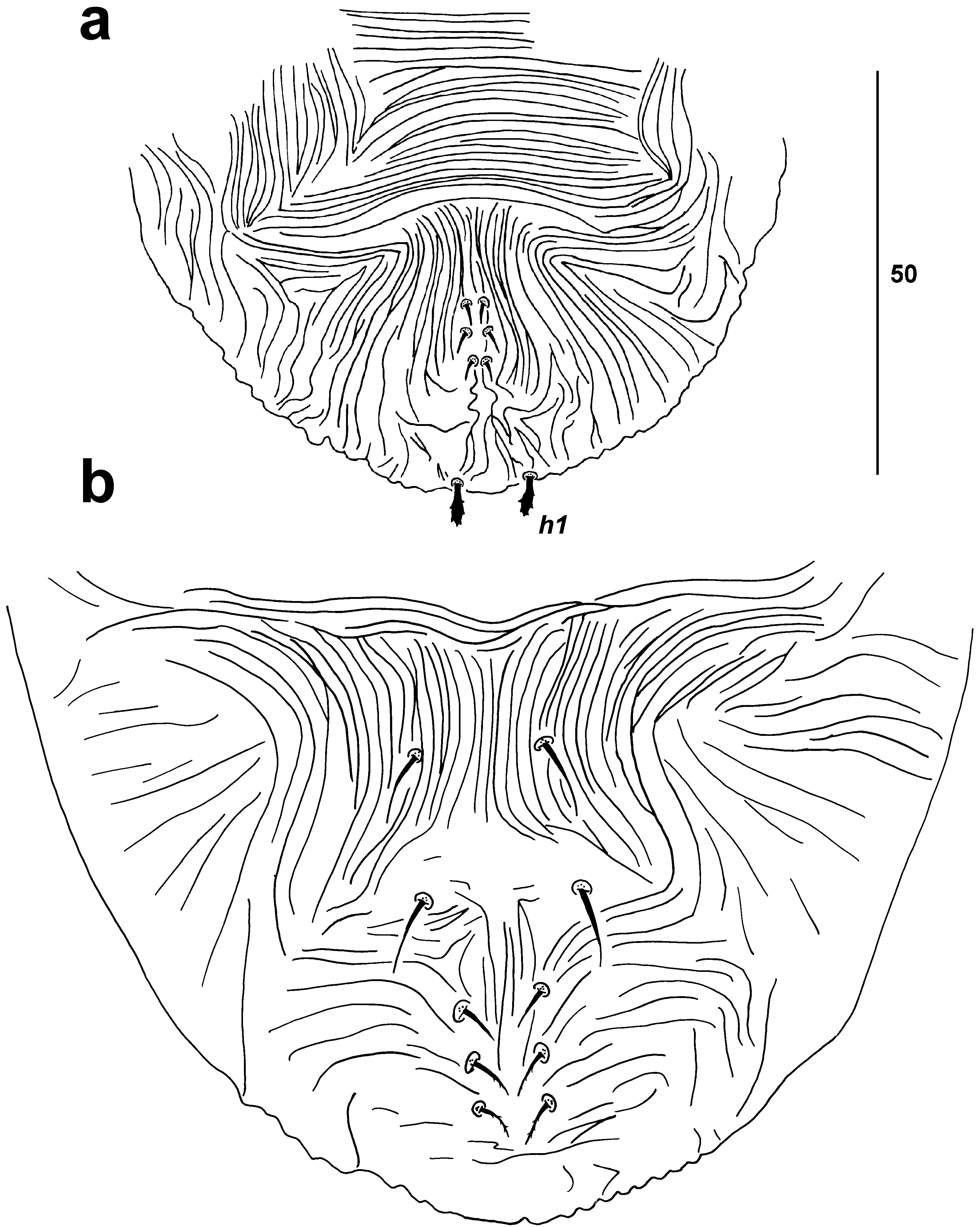
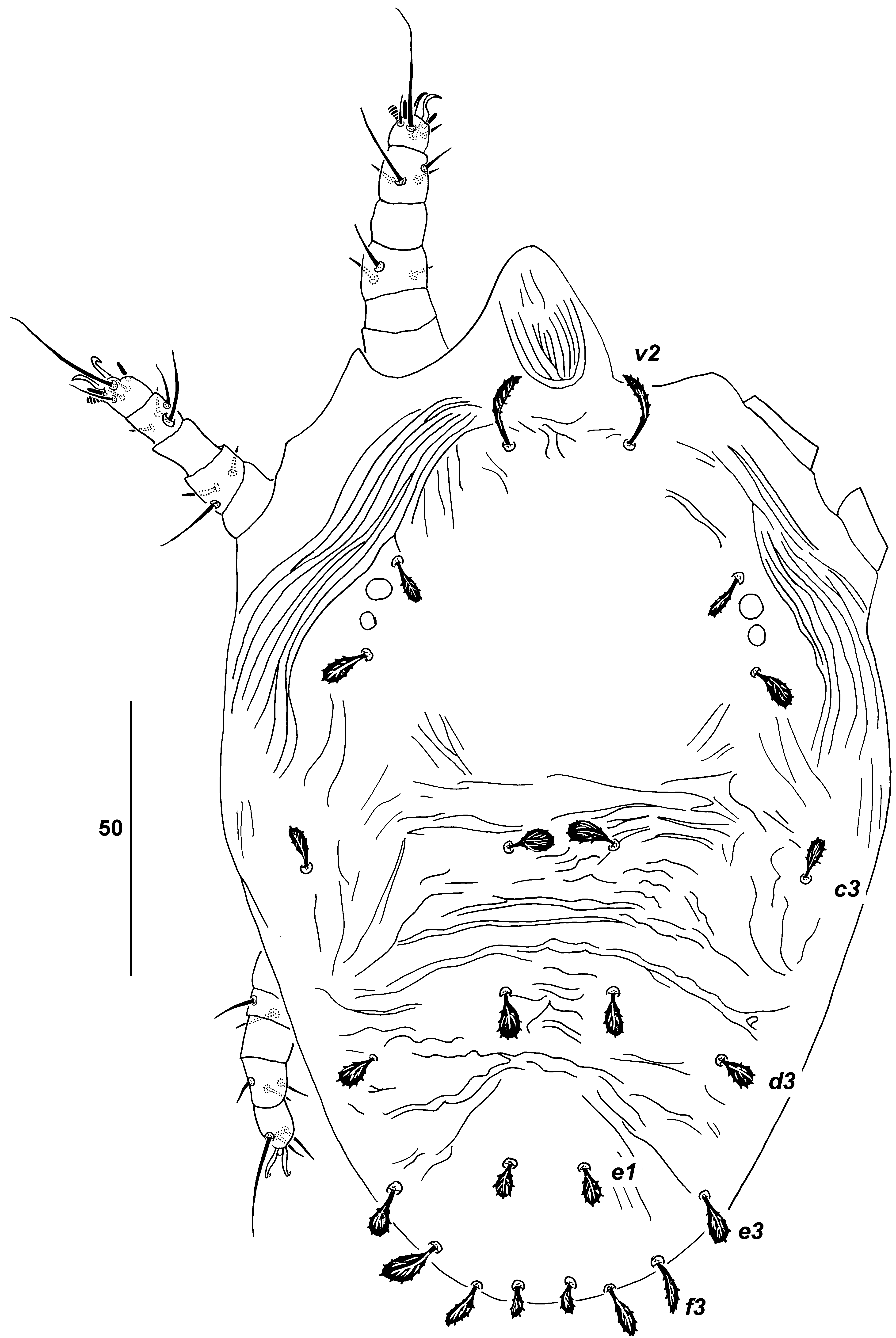
( Figs 7–12)
Type material examined. Holotype female ex. Belah Casuarina cristata (Casuarinaceae) , AUSTRALIA: New South Wales, 86 km S Goondiwindi, approx. 15 km N Moree, Newell Highway, 29°21’20” S 150°00’24” E, 21 August 2007, coll. J.J. Beard (QM). Paratypes. 4 females, 2 pharate females, 2 pharate deutonymphs, 1 protonymph, and 1 larva, same data as holotype (QM, ANIC).
Non-type material examined. 8 females, 7 pharate females, 4 deutonymphs, 11 protonymphs, 3 pharate protonymphs, and 11 larvae ex. Ca. cristata , AUSTRALIA: Queensland, 17 km west of Dalby on Moonie Highway, 27°14’13” S 151°08’52” E, 0 5 May 2007, coll. J.J. Beard and P.I. Forster (QM, USNM; BRI voucher PIF32479); 8 females, 2 protonymphs, and 4 larvae ex same host, AUSTRALIA: Queensland, 45 km south of Hebel along Castlereagh Highway, near Lightning Ridge, 28°44’43” S 148°09’12” E, 0 6 May 2007, coll. J.J. Beard and P.I. Forster (QM; BRI voucher PIF32488).
Diagnosis. Prodorsal shield with coarse, longitudinally lineate sculpturing. Dorsal opisthosomal cuticle with longitudinal striate sculpturing posteriorly; smooth cuticle between setae c1-d1; longitudinal folding between setae d1-e1; oblique folds and striate sculpturing laterally. Ventral setae ps1–2 thin, barbed, seta ps3 smooth. Trochanters I–IV 0-0-1-0 (v ′ absent on tr I–IV; l' present on tr III, added in protonymph). Spermathecal tube long, narrow, ca. 95 long before balloon-like membranous vesicle 4 long, 3 wide.
FEMALE (n = 21). Dorsum. ( Fig. 7) Body measurements: distance between setae v2 -h1 265–300 [300]; sc2- sc2 91–93 [91]; other measurements: v2-v2 38 –40 [38], sc1-sc1 82–85 [83], c1-c 1 24–28 [28], c3-c3 116–125 [125], d1-d 1 20–25 [25], d3-d3 99–110 [108], e1- e 1 22–26 [23], e3- e3 97–110 [110], f3-f3 88–99 [99], h1-h 1 21– 24 [24], h2-h2 63–74 [74]. Gnathosoma completely concealed beneath prodorsum. Anterior margin of prodorsum with 1 pair of blunt membranous triangular lobes originating from beneath prodorsal margin, notch formed between lobes 10–15 deep. Prodorsal shield weakly developed with coarse, longitudinal lineate pattern. Opisthosomal shield weakly developed with smooth cuticle medially, coarse, longitudinal-oblique lineate pattern laterally and posteriorly. Lateral cuticle surrounding shields weakly striated. All dorsal setae broadly lanceolate, barbed; medial opisthosomal setae shorter than lateral setae. Setal lengths: v 2 17–18 [18], sc 1 14–15 [15], sc 2 17– 20 [17], c 1 13–16 [16], c 3 18–19 [18], d 1 10–11 [10], d 3 16–19 [16], e 1 9 –10 [10], e 3 16 –18 [17], f 3 17–18 [18], h 1 12–13 [13], h 2 15–17 [17]. Palps. ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 a) Setal formula 0, 0, 0, 2 (1s+1e). Tarsal eupathidium 6 long; solenidion 7 long. Vent er. ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 b) Cuticle with fine transverse striae between setae 1a -3a, longitudinal between setae 3a -4a, transverse striae to midway between 4a and ag, then longitudinal striae becoming coarse around genital area. Genital setae inserted in more-or-less transverse row, g1 inserted slightly posterior to level of g2. Genital area smooth, membranous, 20–25 [25] long, 35–40 [35] wide; anal setae ps1–3 inserted medially on weakly defined anal plates in longitudinal line. Coxal setae 1a, 1b, 2b, 2c, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b fine; setae g1–2 lanceolate, setae ag1, ps1–2 narrowly lanceolate, barbed, ps3 fine. Setal lengths: 1a 40–45 [broken], 1b 20–25 [broken], 2b 12–15 [12], 2c 12–16 [13], 3a 25–40 [25], 3b 12–15 [12], 4a 30–36 [35], 4b 11–15 [15], ag 1 9–11 [9], g 1 9–11 [11], g2 10 [10], ps1 6–7 [7], ps2 6–7 [7], ps3 5–6 [6]. Spermatheca. ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 c) Spermathecal tube long, narrow, becoming convoluted distally, maximum width 1, ca. 95 long before balloon-like spermatheca 4 long, 3 wide. Genital opening just anterior to setae ps3. Legs. ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 ) Setal formula for legs I–IV (coxae to tarsi) 1-0-3-0- 4-8(1), 2-0-3-0-4-8(1), 1-1-2-0-3-4, 1-0-1-0-3-4. Tarsi I and II each with 1 antiaxial solenidion ω" (ta I 9 [9] long, ta II 8 [8] long) and 2 eupathidia pζ'-pζ" (6 long). Leg setation as in Table 1 except: cx I without 1c; tr I–IV without v ′; ge I–III without l ′, ge I–II without d, l′′; ta I–IV without tc′′.
MALE. Unknown.
DEUTONYMPH (n = 5). Dorsum. ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 ) Body measurements: distance between setae v2 -h1 235–250, sc2- sc2 90–96; other measurements: v2-v 2 25–29, sc1-sc1 83–88, c1-c 1 22–25, c3-c3 114–122, d1-d 1 20–23, d3-d3 88–96, e1- e 1 18–20, e3- e3 88–97, f3-f3 79–85, h1-h 1 18–22, h2-h2 48–56. Anterior prodorsal lobes not developed. Prodorsal shield smoothly rounded. Opisthosoma with setae c1 on weak, irregular plate, d1 on paired, weak, irregular platelets; otherwise coarse transverse striae between areas of smooth cuticle. Setal lengths: v 2 13–15, sc 1 13–15, sc 2 15–16, c 1 14–16, c 3 14–17, d 1 13–15, d 3 15–17, e 1 11 –13, e 3 12 –14, f 3 12–15, h1 10, h 2 12–15. Palps. Palps similar to adult. Solenidion 4 long, eupathidium 4–5 long. Venter. ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 b) Cuticle with transverse striae becoming longitudinal posteriorly. Coxal setae fine. Setae ps1–2 barbed, ps3 smooth. Setal lengths: 1a 22–25, 1 b 12–13, 2 b 9–11, 2 c 10–13, 3 a 17–20, 3 b 9–10, 4 a 16–22, 4 b 8–10, ag 1 8–10, g 1 10–11, ps1 4–5, ps2 5, ps3 5. Legs. Setal formula for legs I–IV same as adult. Tarsi I and II each with 1 antiaxial solenidion ω" (5 long) and 2 eupathidia pζ'-pζ" (5 long).
PROTONYMPH (n = 3). Dorsum. Body measurements: distance between setae v2 -h1 190–225, sc2-sc2 81– 84; other measurements: v2-v 2 23–25, sc1-sc1 68–70, c1-c 1 21–22, c3-c3 110–113, d1-d 1 19–23, d3-d3 82–85, e1- e 1 16–19, e3- e3 76–79, f3-f3 67–69, h1-h 1 17–25, h2-h2 36–43. Anterior prodorsal lobes not developed. Prodorsal shield weakly developed, smooth. Opisthosoma with setae c1 and d1 on paired, weak, irregular platelets; otherwise sparse striae between areas of smooth cuticle. Setal length: v 2 12–15, sc 1 10–12, sc2 14, c1 15, c 3 14–16, d 1 10– 13, d 3 11–15, e 1 8 –10, e3 13, f3 11, h1 7, h 2 9–11. Palps. Palps similar to adult. Solenidion 3–4 long, eupathidium 4 long. Venter. Cuticle with transverse striae becoming longitudinal posteriorly. Coxal setae fine. Setal lengths: 1a 25–30, 1 b 8–10, 2 b 8–10, 3 a 17–20, 3 b 6–9, ag 1 7–12, ps1 3–4, ps2 3–4, ps3 3–4. Legs. Setal formula for legs I–IV (coxae to tarsi) 1-0-3-0-4-8(1), 1-0-3-0-4-8(1), 1-1-2-0-3-4, 0-0-1-0-3-3. Tarsi I and II each with 1 antiaxial solenidion ω" (4 long) and 2 eupathidia pζ'-pζ" (5, 4–5 long). Leg setation as in deutonymph except: seta 1c absent; seta 4b absent; tarsi IV without tc′′. Setae l' added to tr III.
LARVA (n = 16). Dorsum. ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 ) Body measurements: distance between setae v2 -h1 130–160, sc2-sc2 64– 69; other measurements: v2-v 2 20–21, sc1-sc1 55–60, c1-c 1 17–18, c3-c3 87–96, d1-d 1 18–19, d3-d3 58–61, e1- e 1 8–11, e3- e3 46–57, f3-f3 33–41, h1-h1 8, h2-h 2 14–22. Anterior prodorsal lobes not developed. Prodorsal shield weakly developed, smooth. Opisthosoma without platelets, with coarse transverse wrinkled striae, becoming oblique posteriorly. Setal lengths: v 2 12–13, sc1 7–8, sc 2 10–11, c 1 9–10, c 3 8–10, d1 8–9, d 3 9–10, e1 6 –8, e 3 9 – 11, f 3 9–10, h1 5–6, h2 9. Palps. Palps similar to adult except solenidion 3 long and eupathidium 5–6 long. Venter. ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 a) Cuticle with transverse striae becoming longitudinal posteriorly. Coxal setae fine. Setal lengths: 1a 16– 21, 1 b 11–12, 3 a 14–23, ps1 3–4, ps2 3–4, ps3 3–4. Legs. ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 ) Setal formula for legs I–III (coxae to tarsi) 1-0- 3-0-4-7(1), 0-0-3-0-4-7(1), 0-0-2-0-3-3. Tarsi I and II each with 1 antiaxial solenidion ω" (3 long) and 2 eupathidia pζ'-pζ" (4 long). Leg setation as in protonymph except: seta 2b absent; seta 3b absent; tr I–III nude; tarsi I–III without seta tc ′.
Hosts and distribution. This species was collected from Belah , Ca. cristata from northwestern New South Wales and southwestern Queensland.
Etymology. The specific name is derived from costa (rib) and cola (dweller), alluding to the habit of these mites to lodge in between the ribs on stems of she-oaks.
Remarks. This species was a darkish matt red colour in life and was found on the stems, with Pentamerismus sititoris and Philippipalpus belah .
Chaudhripalpus costacola can be separated from Ch. creelae by the absence of v' on trochanters I–IV (present on tr I–II in Ch. creelae ) and the presence of narrow setiform setae ps1–2 (broadly lanceolate in Ch. creelae ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |