Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) alba Chaudhuri, Debnath et Nandi
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4564.1.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E3EB75E0-CB37-4B60-A554-7E3F450DC581 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5271387 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B05940-FFA8-FFA5-FF50-F91CFAA0D2A4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) alba Chaudhuri, Debnath et Nandi |
| status |
|
Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) alba Chaudhuri, Debnath et Nandi View in CoL
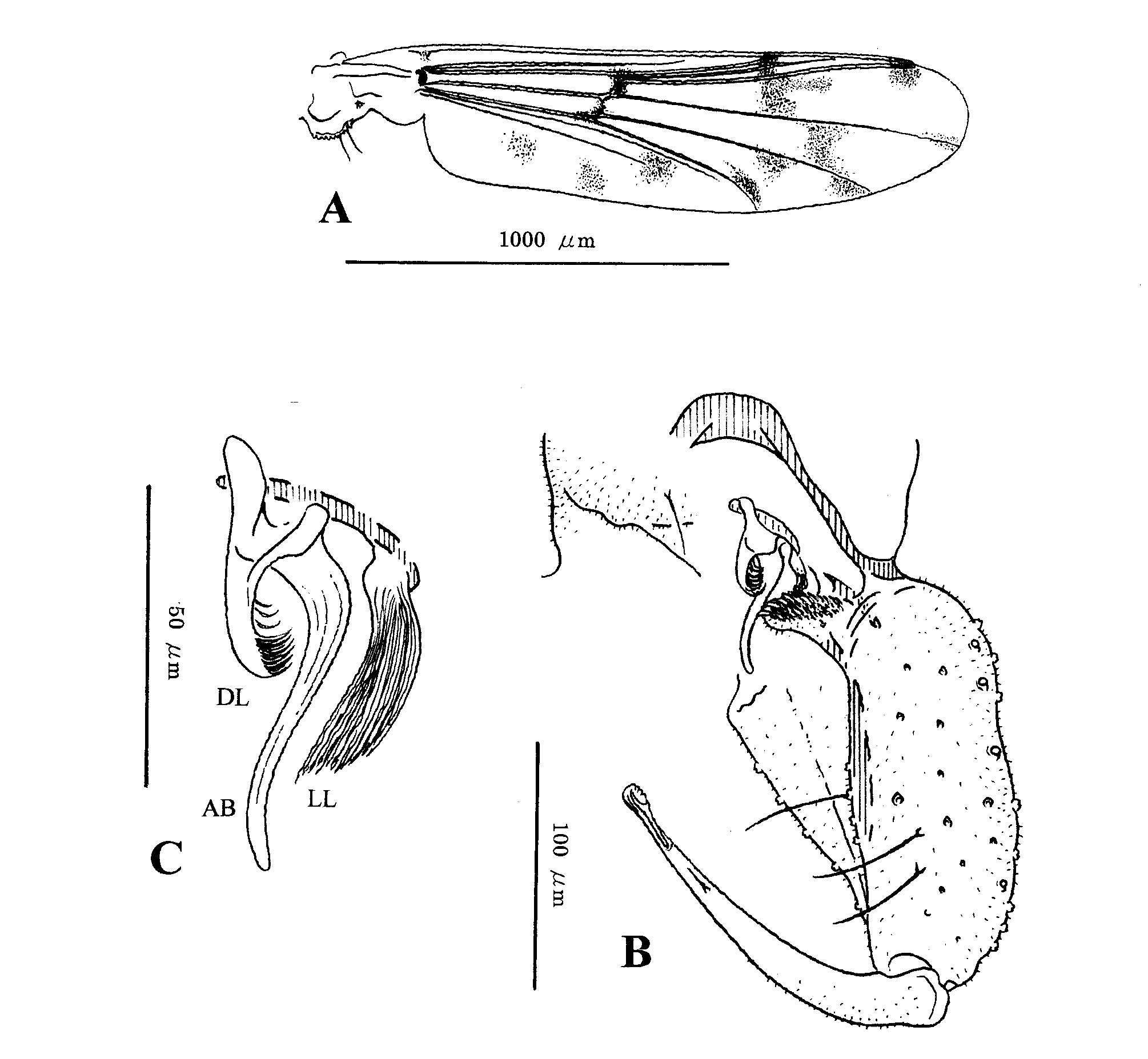
( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 )
Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) alba Chaudhuri, Debnath et Nandi, 1983: 902 View in CoL ; Haza et al. 2011: 330.
Material examined. 1 male, CHINA: Guangdong Province, Shantou City, Nan’ao county, Shen’ao Bay near Marine Field Station of Shantou University , 25–26.ix.2016 , light trap; 1 male, Macau Special Administrative Region, Co-Tai Conservation Zone , 20.vii.2012 ; 5 males, as previous except 12.vi.2013; 3 males, as previous except 20.vii.2014.
Description. Male (n=10). Total length 2.4–2.9, 2.7 mm.
Coloration. Head vertex, clypeus and all palpomeres brown. Thorax brownish except yellowish pleural membrane. Abdomen pale yellow with subcutaneous pigmentaion; T VI–VIII and gonocoxite of hypopygium somewhat darkened. Wing ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ) with dark spots on RM, FCu, and at apices of R 1 and R 4+5; membrane dark spot in middle of cell r 4+5 proximal to that in middle of cell m 1+2. Legs white with dark bands. Fore- and midfemora darkened on basal 2/3, each with sub-apical dark band. All tibiae each with 3 dark bands; sub-basal and median bands in foretibia located 0.76–0.80, 0.79 (9) and 0.38–0.41, 0.40 (9), respectively, from apex.
Head. Temporals 25–31, 27. AR 1.5–1.7, 1.6. Clypeus trapezoid with 23–35, 28 setae. Lengths of palpomeres 1–5 (µm): 37–44, 41 (9); 74–84, 79 (9); 103–123, 114 (9); 76–91, 86 (9); 172–207, 189 (9). Pm 4 0.73–0.79, 0.75 (9) times as long as Pm 3; Pm 5 2.0–2.4, 2.2 (9) times as long as Pm 4.
Thorax. Antepronotum laterally with 7–13, 10 (8) setae. Acrostichals 46–57, 51 (9), biserial, diverging posteriorly; dorsocentrals 14–20, 18, uniserial; humerals 11–16, 14; prealars 12–21, 18; supraalars 1. Scutellum with transverse row of 9–14, 12 (8) long posterior setae and group of 20–29, 24 (6) short anterior setae.
Wing. Length 1.6–1.8, 1.7 mm. Squama with 25–37, 28 setae. VR 0.83–0.88, 0.85.
Legs. Ti I spur 48–52, 50 (8) µm long with 6–8, 7 (6) lateral teeth. Ti II spurs 50–60, 55 and 25–30, 27 µm long, with 6–8, 6 (8) and 3–5, 4 (8) lateral teeth, respectively; inner spur 1.8–2.2, 2.1 times as long as outer spur. Ti III spurs 57–64, 58 and 25–31, 27 µm long, with 4–5, 4 (5) and 3–5, 4 (9) lateral teeth, respectively; inner spur 2.0–2.4, 2.2 times as long as outer spur. Ti III comb consisting of 5–6, 5 bristles. Sub-apical pseudospurs present on ta 1–3 of all legs. Lengths and proportions of legs as in Table 1.
Hypopygium ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ). T IX with 1–3, 1 seta on each side. Gonocoxite 150–163, 156 µm long, with weak basolateral bulge. Aedeagal complex ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ) with dorsal lobe 28–33, 31 µm long, 0.46–0.53, 0.51 times as long as blade, bearing apical brush; blade 60–63, 61 µm long, sinuate, tapering toward rounded apex; lateral lobe well developed, 49–53, 51 µm long, 0.78–0.88, 0.83 times as long as blade; lateral filaments not evident in dorsal view. Gonostylus 145–155, 150 µm long, 0.92–0.99, 0.96 times as long as gonocoxite, with sub-terminal seta expanded apically.
Larva. Unknown.
Remarks. The male resembles that of A. (A.) monilis (Linnaeus) in the aedeagal complex with a dorsal lobe bearing an apical brush, a sinuate blade tapering toward a rounded apex and a well-developed lateral lobe, but differs from it in the wing with two dark spots along the costal margin and the aedeagal blade with no basal projection. In A. (A.) monilis , the wing possesses three spots at the apices of R 1, R 3 and R 4+5, and the aedeagal blade has a basal pointed projection ( Fittkau 1962, fig. 397; Roback 1971, figs 573–575; Niitsuma 2013, fig. 3).
In the redescription of A. (A.) monilis by Niitsuma (2013), the lateral lobe (LL) was mistaken for the lateral filaments (LF). What he has indicated as LF in his fig. 3 is the lateral lobe with filaments on the membranous base, and the lobe merges with the lateral filaments that are more lateral and continue further by merging with shorter filaments on the ventral side of the basidorsal lobe (B. Bilyj, pers. comm.). The structure is better defined in the lateral view. The males of A. (A.) alba and A. (A.) monilis may be separable from each other by the lateral lobe in the dorsal view, too, which was overlooked in the original description of the former species (N. Hazra, pers. comm.). The relative length to the aedeagal blade is 0.78–0.88 in A. (A.) alba , and more than 1.0 in A. (A.) monilis (see Niitsuma 2013, fig. 3).
The distribution of A. (A.) alba extends from West Bengal State in India to Guangdong Province in China.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) alba Chaudhuri, Debnath et Nandi
| Niitsuma, Hiromi & Tang, Hongqu 2019 |
Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) alba Chaudhuri, Debnath et Nandi, 1983 : 902
| Chaudhuri, P. K. & Debnath, R. K. & Nandi, S. K. 1983: 902 |