Miniopterus egeri, Goodman, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5735202 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5735355 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E84887F9-FFC7-D649-0AEA-F5D3186635EB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Miniopterus egeri |
| status |
|
33. View Plate 53: Miniopteridae
Eger’s Long-fingered Bat
French: Minioptere d'Eger / German: Eger-Langfligelfledermaus / Spanish: Miniéptero de Eger
Other common names: Eger’s Bent-winged Bat
Taxonomy. Miniopterus egeri Goodman et al., 2011 View in CoL ,
“ Madagascar: Province de Toamasina, Forét de Sahafina, 9.5 km W Brickaville , 18°48°377S, 48°58’48”E, 50 m. ”
Miniopterus egeri was formerly included in M. petersoni . Monotypic.
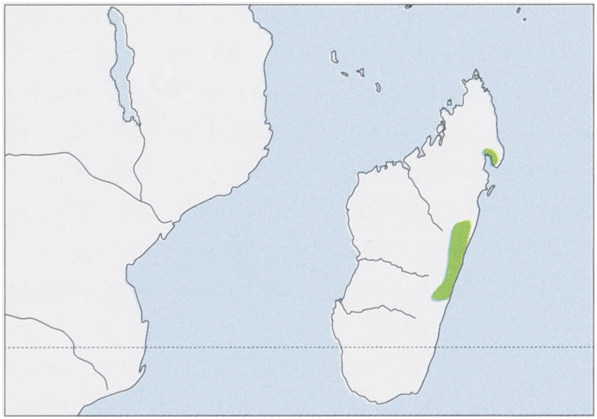
Distribution. E Madagascar. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body ¢.49-51 mm, tail 40-44 mm, ear 10-11 mm, hindfoot 5-7 mm, forearm 37-40 mm; weight 4-2-7-6 g. Dorsal and ventral pelage of Eger’s Long-fingered Bat is slightly long, dense, and a mix of medium to dark brown interspersed with distinctly lighter brown fur. Wing membranes and uropatagium are dark brownish black and largely naked and have no noticeable change in color across their surfaces. Tragus (5-6 mm) is notably thick along shaft and slightly constricted on lower distal side; length of proximal edge has distinct flange that folds slightly anterior-medially; and downward deflected distal tip is notably thickened and slightly fleshy. In comparison, Peterson’s Long-fingered Bat ( M. petersoni ) has distinctly thinner tragus shaft, constriction of lower proximal portion is notably more pronounced, and distal tip has slightly raised and rounded structure. Tragus of the Sororcula Long-fingered Bat ( M. sororculus ) is similar in length to Peterson’s Longfingered Bat but distinctly more spatulated and without notable tapered distal head.
Habitat. Varies from intact native forests to degraded anthropogenic habitats at elevations of 5—1300 m. Eger’s Long-fingered Bat is not believed to be forest dependent.
Food and Feeding. Eger’s Long-fingered Bat probably eats soft insects captured in flight as do other long-fingered bats.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. Eger’s Long-fingered Bat is nocturnal. A day roost was found in a natural rock shelter surrounded by slightly disturbed natural lowland humid forest; caves and even tree holes are probably also used as roosts. Echolocation calls have downward FM signals, with maximum frequencies of 107-123 kHz, minimum frequencies of 48-50 kHz, peak frequencies of 53-2-56-3 kHz, durations of 2-5-3-4 milliseconds, and intervals of 43-2—81-8 milliseconds.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red Last.
Bibliography. Goodman (2017e), Goodman et al. (2011), Ramasindrazana et al. (2011).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Miniopterus egeri
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Miniopterus egeri
| Goodman 2011 |