Coccobius leptocerus Wang, Huang & Polaszek
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3774.5.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3FF3AC6A-1AFE-45C9-AEF2-51A353A7A758 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6141277 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E542415C-0572-5851-7EE2-ECA755ECFBD1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Coccobius leptocerus Wang, Huang & Polaszek |
| status |
sp. nov. |
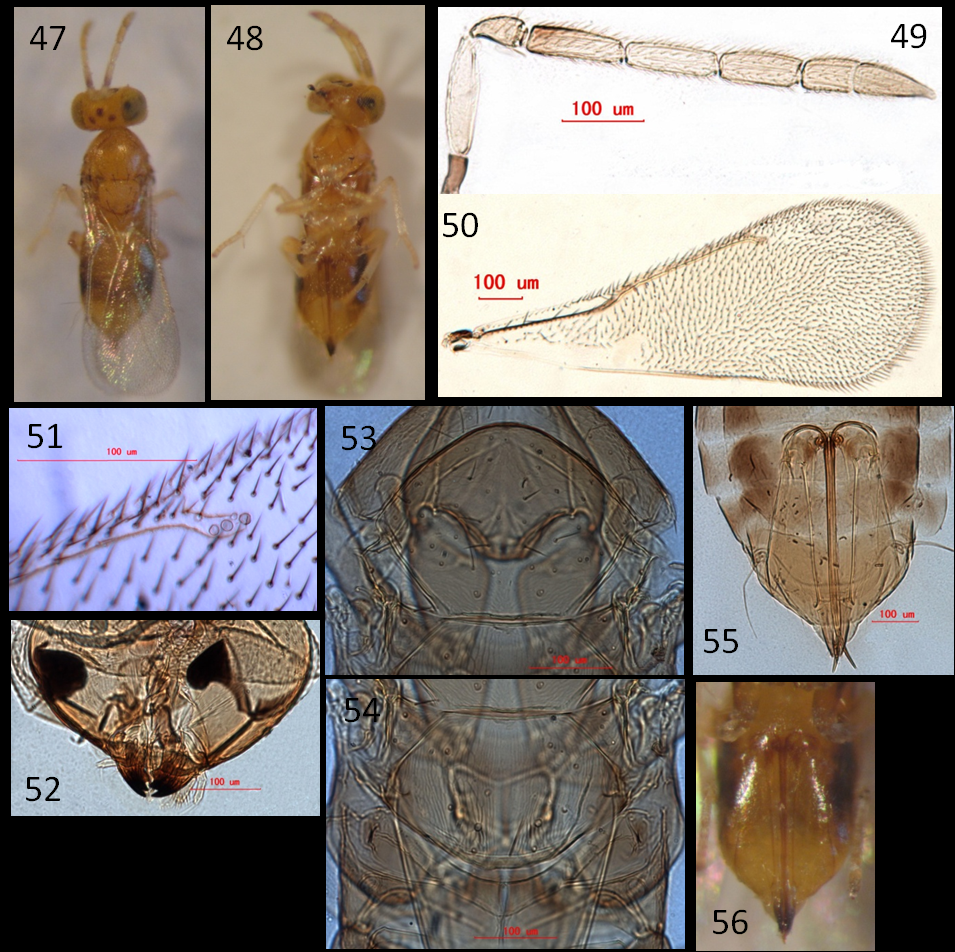
Coccobius leptocerus Wang, Huang & Polaszek , sp. nov.
( Figs 47–58 View FIGURES 47 – 56 View FIGURES 57 – 58 )
Type material. Holotype female. China: Guangxi, Nanning, 29 December 2012 (coll. Zhu-Hong Wang & Jian Huang), ex. a diaspidid scale in the leaf sheath of bamboo. Deposited as a slide mounted specimen in College of Plant Protection, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China ( FAFU). Paratype, 1 ♀, with same data as holotype, but collected on surface of a leaf of a tree at the same place ( FAFU).
Female. Body length: 1.49 mm.
Colour. Body yellow to brownish yellow, metasoma with T1–T4 and sterna 1–4 brownish yellow in middle and brown to dark brown on sides, T5 mostly brown to dark brown; mesopleuron brownish yellow to brown; mandible dark brown; eyes pale grey, ocelli brownish red. Antenna with radicle, base of F1 dark brown; scape, pedicel, remainder of F1, F2 pale yellow; F3 and clava pale yellow to brownish yellow. Wings hyaline. Legs pale yellow, fore and hind tibiae and femora brown, mid tibia and femur pale yellow. Third valvula apically dark brown.
Head. Vertex with reticulate sculpture; eyes finely setose; mandible with 3 teeth. Antennal scape about 4.03× as long as wide; pedicel short, 0.54× as long as F1; F1 and F2 distinctly longer, F1 3.36× as long as wide, slightly longer than (1.06× as long as) F2, F2 3.28× as long as wide, 1.14× as long as F3, F3 2.42× as long as wide, F1–F3 with 3 or 4 longitudinal sensilla respectively; clava distinctly shorter than funicle, C1 1.63× as long as wide, C2 2.81× as long as wide, distinctly longer than C1, each claval segment with 6 or 7 longitudinal sensilla.
Mesosoma. Mid-lobe of mesoscutum with irregular hexagonal cells or reticulation, except faint medially, with 43 setae; distance between axillae about 2.27× the length of an axilla; mesoscutellum 0.74× as long as mid-lobe of mesoscutum, with longitudinal reticulation medially and irregular reticulation laterally, with 3 pairs of setae but with an additional seta on right side, placoid sensilla closer to hind pair of setae than to mid pair; mesopostphragma, measured from apex of mesoscutellum, 1.25× as long as mesoscutellum. Fore wing 2.48× as long as maximum width of wing disc; marginal fringe short, 0.08× as long as maximum width of wing disc; submarginal vein shorter than marginal vein, with 11 setae; marginal vein with about 15 setae along anterior margin; postmarginal vein present but short, 0.29× as long as stigmal vein; wing disc densely setose with relatively broad asetose area posterobasally.
Metasoma. Metasoma about 1.18× as long as mesosoma; tergites 1–7 with setae as follows: T1, 2+3; T2, 4+4; T3, 5+5; T4, 6+5; T5, 5+5; T6, 6 between cercal plates; T7, 16 in three rows; ovipositor basally located at base of T3, slightly projecting beyond apex of metasoma, 1.69× as long as mid tibia, third valvula 1.93× as long as mid basitarsus.
Male. Unknown.
Host. An unidentified Diaspididae (Hemiptera) scale in the leaf sheath of bamboo ( Figs 57–58 View FIGURES 57 – 58 ).
Distribution. China (Guangxi).
Etymology. The new species name is derived from the Latin, leptocerus = slender horn.
Diagnosis. Coccobius leptocerus is close to C. odonaspidis (Tachikawa 1964) , which was collected from the white bamboo scale Odonaspis secreta Cockerell on bamboo in Japan, but can be distinguished from the latter by the following: body colour yellow to brownish yellow, except metasoma with T1–T4 laterally and T5 mostly brown to dark brown; antennal radicle and base of F1 dark brown; scape, pedicel, remainder of F1, F2 pale yellow; F3 and clava pale yellow to brownish yellow; mandible with three distinct, pointed teeth; and F1 subequal in length to (1.06× as long as) F2, and F2 longer than F3. In C. odonaspidis the head and mesosoma are shining black, the metasoma is pale yellow with sharply defined black bands on either side from the base to the spiracles; the antennal radicle, scape and clava are black (lighter towards the tips), F1 is black, and the remainder of the antennae is pale yellowish white; the mandible has two teeth and a truncation; and F1 is distinctly longer than F2 and F2 is subequal in length to F3.
In the key to Chinese species given by Wang et al. (2014), C. leptocerus keys to couplet 5, but can be readily distinguished from all other Chinese species by the following: the mandible with three distinct, pointed teeth; antennal funicle segments being distinctly longer and slender, especially F1 and F2, as well as the different body colour and different antennal colour pattern.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |