Sycophila mayri (Erdös 1959)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2013.791937 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10536609 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E82E7B4A-3B41-E62D-AF78-C870FD4C9868 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Sycophila mayri (Erdös 1959) |
| status |
|
( Figures 3A View Figure 3 , 4D View Figure 4 , 5D View Figure 5 , 6D View Figure 6 , 7D View Figure 7 , and 8D View Figure 8 )
Description
Body length 1.7 mm (range 1.3–2; n = 7); body width 0.8 mm (0.7–1.0) ( Figures 4D View Figure 4 and 5D View Figure 5 ); body barrel-shaped, slightly depressed and tapering anteriorly and posteriorly with lateral margins of abdominal segments 1–6 almost straight; ratio L/W = 2.1; ventral margin of body segments 4–8 in lateral view slightly convex; anterodorsal protuberances absent, with the intersegmental membranes not protruding in the specimens reared from galls on Centaurea scabiosa , whereas in those reared from galls on Centaurea spp. they are present, with the intersegmental membranes of abdominal segments 1–6 slightly protruding ( Figure 5D View Figure 5 ).
Dorsal margin of the vertex straight or slightly concave; ratio SA/DAV = 1.35; anteromedial setae of vertex situated relatively high on the upper face; ventral margin of clypeus distinct for specimens reared from galls on C. scabiosa , whereas it is indistinct for those associated with galls on Centaurea spp. ( Figure 6D View Figure 6 ); labrum with deep divisions reaching the level of labral setae, divided into two lateral flaps and five medial lobes, resulting in seven clearly differentiated and equal divisions; maxillae well differentiated from labium ( Figure 7D View Figure 7 ).
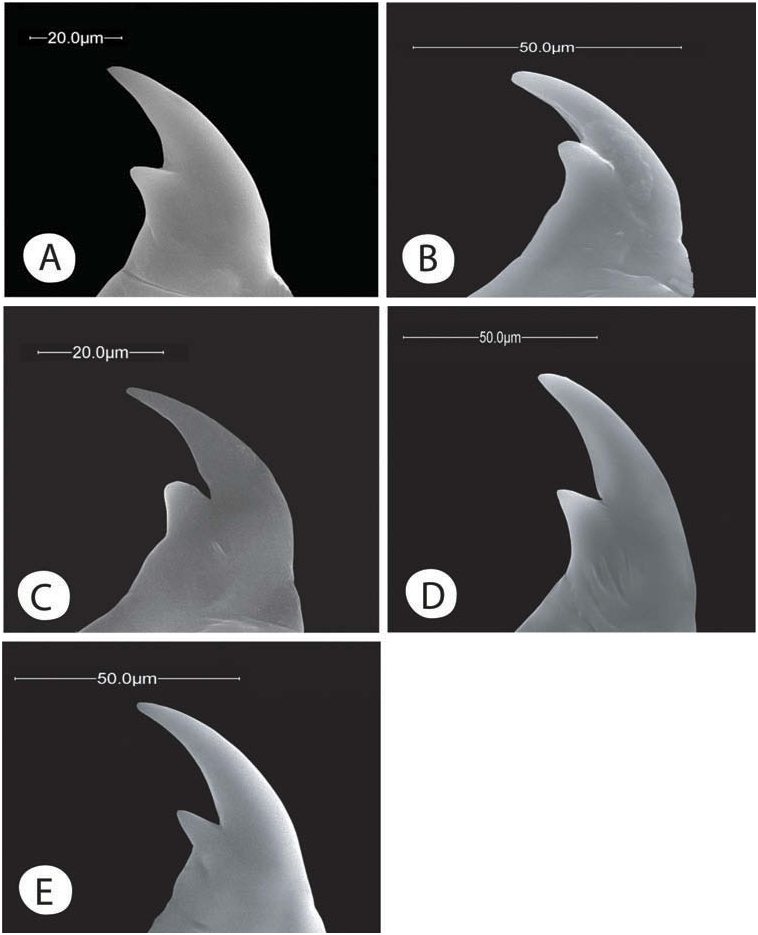
Mandibles bidentate; for specimens reared from galls of Centaurea spp. , ratio L/W 1T = 2.2 ( Figure 8D View Figure 8 ); second tooth triangular, acute at apex; inner margin of mandible, from the base of second tooth, straight, continuous.
Remarks
Specimens reared from different host plants have different descriptions as mentioned above. The rest of the characters are convergent in both S. mayri studied. Otherwise the species is similar to the larvae of S. flavicollis in the elongated shape of the body, but readily distinguished from the latter by a different anteromedial setal position on the head and its acute second mandibular tooth.
Biology
The species S. mayri is a polyphagous primary endoparasitoid associated with cynipid galls on herbs ( Figure 9G View Figure 9 ). It has been reared from galls of Aulacidea and Phanacis on Asteraceae ( Askew et al. 2006) . Specimens for this study were reared from galls of Phanacis centaureae Foerster , on stems of different Centaurea scabiosa L. and Centaurea spp. (Asteraceae) ( Figure 9H View Figure 9 ).
Material examined
ex Phanacis centaureae : on Centaurea scabiosa , Spain, Cuenca: Uña, 2 July 2002, J.L. Nieves leg, (n = 4); on Centaurea spp. , Spain, Madrid: Dehesa de Moncalvillo, 21 April 2005, J.L. Nieves and J.F. Gómez leg, (n = 3).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Eurytominae |
|
Genus |