Macrorynchia fallax, Galea & Maggioni, 2024
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5428.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:041905ED-FCED-4ED5-8248-E9AA8D6271E9 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10870367 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A5566C-FFE3-FF97-FF1D-F9292B10FE67 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Macrorynchia fallax |
| status |
|
Leptothecata View in CoL : Aglaopheniidae
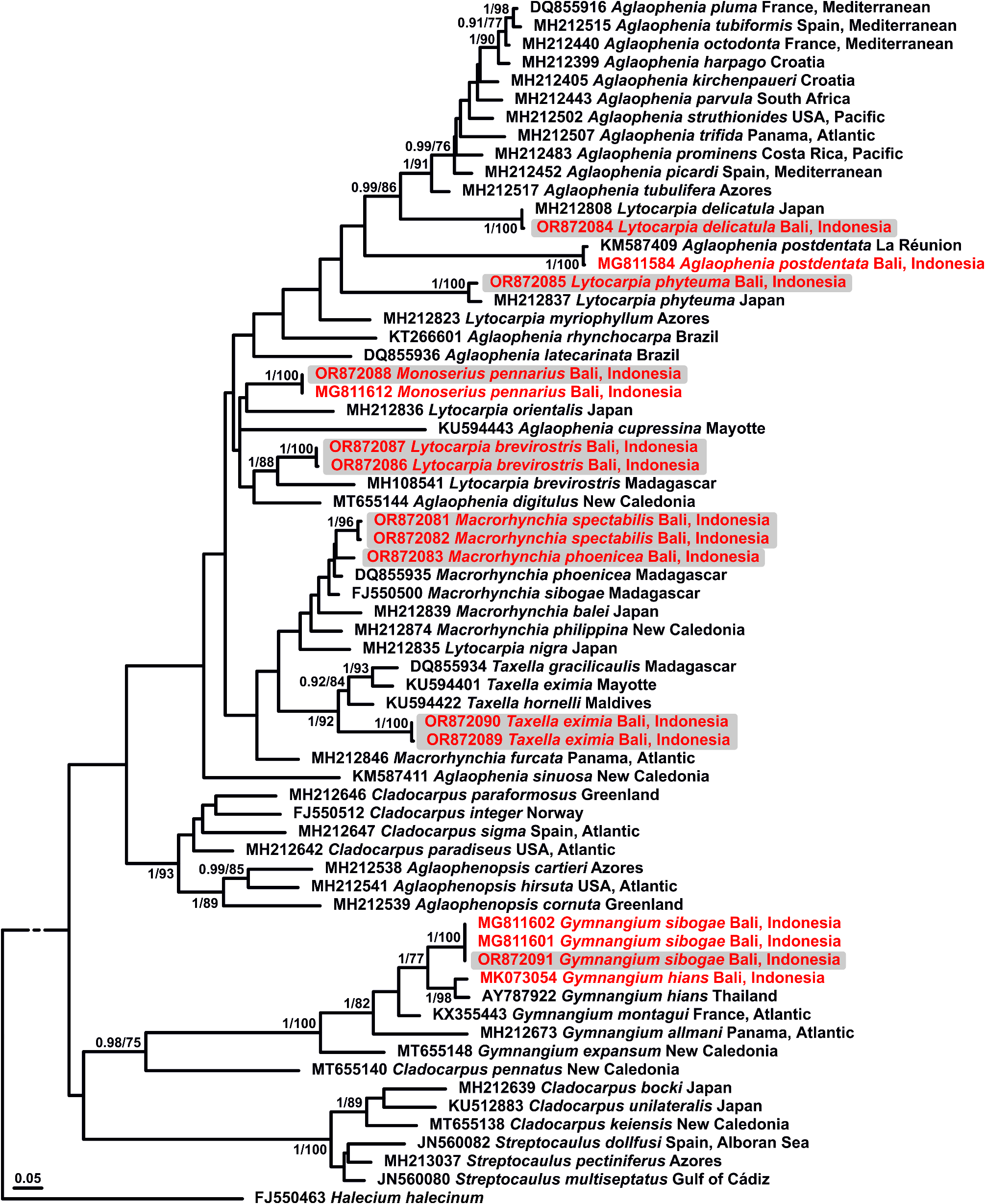
A total of 11 aglaopheniid species from Bali were sequenced, including Aglaophenia postdentata ( Billard, 1913) , Gymnangium hians ( Busk, 1852) , G. sibogae ( Billard, 1913) , Lytocarpia brevirostris ( Busk, 1852) , L. delicatula ( Busk, 1852) , L. phyteuma ( Stechow, 1919b) , Macrorynchia fallax sp. nov., M. phoenicea ( Busk, 1852) , M. spectabilis ( Allman, 1883) , Monoserius pennarius ( Linnaeus, 1758) and Taxella eximia Allman, 1874 . Specifically, genetic data for M. spectabilis are available for the first time, supplementing those obtained earlier for G. hians , G. sibogae and M. pennarius (P. Schuchert, unpublished data). Interestingly, L. brevirostris from Bali shows a high 16S rRNA genetic distance (of 9.2 ± 1.2%) with a sequence from Madagascar, despite forming, altogether, a monophyletic group, possibly suggesting the presence of cryptic species ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 ). Similarly, T. eximia from Bali clusters with other Taxella species ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 ), being nevertheless divergent from a sequence of T. eximia from the Western Indian Ocean (16S rRNA genetic distance of 7.5 ± 1.2%).
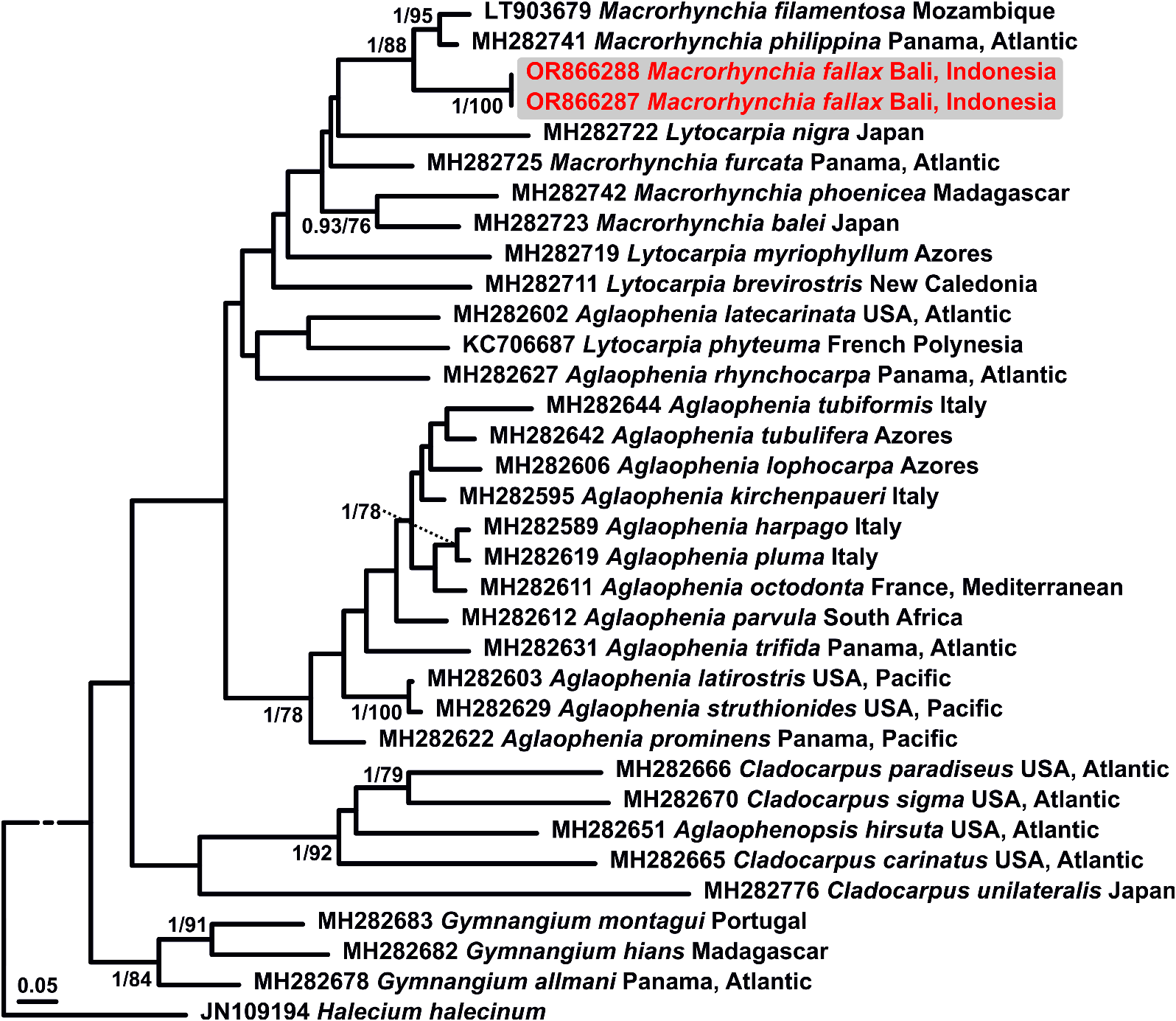
The 16S rRNA region of M. fallax could not be amplified, despite several attempts, while other regions were successfully amplified and sequenced (COI, 18S rRNA, and 28S rRNA). Specifically, a phylogenetic hypothesis based on the COI region was obtained to assess the relationships between M. fallax and other aglaopheniid species ( Fig. 34 View FIGURE 34 ). The two COI sequences obtained for M. fallax are identical to each other and closely related to sequences obtained from M. philippina Kirchenpauer, 1872 and M. filamentosa ( Lamarck, 1816) . However, they show high genetic distances from these two species, viz. 9.9 ± 1.2% and 11.1 ± 1.2%, respectively.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |