Asplenium maguanense S.Q.Liang, R.Wei & X.C.Zhang
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.521.2.5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5533609 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D21A04-B63F-FF89-FF44-FF26AA2EFDE4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Asplenium maguanense S.Q.Liang, R.Wei & X.C.Zhang |
| status |
|
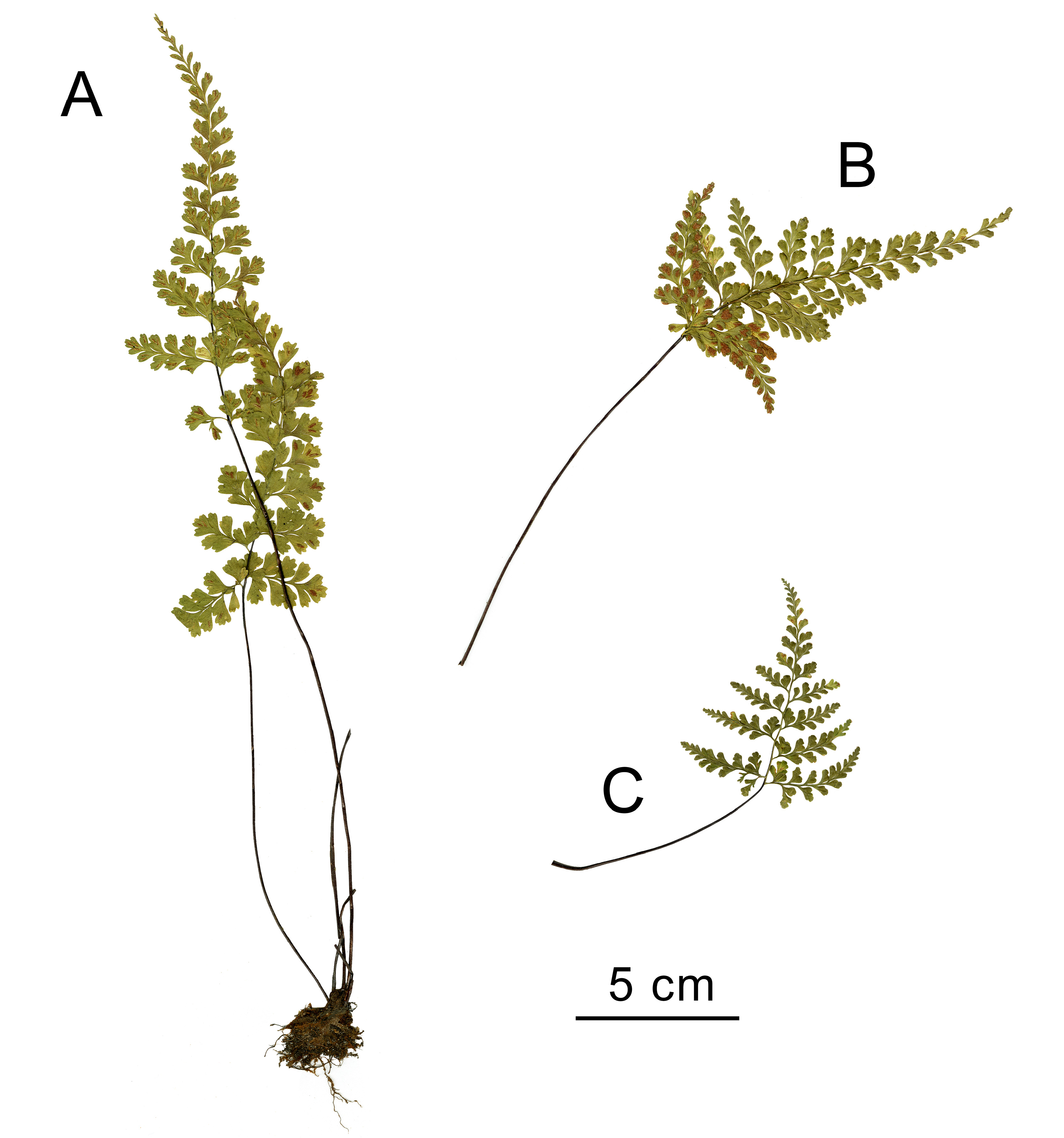
Asplenium maguanense S.Q.Liang, R.Wei & X.C.Zhang View in CoL ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 )
Type:— CHINA. Yunnan: Maguan County, Bazhai Town , Valley behind Langqiao Village , 7 April 2017, Xian-Chun Zhang et al. 8214 (holotype PE!) .
Additional specimens examined:— VIETNAM. Ha Giang: Quan Ba District, Nghia Thuan Commune, Bat Dai Son Nature Reserve, 10 December 2013, Li-Bing Zhang , Liang Zhang & Thi Ngan Lu 6889 ( CDBI, MO, VNMN).
Distribution:—This species is currently only known from southwestern China and northern Vietnam.
Ecology:—It occurs on limestone areas under evergreen forest, at the elevation of 800–1,800 m.
Note:—This species is characterized by bipinnate-pinnatifid to bipinnate-pinnatisect lamina, ultimate segment apex with short teeth, tooth length rarely longer than width, and scale apex ending in a short apical tail shorter than 0.6 mm ( Liang et al. 2019). Asplenium maguanense is morphologically most similar to A. coenobiale Hance (1874: 142) , both species belong to A. coenobiale complex sensu ( Liang et al. 2019, Xu et al. 2020).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.