Bufoceratias cf. wedli
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4121.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:43691D85-5544-42B2-8F57-F87AC3EAD869 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5617540 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/EF45FB7C-C26B-FFA6-3DC0-44CBFC6BFC2F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bufoceratias cf. wedli |
| status |
|
Bufoceratias cf. wedli View in CoL [sensu Pietschmann, 1926]
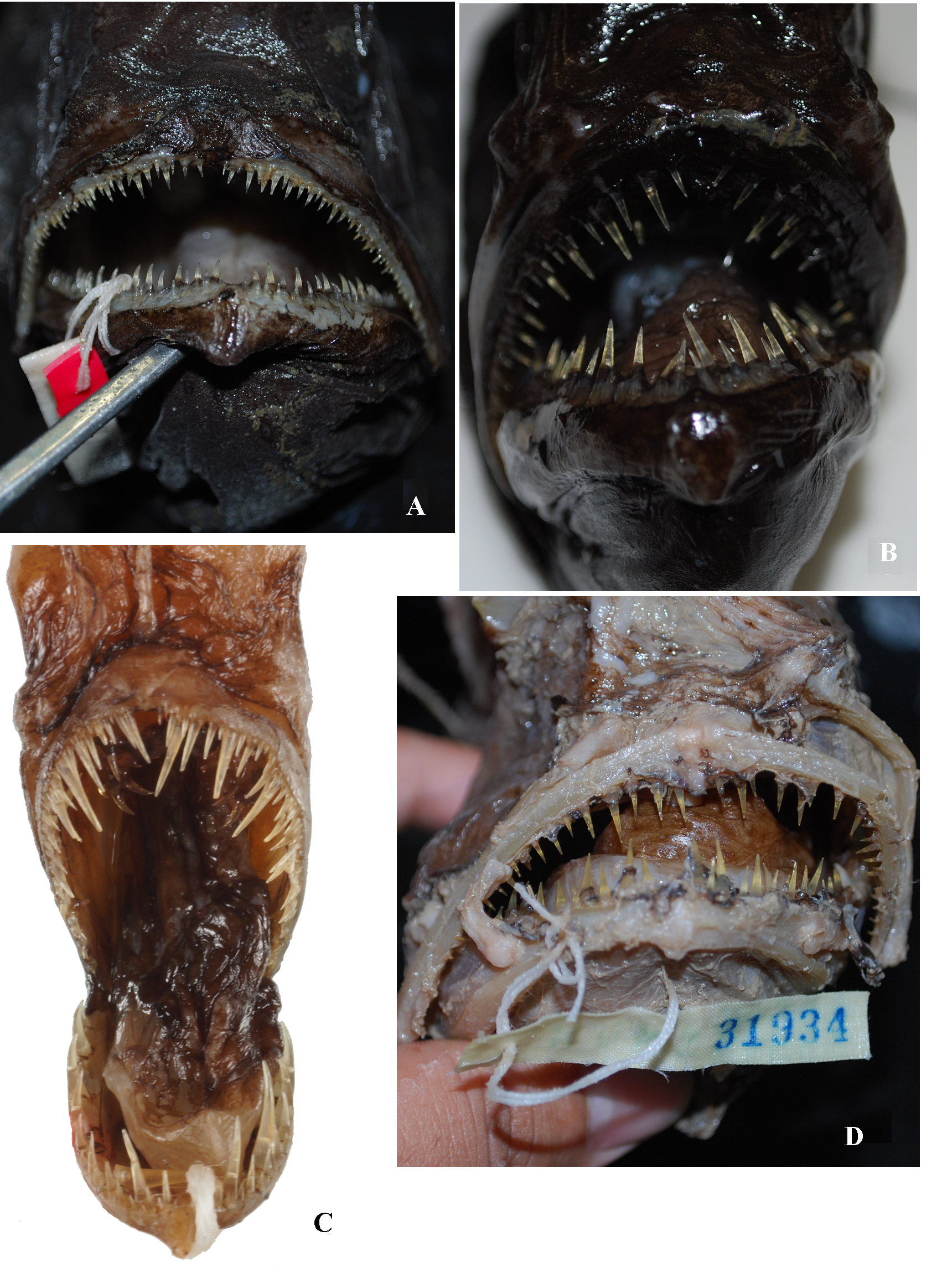
Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6. A D, 9A–B
Material. HUMZ 194334 (1, 131.2), st. 66, 4°33.7'S, 109°13.4'E – 4°32.8'S, 109°11.8'E, off Sumatra, 530–582 m, 11 May 2005.
Description. Dorsal-fin rays 6; pectoral-fin rays 14; anal-fin rays 4; caudal-fin rays 9. Teeth on vomer 9 (4, 5); upper jaw teeth 40; lower jaw teeth 33. Head length 44.3% SL; head depth 52.9; head width 36.6; frontal width 17.0; illicial length 47.5; distance between upper jaw symphysis and origin of illicium 55.0; upper jaw length 39.8; lower jaw length 42.1.
Body short and globular, rounded in lateral view. Mouth large, oblique. Illicium emerging from dorsal surface of head behind sphenotic spines. Illicium relatively short. Esca moderate in size, its total length 25.7% SL and width 5.6% SL, appendages less complex than in B. shaoi ; a broad-based anterior appendage, total length 21.6% SL, with four main branches, each with few secondary branches; a pair of lateral appendages, total length 26.1% SL, one with three main branches and one with four, each main branch with few secondary branches and filaments; a pair of posterior appendages, 16.2% SL, each with many short to moderately long filaments; terminal papilla stout, slightly shorter than esca, 2.7% SL, rounded and slightly expended distally, uniformly pigmented.
Slender fang-like teeth on both jaws, longest teeth on upper jaw 3.8% SL, longest teeth on lower jaw 5.3% SL.
Remarks. The presence of a pair of branched posterior appendages (total length 16.2% SL) and rounded terminal papilla that is expanded distally and fully pigmented suggest this specimen is most similar to B. wedli . However, the specimen has a very short illicium (47.5% SL), compared to that of B. wedli (99.7–147.4% SL, n=12, 19.4–127.0 mm SL), but relatively long compared to that of B. shaoi (24.8–40.0%, n=9, 33.5–101.0 mm SL).
Uwate (1979) described the development of the esca of B. wedli which displays elongation of the escal terminal papilla by 60 mm (SL) and other appendages usually developing by 40 mm with increased branching and filament elongation by 50 mm (SL). In contract, all specimens of B. shaoi (33.5–101.0 mm SL) lack the posterior appendage. Thus, the presence of posterior appendage(s) is herein recognized as a diagnostic character for B. wedli in specimens larger than 50 mm SL.
Previously B. wedli was only known from the Atlantic Ocean. The Indonesian specimen, if confirmed to be B. wedli , will represent the first and only record in the Indian Ocean.
| HUMZ |
Hokkaido University, Laboratory of Marine Zoology |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |