Sidydrassus, Esyunin & Tuneva, 2002
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5194.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3B4E0082-F3B6-485B-8376-68112C27C970 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7148891 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/BA4C87EF-FF9F-4913-FF60-324B52CD1EDA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sidydrassus |
| status |
|
Key to Sidydrassus View in CoL species
Males
1 Median apophysis with a prolaterally bent branch ( Figs 25, 29 View FIGURES 25–30 )........................................ S. shumakovi View in CoL - Median apophysis without a prolaterally bent branch ( Figs 13, 16 View FIGURES 13–18 , 20, 23 View FIGURES 19–24 , 31, 35 View FIGURES 31–36 ).................................. 2 2 RTA 4 times shorter than tibia ( Figs 31–33 View FIGURES 31–36 )............................................................ S. rogue View in CoL - RTA as long as tibia or twice shorter than tibia ( Figs 13–18 View FIGURES 13–18 )................................................... 3 3 RTA as long as tibia ( Figs 13–15 View FIGURES 13–18 )............................................................ S. saiynovi sp. n. - RTA twice as short as tibia ( Figs 16–18 View FIGURES 13–18 )....................................................... S. tianschanicus View in CoL
Females (female of S. saiynovi sp. n. is unknown)
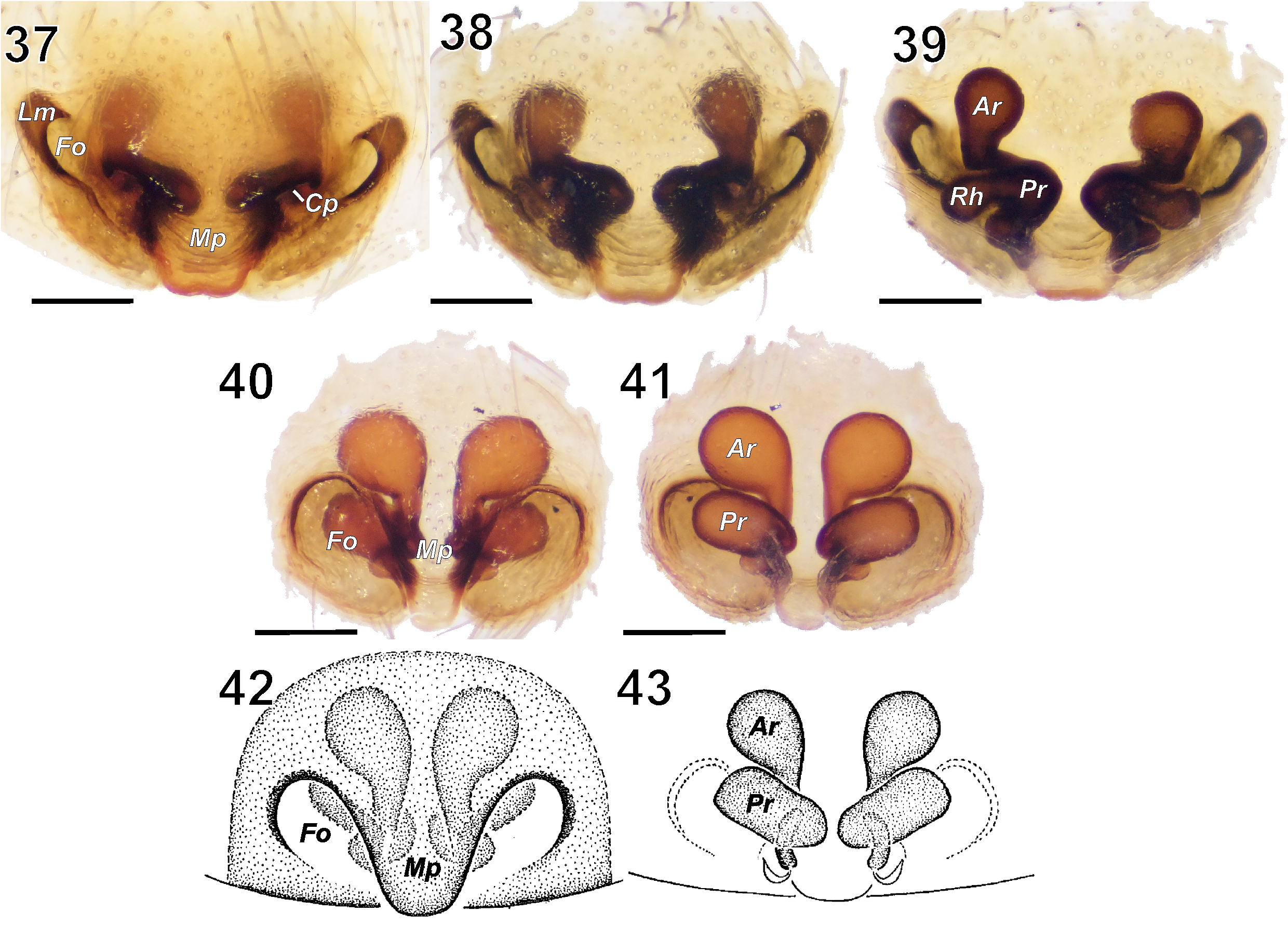
1 Epigynal fovea slit-shaped, not contiguous with the epigastric furrow ( Figs 37–38 View FIGURES 37–43 )........................ S. shumakovi View in CoL
- Epigynal fovea wide and round, contiguous with the epigastric furrow ( Figs 40, 42 View FIGURES 37–43 )................................ 2
2 Epigynal fovea 2.1 times longer than wide, anterior and posterior receptacles equal in size ( Figs 42–43 View FIGURES 37–43 )........................................................................................................ S. tianschanicus View in CoL
- Epigynal fovea 1.7 times longer than wide, anterior receptacles significantly larger than the posterior ones ( Figs 40–41 View FIGURES 37–43 )................................................................................................... S. rogue View in CoL
Possible relationships within Sidydrassus
Of the four species currently assigned to the genus, S. saiynovi sp. n., S. tianschanicus , and S. rogue seem to be closely related as they are similar in having the median apophysis without a prolateral branch, similar proportions of the embolic base, the wide epigynal fovea, the diverging anterior receptacles and posterior receptacles without pronounced heads ( Figs 13, 16 View FIGURES 13–18 , 20, 23 View FIGURES 19–24 , 31, 35 View FIGURES 31–36 , 40–43 View FIGURES 37–43 ). The generotype, S. shumakovi , stays apart and possesses the median apophysis with a prolateral branch, the thick embolic base, the slit-shaped epigynal fovea, the converging anterior receptacles and the posterior receptacles with pronounced heads ( Figs 25, 29 View FIGURES 25–30 , 37–39 View FIGURES 37–43 ). Thus, all the Sidydrassus species can be divided into two species groups: the shumakovi -group (one species) and the tianschanicus -group (three species) ( Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.