Asterina hoensonae, O'Loughlin, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24199/j.mmv.2009.66.18 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10878895 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A029C521-FFEA-A74B-FF5D-DEC7D75CF9E5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Asterina hoensonae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Asterina hoensonae View in CoL sp. nov.
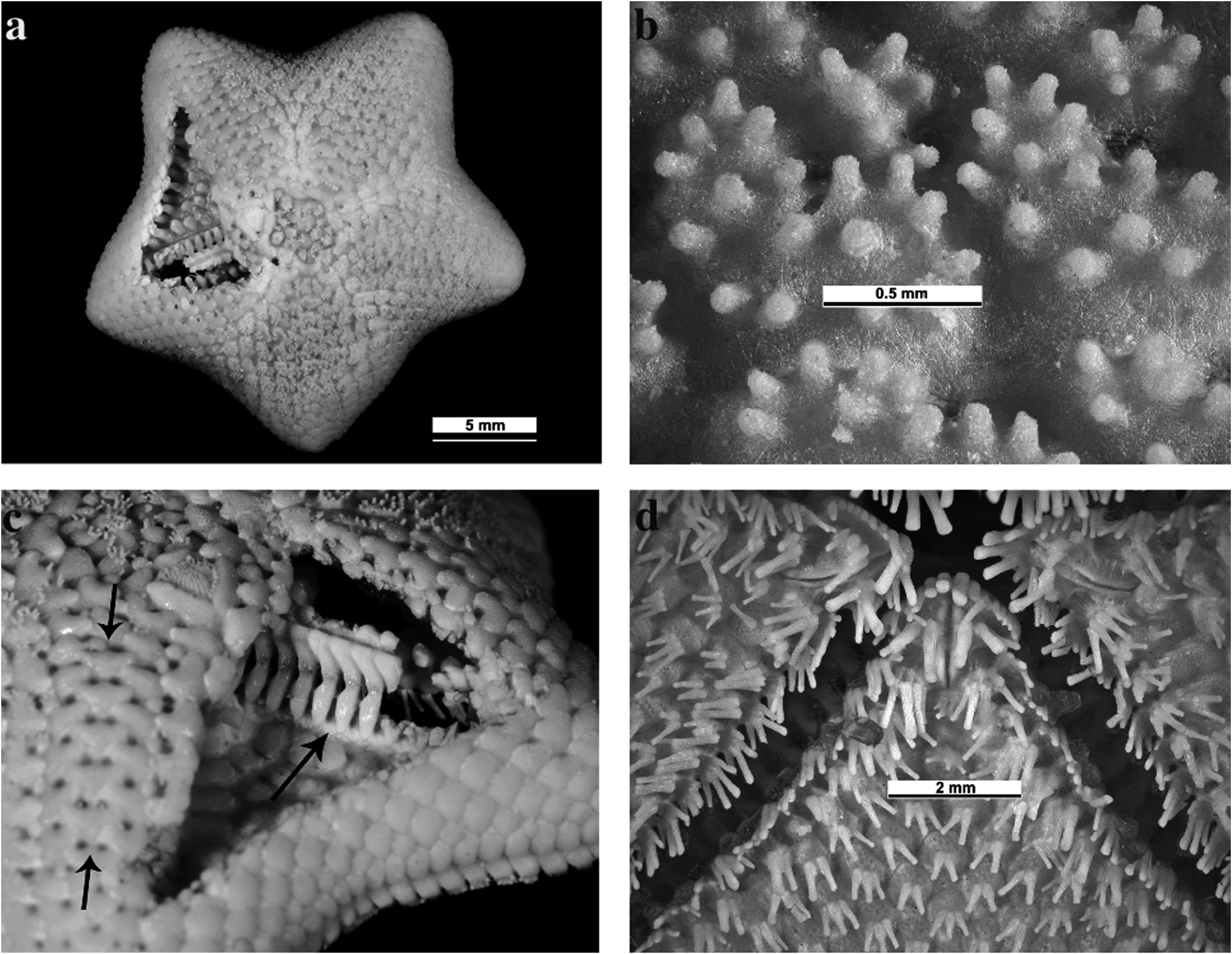
Figure 3a–d View Figure 3
Asterina gracilispina View in CoL .— Mortensen, 1933: 255–256 (non A. gracilispina View in CoL ). — O’Loughlin and Waters, 2004: 11, 15–16 (non A. gracilispina View in CoL ). —A.M. Clark,1974:437 (part non A.gracilispina View in CoL ). —A.M. Clark and Courtman-Stock, 1976: 77 (part non A. gracilispina View in CoL ).
Material examined. Holotype (in alcohol; part dissected): South Africa, Cape Agulhas , 34°S, 20°E, C. Griffiths (University of Cape Town), NHM 1975.10.29.47. GoogleMaps
Description. Small, subpentagonal, R = 12 mm, r = 9 mm; rays 5, discrete, wide at base, short, rounded distally; body integument not evident; low convex abactinally, sides not steep, margin acute, single conspicuous madreporite; gonopores not detected; absence of pedicellariae; absence of superambulacral and superactinal plates; margin supported by internal contiguous projections of abactinal and actinal plates; glassy convexities on plates.
Abactinal: plates imbricate, surface flat, not broken by raised edges of plates, plates not notched, shallow concave proximal indentations for papulae; doubly papulate carinal series of plates along upper ray; papular spaces large, 0–2 secondary plates per space, 0–3 large papulae per space, 10 longitudinal series of papulae across mid ray; disc distinctly bordered; spinelets digitiform to subgranuliform, short, blunt, up to about 0.15 mm long, cover projecting abactinal plates, up to 16 spinelets per plate.
Margin: superomarginal and inferomarginal plates longitudinally elongate, in regular series, up to about 11 slightly conical subgranuliform spinelets spread over each superomarginal plate, subequal with inferomarginal spinelets, projecting inferomarginal plates with up to about 16 spinelets.
Actinal: interradial plates in variably longitudinal and oblique series; complete series of adradial actinal plates and spines.Actinal spines per plate: oral 9 (series tapering uniformly from tall proximally to short distally, tallest spines slightly swollen distally, smallest pointed distally); suboral 3; furrow 6; subambulacral 4; adradial actinal 2–3; actinal interradial 2–3 mid ray, 3–5 distally; spines digitiform, webbed.
Distribution. South Africa, Cape Agulhas (E of Cape Town).
Etymology. Named in appreciation of the contribution to this work by Elizabeth Hoenson of the South Africa Museum, who went to considerable lengths to make available essential loans for this work.
Remarks. The new species has the diagnostic characters of genus Asterina Nardo as detailed in the emended diagnosis by O’Loughlin and Rowe (2006): 5 discrete rays; not fissiparous; disc distinctly bordered; carinal series of doubly papulate plates; extensive papulate areas, numerous papulae and secondary plates; abactinal spinelets digitiform to subgranuliform; predominantly 2–3 digitiform actinal spines per plate; lacking superambulacral and superactinal plates; margin supported internally by contiguous projections of abactinal and actinal plates.
Some characters distinguishing Asterina hoensonae sp. nov. from Asterina gracilispina are listed under A. gracilispina above. Asterina hoensonae is distinguished from most of the remaining species of Asterina ( A. gibbosa , A. ocellifera , A. pancerii , A. phylactica and A. stellifera ) by lacking pedicellariae; and from A. fimbriata by having a distinctly bordered disc.
I discuss this specimen under Asterina gracilispina above. It is the specimen I wrongly accepted as being Asterina gracilispina in O’Loughlin and Waters (2004).Another specimen (False Bay, 26 m; R = 10 mm) in the South Africa Museum, referred “with considerable doubt” to A. gracilispina by Mortensen (1933), is probably A. hoensonae (see above). Specimens from Algoa Bay and Mossel Bay referred to A. gracilispina by A.M. Clark (1974) and A.M. Clark and Courtman-Stock (1976) are probably A. hoensonae (see above).
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Asterina hoensonae
| O'Loughlin, P. Mark 2009 |
A. gracilispina
| O'Loughlin, P. M. & Waters, J. M. 2004: 11 |
A. gracilispina
| Clark, A. M. & Courtman-Stock, J. 1976: 77 |
A.gracilispina
| Clark, A. M. 1974: 437 |
Asterina gracilispina
| Mortensen, Th. 1933: 255 |