Rhinobatos manai, White, William T., Last, Peter R. & Naylor, Gavin J. P., 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4175.6.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D5E99C62-D61E-4303-9D1A-BC68EEAD4E5D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5618476 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C6458797-FFD7-FFAB-5F97-FB2456E9FD8F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhinobatos manai |
| status |
sp. nov. |
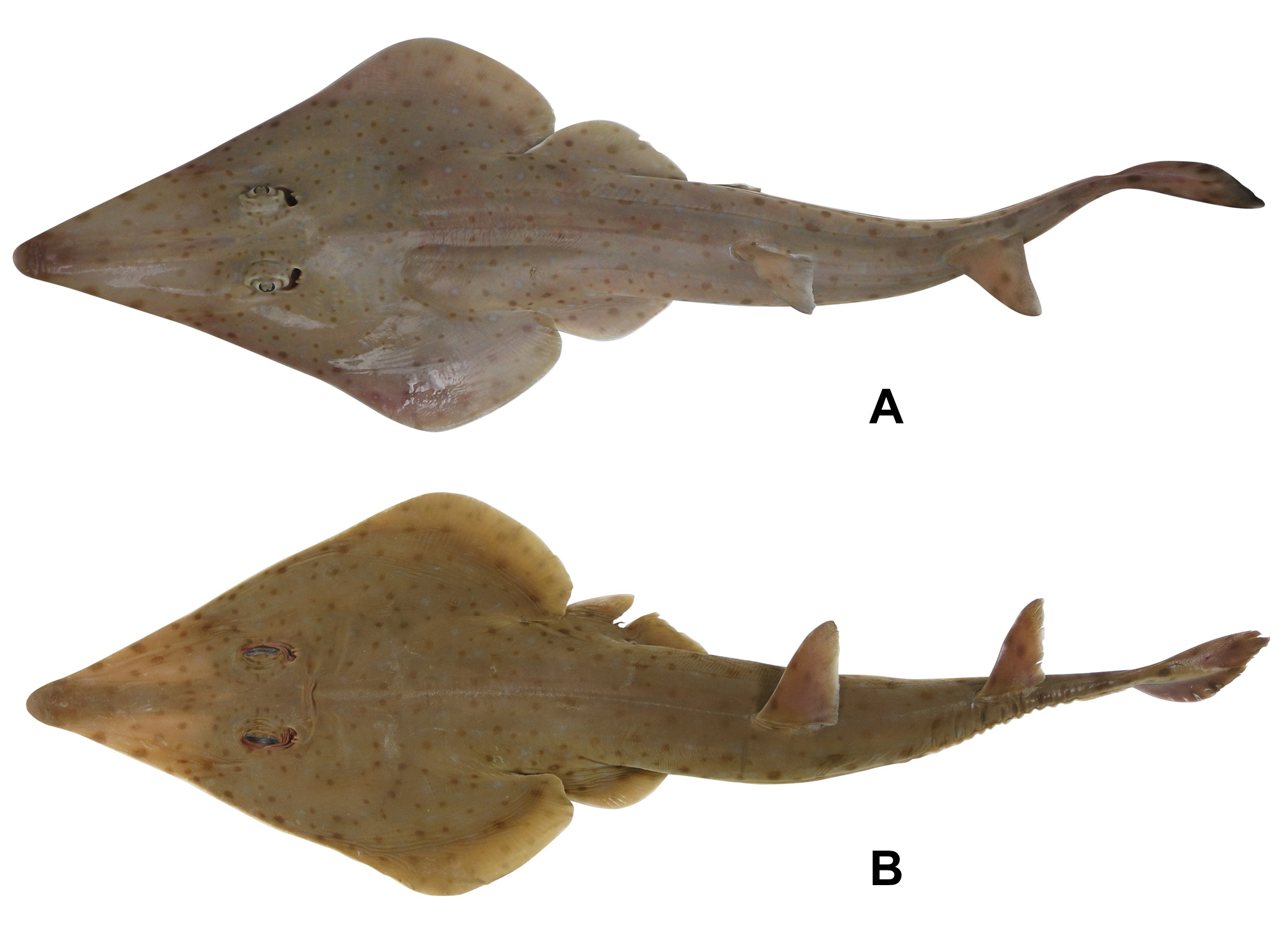
Rhinobatos manai sp. nov.
Papuan Guitarfish
( Figs. 1–6 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 ; Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Holotype. NTUM 11500 , adult male 731 mm TL, northwest of Kavieng , New Ireland, Papua New Guinea, 02°30’S, 150°44’E, 191–290 m depth, 7 Sep 2014. GoogleMaps
Diagnosis. A Rhinobatos distinguished by the following combination of characters: disc wedge-shaped, its dorsal surface covered in minute dermal denticles but without thorns; snout long, snout length 3.6 times interspiracular distance; orbit moderately large, diameter 1.7 times spiracle length; nostrils oblique, length 1.6 times internarial distance; anterior nasal flaps inserted into internarial space well away from nostril margin; posterior nasal flaps broad; ridges of rostral cartilage well-separated dorsally and almost parallel; prebranchial sensory-pore patch narrow, extending to first gill slit; distance between first gill slits 1.5 times distance between fifth gill slits; distance between fifth gill slits 3.4 times in ventral head length; postscapular sensory canal long, not grooved, extending more than three-quarters distance to pectoral-fin insertions; dorsal fins moderately tall; pelvicfin inner margin shorter than its base; interdorsal distance more than 3.1 times first dorsal-fin base; outer spiracular fold distinctly larger than inner fold; dorsal margin of caudal fin ~2 times preventral margin; 171 post-synarcual (free) vertebral centra; 188 total vertebral centra; 52 nasal lamellae; and dorsal disc brownish, covered with welldefined rusty brown spots and blotches and poorly defined white spots with greyish edges.
Description. Disc wedge shaped, bluntly angular anteriorly, angle anterior to eyes about 56°; outer margins broadly rounded, more narrowly rounded distally; length 1.37 times width. Pelvic fins elongate, short-based, base length about 0.78 of inner margin; length 1.73 times their base length, 2.75 times width; anterior margin convex, apex broadly rounded, posterior margin weakly convex. Tail elongate, slender, tapering gradually; in cross-section nearly flat ventrally, rounded dorsally; length from anterior cloaca to tail tip 1.39 times precloacal length, 1.34 times disc length, 6.32 times body width at pelvic-fin insertions; tail width 1.99 times depth at pelvic-fin insertions, 2.41 times at first dorsal-fin origin, 1.68 times at second dorsal-fin origin. Dermal fold ventrolateral on tail, originating slightly anterior to free rear tip of pelvic fin, reaching just behind ventral caudal fin origin; fold well developed, maximum width in interdorsal space about a quarter width of spiracle.
Adult males ......continued on the next page R. manai R. whitei
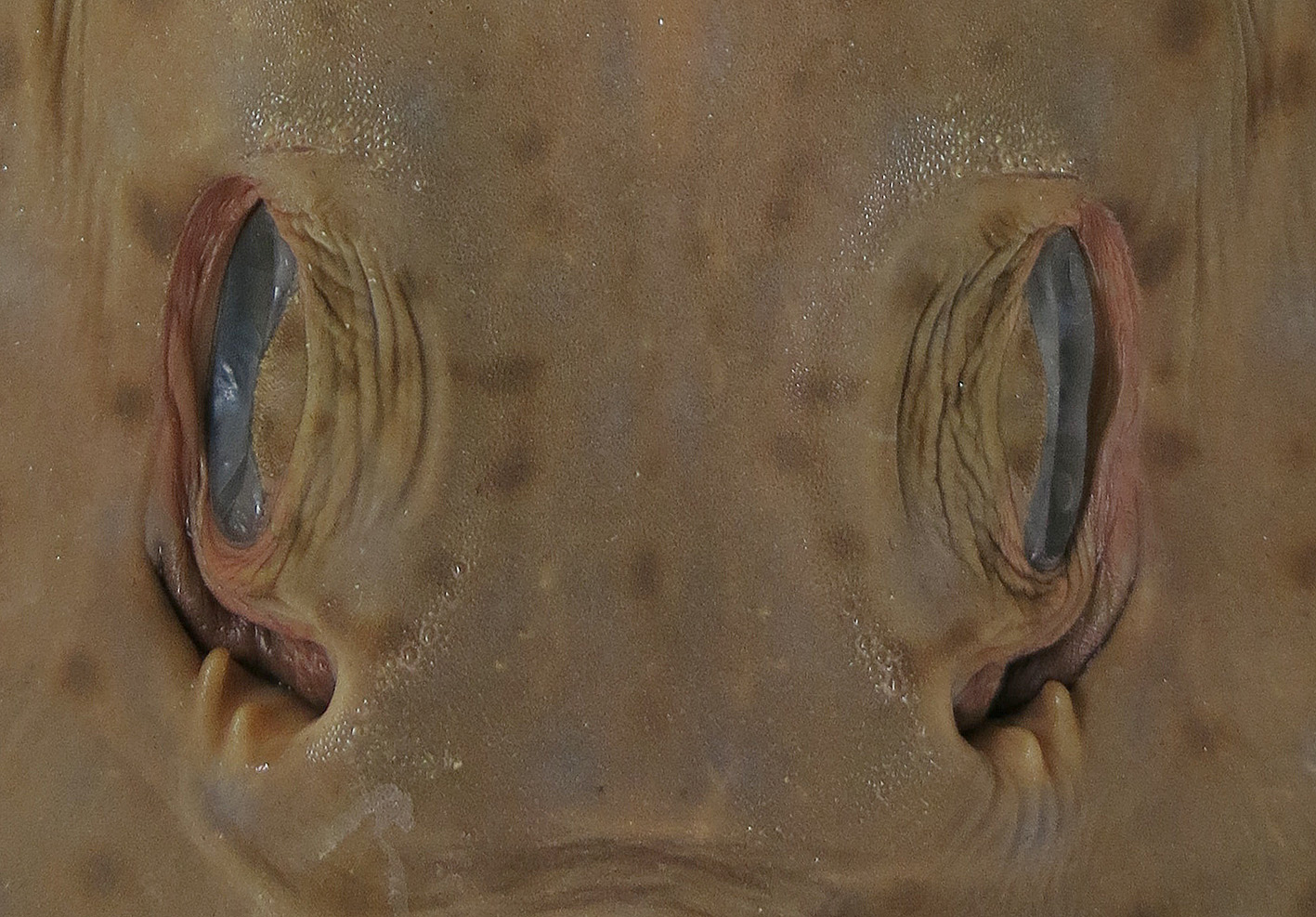
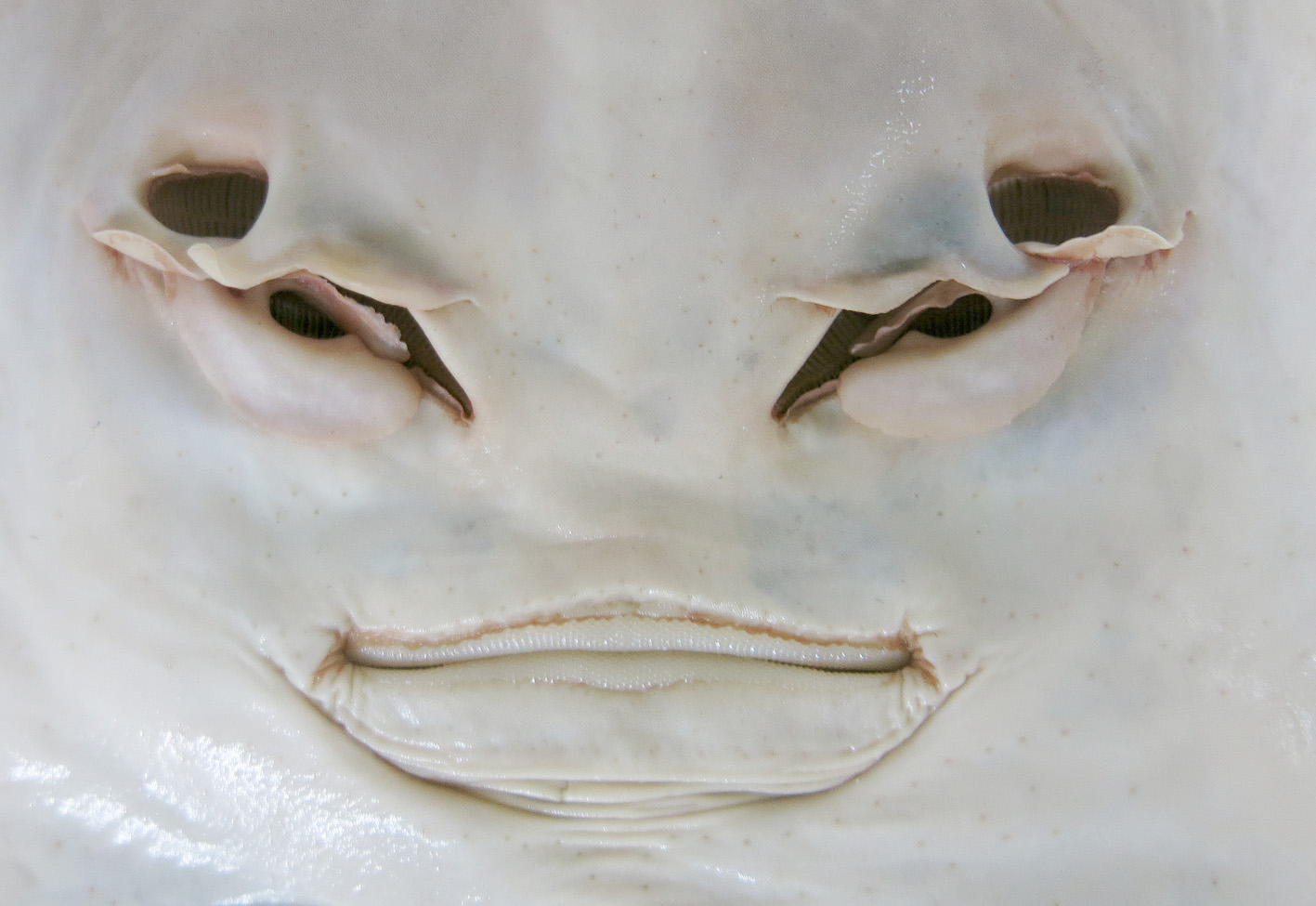
Adult males Head elongate, ventral length 28.6% TL; snout moderately long and bluntly pointed; preoral snout length 3.58 times mouth width, 7.32 times internarial distance, 1.44 times dorsal caudal fin margin, 6.69 times distance from nostril to margin of disc; snout length (direct) 3.58 times interspiracular length, 4.99 times orbit diameter, 5.10 times interorbital width; interorbital space weakly concave, relatively broad; eye dorsolateral, not elevated or protruding; orbit relatively small, diameter 1.65 times spiracle length, 1.02 times interorbital width. Spiracle narrowly bean-shaped, moderately large; two weakly compressed spiracular folds on posterior margin, innermost fold half or less length of outer fold, distance between bases of folds subequal to length of inner fold. Nostril moderately large, oblique, nasal flaps well developed; anterior aperture suboval, width slightly exceeding length; nostril length 3.32 times anterior aperture width, 1.69 times anterior nasal-flap base length, 1.45 times distance from nostril to edge of disc, 1.59 times internarial width. Anterior nasal flap relatively well developed with long, slender process anteriorly; flap base 1.84 times its width at process, 1.97 times anterior aperture width; insertion in internarial space well mesial to nostril margin, its distance from nostril about equal to half width of anterior nasal aperture; distance between their insertions 3.67 in distance between lateral margins of anterior apertures, 0.97 in internarial width; process of flap about twice as long as wide at its base, overlapping posteromesial edge of posterolateral nasal flap and determining inner margin of anterior aperture. Posterolateral nasal flap lobe-like, broadest medially, length 3.36 times width; originating at lateral extremity of anterior nasal aperture, extending postero-medially as a free fold almost to medial margin of posterior flap. Posterior nasal flap broadly lobe-like, base length 2.58 times its width, not reaching innermost end of nostril, inserted well forward of posterior tip; width subequal to anterior aperture width, 1.09 times posterolateral nasal-flap width. Nasal lamellae 52.
Mouth moderately wide, width 1.29 times nostril length, 7.26 in precloacal length; positioned about level with hind margin of orbit; jaws not greatly thickened. Upper jaw weakly convex, upper lip arched slightly, no preoral groove; lower lip pronounced, not separated from post-oral groove by ridges of strongly corrugated skin; short lateral grooves around corners of mouth. Teeth small, blunt, crowns rhomboidal; teeth quincuncial, ~92 rows in upper jaw and ~86 rows in lower jaw; upper and lower jaw teeth similar in shape and size. Gill openings weakly sshaped, fifth less so; length of third gill slit 2.94 in nostril length, 5.53 in distance between fifth gill slits; distance between first gill slits 1.47 times distance between fifth gill slits; distance between fifth gill slits 2.98 times internarial distance, 1.46 times mouth width, 3.40 in ventral head length.
Dorsal fins of moderate size, upright, relatively narrow, not falcate, apices narrowly rounded to almost angular; anterior margins convex distally, posterior margins nearly straight; free rear tips forming right angle, not produced; first dorsal-fin slightly taller than second, length of first dorsal fin 0.82 times its height, base length 1.99 times inner margin length; second dorsal-fin length 0.85 times its height, base length 2.58 times inner margin length. First dorsal-fin origin well behind pelvic-fin rear tip, interspace 0.73 times interdorsal distance; interdorsal space relatively short, 1.78 times second dorsal-fin height, 3.08 times base length of first dorsal-fin, 1.95 times interspace between second dorsal-fin insertion and upper origin of caudal fin. Caudal fin small, dorsal caudal margin 1.98 times preventral margin length. Mature clasper slender, relatively short, inner length 13.1% TL; tip acute, glans weakly expanded.
Dermal denticles minute, close-set, covering entire body and fins; thorns and tubercles absent; dorsal surface with narrow series of slightly enlarged, seed-like denticles around orbit, along midline, and on scapular region; around orbit, enlarged denticles most pronounced anteriorly at preorbit and posteriorly, with posterior patch extending over upper spiracle margin; along midline, enlarged denticles most pronounced above abdomen; weakly represented between dorsal fins and barely evident on caudal peduncle; enlarged denticles irregular in size and shape, largest with crenulate anterior margins; dorsal surface of claspers naked at tip and near pelvic-fin insertion. Ventral surface uniformly covered with minute denticles, including upper lip edges, near insertion of anterior nasal flap, below posterolateral and posterior nasal flaps, and on tail beneath pelvic fins, and most of claspers; a dense covering of small denticles over nasal lamellae.
Prebranchial sensory pore patch relatively narrow, extending posteriorly to level of first gill slit. Postscapular sensory canal long, notched near fifth gill slits, terminating about an orbit diameter from pectoral-fin insertions; canal deeply embedded, not forming shallow groove.
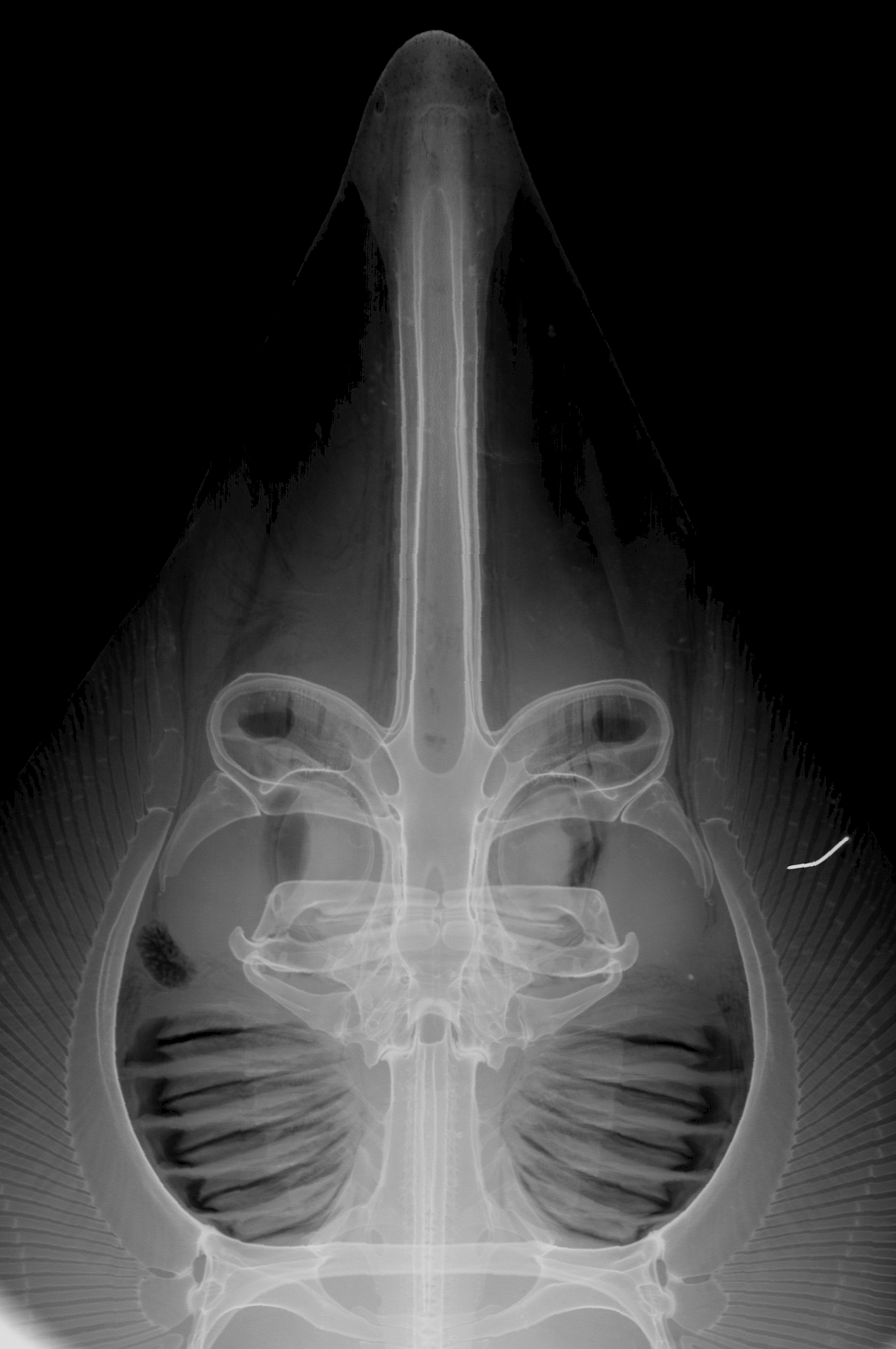
Rostral cartilage in holotype long and broad, its shaft not increasing in width in a posterior direction; rostral node broadly expanded and elongate, rounded apically, not angular, axis at widest part of node 9.4% of length of rostral cartilage from snout tip; precerebral cavity broad and uniformly convex posteriorly, narrowly rounded anteriorly at rostral node; rostral cartilage length ~67% of length of neurocranium, ventral edges of rostral cartilage united; nasal capsules large, their transverse axes anterolaterally directed; maximum width across capsules 1.52 times nasobasal length of cranium (base of rostrum to occipital condyles); nasal capsules slightly wider than long; basal plate narrow, its minimum width 5.04 times in nasobasal length; cranial roof with small, narrowly oval fenestra, located well behind precerebral cavity (separated by ~1.4 times its length).
Pectoral skeleton with 30 propterygial, 7 mesopterygial, 2 neopterygial, 27 metapterygial, 66 total radials; anterior radials of propterygium extending forward of nasal capsules by about 10.6% of rostral length. Total pelvic radials 1+24+1; first greatly enlarged, on puboischiadic bar; 24 basipterygial radials; clasper calcified. Vertebral column with 188 total centra (synarcual and free), 171 post-synarcual centra; 17 synarcual centra; 25 monospondylous centra, all centra with ribs; 108 diplospondylous precaudal centra, about 38 diplospondylous caudal centra.
Colour. In preservative: Body pale yellowish brown dorsally covered with a complex pattern of small, rusty brown spots and blotches, and small whitish spots with greyish edges; rusty brown spots diffuse-edged and somewhat irregular in size, mostly circular, larger near disc edges and on lateral trunk; whitish spots sparser and more diffuse, poorly defined anteriorly and posteriorly on body; paler near hind margin of pectoral and pelvic fins; paler yellowish brown on translucent areas of snout, lateral cutaneous fold of tail, and between ridges of rostral cartilage; dorsal and caudal fins also with several brownish spots. Ventral surface uniformly white; no dark tip on snout apex.
Size. Only known from the holotype, a 731 mm TL adult male.
Distribution. Holotype collected northwest of Kavieng (02°30’S, 150°44’E), New Ireland, in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea at depths of 191– 290 m.
Etymology. Epithet in recognition of Dr Ralph Mana of the University of Papua New Guinea whose invaluable work on the BioPapua projects throughout Papua New Guinea has led to a considerable increase in our knowledge of the deepwater fish fauna of this region.
Molecular analysis. The analysis of the NADH2 data suggests that Rhinobatos manai represents a lineage that is distinct from, but closely related to, R. sainsburyi and that these two species, in turn, are sister to a clade containing two recently described species from Borneo and the Philippines, R. borneensis Last, Séret & Manjaji- Matsumoto, 2016 and R. whitei Last, Corrigan & Naylor, 2014 , respectively. We caution however that this inference is based on a single mitochondrial marker. Inclusion of multiple nuclear markers could affect the presented inference.
Comparisons. The distinctive dorsal colour pattern of small, rusty brown spots and whitish spots with greyish edges distinguishes this species from all other species of Rhinobatos . In comparison, R. borneensis , R. holcorhynchus Norman, 1922 , R. jimbaranensis Last, White & Fahmi, 2006 , R. lionotus Norman, 1926 , R. nudidorsalis Last, Compagno & Nakaya, 2004 , R. sainsburyi , and R. schlegelii Müller & Henle, 1841 , all lack such prominent spotting (dorsal coloration uniform or with larger irregular blotches). Rhinobatos albomaculatus Norman, 1930 , R. annandalei Norman, 1926 , R. penggali Last, White & Fahmi, 2006 , and R. punctifer Compagno & Randall, 1987 have a colour pattern consisting primarily of white spots, but none of these have a combination of whitish and brownish spots. Rhinobatos hynnicephalus Richardson, 1846 has a variable pattern of small dark spots on the dorsal surface, either aggregated in small to large clusters or free. The dorsal surface of R. irvinei Norman, 1931 has a distinctive colour pattern of pale orange blotches with dark margins and black spots. Rhinobatos rhinobatos Linnaeus, 1758 lacks spots and often has faint bluish grey stripes and blotches on the dorsal body. Rhinobatos whitei has the most similar dorsal coloration to R. manai sp. nov., consisting of poorly defined white spots and large diffuse dusky and orange blotches. However, R. manai differs in having much better defined rusty brown spots and faint white spots with a greyish edge.
Based on its NADH2 sequence, Rhinobatos manai belongs to a subgroup of Eastern Indian and Western Central Pacific species, i.e. R. borneensis , R. jimbaranensis , R. cf. lionotus , R. sainsburyi and R. whitei ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ).
This subgroup of species typically have weak colour patterns with variably developed rusty brown spots or blotches (sometimes plain), with only R. manai and R. whitei also possessing whitish spots. Although closest to R. sainsburyi based on the NADH2 sequence data, R. manai is clearly distinct from this species in having: a much longer snout (preorbital length 17.6 vs. 13.1–14.7% TL; preoral length 20.6 vs. 15.5–17.9% TL; prenarial distance 16.4 vs. 12.0–13.6% TL), larger distance between anterior nasal flap insertions (2.9 vs. 2.0–2.3% TL), more total free vertebrae (188 vs. 175–185), slightly more pectoral radials (66 vs. 59–65), and in coloration (large rusty brown blotches and no white spots vs. smaller, more regular and better defined rusty brown spots and whitish spots present).
Morphologically, R. manai is closest to the recently described R. whitei from the Philippines and seems to differ only in the following subtle morphological characteristics: distance across anterior nasal apertures (10.6 vs. 8.5–9.7% TL); slightly larger nostrils (nostril length 4.5 vs. 3.4–4.1% TL); dorsal fins slightly more separated (interdorsal distance 13.2 vs. 11.3–12.9% TL); and a slightly taller second dorsal fin (7.2 vs. 5.5–7.0% TL). These two species are most readily distinguished based on their coloration as mentioned previously.
TABLE 1. Morphometric data for the holotype of Rhinobatos manai sp. nov. (NTUM 11500) Measurements expressed as percentages of total length.
| Holotype | Min. | Max. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total length | 731 | 556 | 641 |
| Disc width—maximum | 31.6 | 30.9 | 32.6 |
| Disc length | 43.4 | 41.3 | 42.7 |
| Head length—dorsal | 23.3 | 21.7 | 23.2 |
| Head length—ventral | 28.6 | 27.7 | 29.2 |
| Snout length (presocket) | 17.6 | 15.4 | 17.0 |
| Orbit diameter | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.2 |
| Spiracle length | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Orbit and spiracle length | 4.6 | 4.8 | 5.1 |
| Interorbital width | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.7 |
| Interspiracular width | 4.9 | 5.1 | 5.2 |
| Preoral length | 20.6 | 18.2 | 19.8 |
| Mouth width | 5.8 | 5.7 | 6.4 |
| Prenarial distance | 16.4 | 14.4 | 16.1 |
| Nostril length | 4.5 | 3.8 | 4.0 |
| Anterior aperture—width | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.3 |
| Anterior nasal flap—base length | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.9 |
| Anterior nasal flap—width | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 |
| Posterolateral nasal flap—total length | 3.6 | 3.3 | 3.4 |
| Posterolateral nasal flap—width | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Posterior nasal flap— base length | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.9 |
| Posterior nasal flap—width | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
| Distance across anterior nasal apertures | 10.6 | 8.9 | 9.4 |
| Internarial distance (minimum) | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.7 |
| Distance between anterior nasal flaps | 2.9 | 2.3 | 2.6 |
| Distance from nostril to disc margin | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.3 |
| Third gill opening—width | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| Distance between first gill openings | 12.3 | 12.5 | 13.1 |
| Distance between fifth gill openings | 8.4 | 8.5 | 9.1 |
| Pelvic fin—length | 14.1 | 13.4 | 13.8 |
| Pelvic fin—anterior margin length | 8.1 | 7.7 | 8.1 |
| Pelvic fin—width | 5.1 | 5.6 | 5.8 |
| Pelvic fin—base length | 8.1 | 6.6 | 7.0 |
| Pelvic fin—inner margin length | 6.3 | 7.6 | 7.8 |
| First dorsal fin—length | 6.5 | 6.7 | 7.1 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |