Silvestrichilis chinensis Kaplin, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.25221/fee.376.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D417CC41-328B-45F5-A798-9F57840A8EC2 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C6BAB796-75C3-40C5-AFD3-4F030E7B41CF |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:C6BAB796-75C3-40C5-AFD3-4F030E7B41CF |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Silvestrichilis chinensis Kaplin |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Silvestrichilis chinensis Kaplin , sp. n.
http/ urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C6BAB796-75C3-40C5-AFD3-4F030E7B41CF
Figs 1–13 View Figs 1–7 View Figs 8–13
MATERIAL. Holotype – ♀, China: Sichuan, W Nignan Xian, 3.3 km WSW Xiaotiancun village , 27°02ʹ13ʹʹ N, 102°37ʹ18ʹʹ E, h = 1540 m, 27.VI 2018, leg. I. Belousov, I. Kabak GoogleMaps
[ VIZR] (in slides).
DESCRIPTION. FEMALE. Holotype. Body length 10.8 mm; body width 3.1 mm. Total eyes width 1.07 mm; eye length 0.44 mm. Paired ocelli width 0.31 mm; length 0.12 mm.
Coxae styli length 0.65–0.70 mm. Ovipositor length 3.8 mm.
General body color whitish, practically without hypodermal pigment. Antennal base, frons,
clypeus, galea and lacinia of maxillae, mandibles and coxae of all legs with purple hypodermal pigment of weak or medium intensity. Color of scales on surface of body brownish. Antennae slightly shorter than body. Distal chains of flagellum divided into 11 annuli. Cerci partially broken.
Eyes adjacent, slightly transverse, motley, dark brown, with bluish specks, lighter near the contact line of the eyes (in alcohol). Ratio length to width of compound eye about 0.85;
ratio of length of contact line to length of eye about 0.36. Paired ocelli sublateral, oval, light brown with white narrow borders, 2.6 times as wide as long. Distance between inner margins of ocelli about 0.48 and between their outer margins 0.96 total width of compound eyes
( Fig 1 View Figs 1–7 ).
Maxillary palps broken, have only three palpomeres. Second maxillary palpomere 1.1
times as long as 3rd palpomere ( Fig. 5 View Figs 1–7 ). Apices of lacinia 2-toothed ( Fig. 4 View Figs 1–7 ). Apices of mandibles 4-lobed ( Fig. 3 View Figs 1–7 ). Ultimate labial palpomere oval-triangular, 1.3 times as long as wide
( Fig. 2 View Figs 1–7 ).
Fore femora, fore and middle tibiae dilated ( Fig. 6 View Figs 1–7 ). Ratios of length to width of femora,
tibiae and tarsi given in Table 1. Middle legs shorter than fore ones. Hind legs the longest.
Fore tarsi 1.1, hind ones 1.2 times as long as middle tarsi. Fore tibiae 1.1, hind ones 1.4 times as long as middle tibiae. Ratio length of apical hind tarsomere to whole hind tarsus about 0.36
( Fig. 7 View Figs 1–7 ). Tarsi and tibiae with acicular macrochaetae. First fore, middle and hind tarsomeres with 2–3 acicular macrochaetae, 2nd fore and middle tarsomeres with 5–6, hind ones 7–8;
3rd middle and hind tarsomeres with 1–2 such macrochaetae. Middle tibiae with 1–2, hind ones with 3–4 acicular macrochaetae. Second middle and hind tarsomeres also with thick shortened, vertically erect macrochaetae characteristic of the genus Silvestrichilis , their number
2–3 ( Fig. 7 View Figs 1–7 ). Styli present on middle and hind coxae. Ratio of stylus length to coxa width
1.6–1.7.
female.
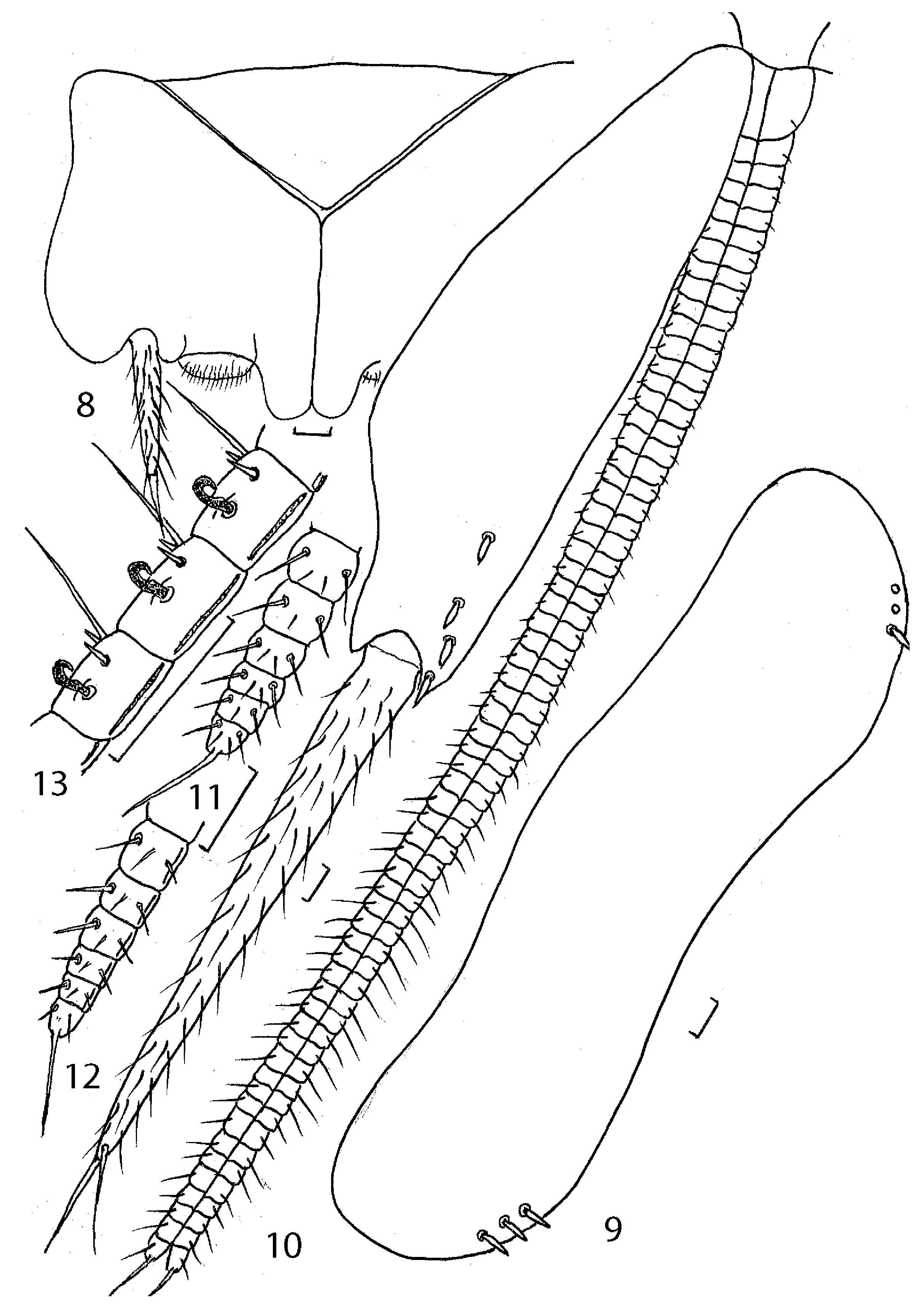
Thoracic tergites, urotergites I–III, urocoxites I–VIII and urosternites without macrochaetae. Urotergites IV with 1–2 + 1–2, urotergites V–VI with 3 + 3, VII with 3–4 + 3–4,
VIII–IX with 4 + 4, X with 3 + 3 sublateral macrochaetae ( Fig. 9 View Figs 8–13 ). Urocoxites IX with 4 + 4
inner lateral macrochaetae ( Fig. 10 View Figs 8–13 ).
2 – labial palp; 3 – distal part of mandible; 4 – galea and lacinia of maxilla; 5 – basal part of maxillary palp; 6 – fore leg (part); 7 – hind tarsus. Scale bars = 0.1 mm.
coxite VII; 9 – urotergite X; 10 – anterior gonapophyses with urocoxite IX; 11 – apical part of anterior gonapophyse; 12 – apical part of posterior gonapophyse; 13 – 7–9th divisions
(from apex) of posterior gonapophyse. Scale bars = 0.1 mm.
Ovipositor long, segmented, of type I, slightly extending beyond apices of urostyli IX
( Fig. 10 View Figs 8–13 ). Anterior gonapophyses with 64, posterior gonapophyses with 63–65 divisions. All divisions of anterior gonapophyses with setae, 36–38 basal divisions of posterior gonapophyses glabrous. Apical spines of gonapophyses as long as 3–4 apical divisions combined. Apical divisions of anterior gonapophyses with 4–5, posterior gonapophyses with 2–3 setae (not counting sensory setae and apical spines) ( Figs 11, 12 View Figs 8–13 ). 7–24th divisions (from apex) of posterior gonapophyses with 1 lateral outer short and dark hook-shaped seta characteristic of posterior gonaspophyses of females of the genus Silvestrichilis ( Fig. 13 View Figs 8–13 ). Total number of hook-shaped setae 18 pairs.
MALE. Unknown.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS. Silvestrichilis chinensis sp. n. clearly differs from the other known species of this genus by the structure of ovipositor. Posterior gonapophyses of
S. chinensis with 18 hook-shaped setae on 7–24th divisions (from apex). Ovipositor of S.
confucius from China and also S. tuceti Janetschek, 1955; S. molchanovi Kaplin, 1982 ; quite possibly S. heterotarsus (Silvestri, 1942) and S. trispina (Wygodzinsky, 1939) without hookshaped setae. Posterior gonapophyses of other species of this genus with 6–11 and only S.
zazimkoi Kaplin, 2007 from Caucasus with 15 hook-shaped setae ( Kaplin, 2018). Ovipositor of S. chinensis sp. n. with 63–65, S. сonfucius with 53–61, S. zazimkoi with 68–70 divisions;
posterior angle of urosternites II–V 93–94 °, 85–90 ° and 78–89 °, respectively; ratio of length of contact line to length of eye about 0.36, 0.40–0.51 and 0.16–0.18, length to width ratio of apical labial palpomere of female 2.6, 2.3 and 2.3–2.4.
ETYMOLOGY. The new species is named after China, where it was collected.
| VIZR |
Collection for plant protection, All-Russian Institute of Plant Protection |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |