Ventrifossa garmani, : Okada & Matsubara, 1938
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/megataxa.3.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B711B23F-FECA-8732-DA3F-C00AFEFD7A7F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ventrifossa garmani |
| status |
|
Ventrifossa garmani View in CoL ( Jordan & Gilbert in Jordan & Starks, 1904)
[Japanese name: Sagami-sokodara]
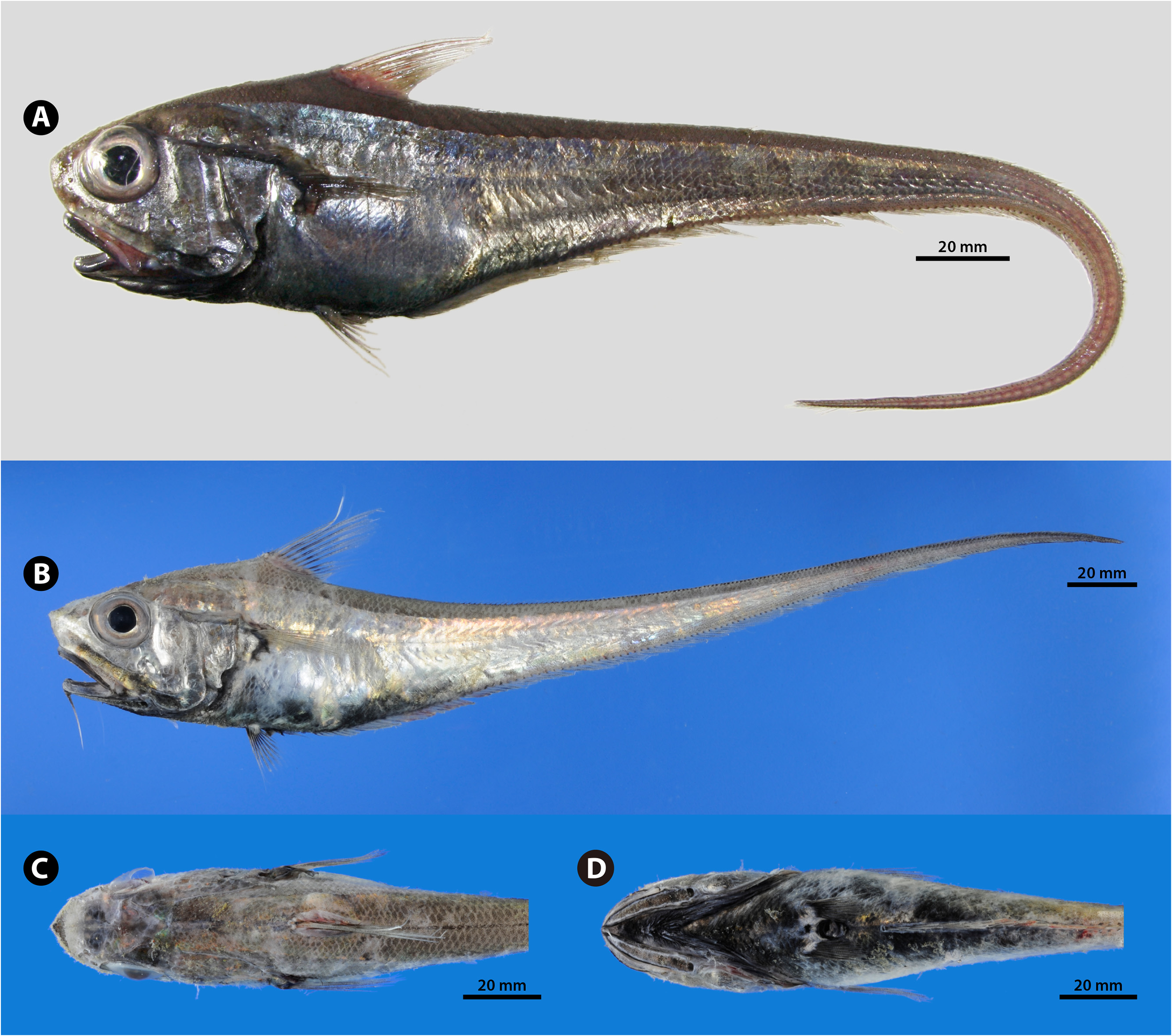
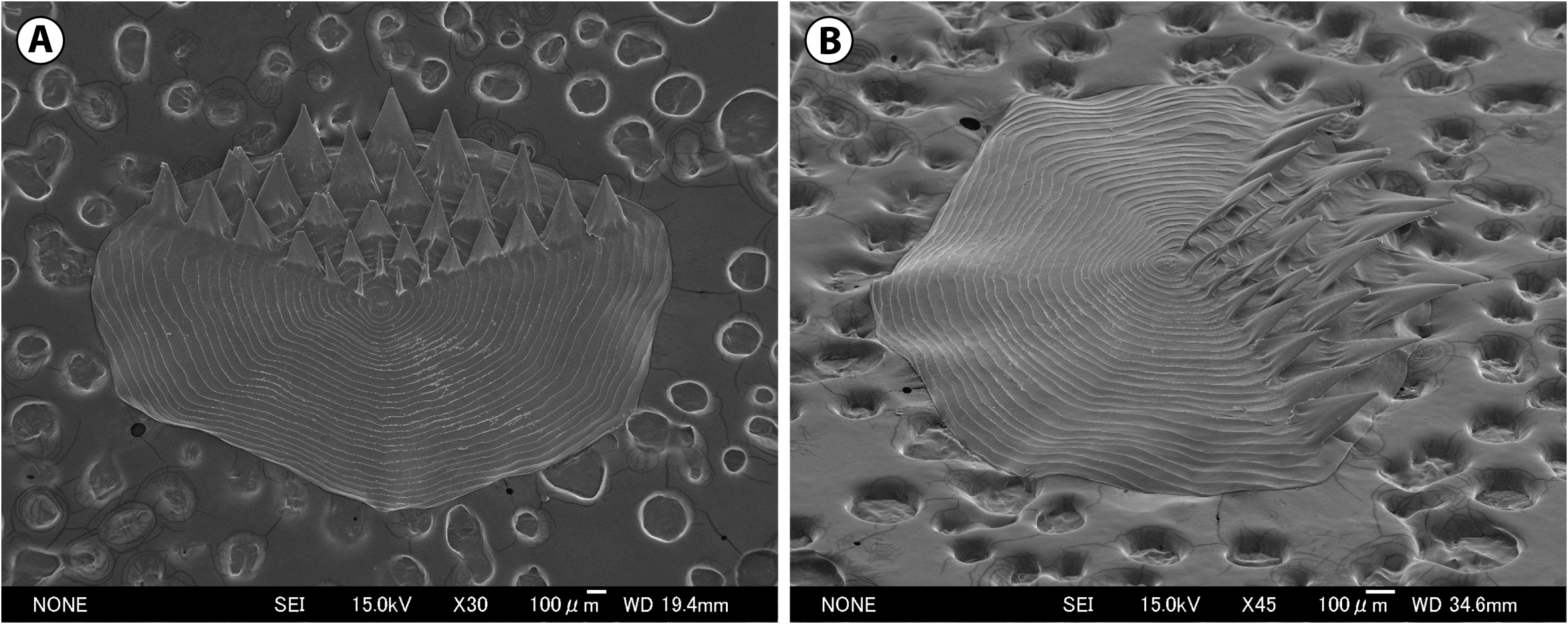
( Figs. 196–198 View FIGURE 196 View FIGURE 197 View FIGURE 198 ; Appendix 3-12C)
Coryphaenoides garmani Jordan & Gilbert View in CoL in Jordan & Starks, 1904:610, unnumbered fig. [original description; holotype: USNM 50933, from Sagami Bay, Albatross sta. 3695, in 110–259 ftm (202–474 m); paratypes from Sagami-nada and Suruga Bay]; Franz 1910:26 [brief description; 3 spec. from “Sagamibai” (= Sagami Bay)]; Jordan et al. 1913:416, fig. 386 (listed; Japan; new Japanese name: “Sagami-sokodara”); Jordan & Thompson 1914:306 [2 spec. from Boshu (= Chiba) and Misaki; FMNH 57245 and FMNH 57387]; Kamohara 1931b:544 (listed; Kochi); Kamohara 1934a:54 (listed;Kochi); Kamohara 1938:72 (selected counts and measurements; spec. from Kochi Pref.); Kamohara 1950:279 (listed; Kochi and Wakayama Pref.); Kuroda 1951:391 (listed; Suruga Bay); Uchinomi 1951:76 (listed; southern part of Kii Peninsula); Kamohara 1952:98 (selected counts and measurements; spec. from Kochi Pref.).
Lionurus garmani: Gilbert & Hubbs 1916:193 (new combination; brief description; 30 spec. from East China Sea , off Cape Shionomisaki , Pacific off Tohoku , Suruga Bay, and Sagami Bay).
Ventrifossa garmani: Okada & Matsubara 1938:452 View in CoL (in key; Japan); Matsubara 1955:1315 (in key; Japan); Kobayashi 1956:72 (listed; Enshu-nada); Kamohara 1958:74 (listed; Kochi Pref.); Kamohara & Okamura 1958:32, pl. 31, fig. 152 (compiled; Japan); Kamohara 1961b:68, pl. 68, fig. 2 (compiled; Japan); Kuroda 1962:7, fig. 2 (description of fresh color; 3 spec. from Suruga Bay); Kamohara 1964:96 (listed; Kochi Pref.); Matsubara 1965:508 (compiled; Japan); Okamura 1970a:74, pl. V, text-fig. 33 (description; biological notes; 131 spec. from Pacific off southern Japan from Choshi to Totoro); Okamura 1970b: table 1 (listed; Japan); Nakajima 1975:55 (listed; Enshu-nada); Tominaga & Uyeno 1981:489 (listed; Japan); Okamura 1982:145, 348, fig. 89 [brief description; 6 spec. from Kyushu-Palau Ridge and Tosa Bay; photo based on BSKU spec. (catalog no. unknown)]; Ohta 1983: table A (listed; Suruga Bay); Ozawa 1983:13 (listed; off Makurazaki, Kagoshima Pref., East China Sea); Okamura 1984a:213, 360, fig. 148 [brief description; 6 spec. from Okinawa Trough; photo based on BSKU 36046 (from Mimase fish market)]; Okamura 1984b:93, pl. 81, fig. E (compiled); Akazaki 1984:265 (listed; Aoshima, Miyazaki Pref.); Okamura 1988:93, pl. 81, fig. E (compiled); Iwamoto 1990:300, fig. 678 (synopsis); Nakabo 1993:359 (in key; Japan); Shao 1993:172 (compiled; Taiwan); Shinohara et al. 1996:170 (2 spec. listed from Pacific off Tohoku); Suzuki & Kataoka 1997:82, pl. 32, fig. 176 (brief description; 1 spec. from Kumano-nada); Okamura 1997:128, fig. 9 (compiled); Shinohara & Matsuura 1997:292 (listed; Suruga Bay); Nakabo 2000:423 (in key; Japan); Shinohara et al. 2001:306 (79 spec. listed from Tosa Bay); Nakabo 2002:423 (in key; Japan); Yoda et al. 2002:11 (listed; East China and Yellow Seas); Nakajima 2003:53 (brief description; 1 spec. from Enshunada); Chiou et al. 2004a: table 1 (listed; Taiwan); Fukui & Tsuchiya 2005:311, figs. 1–2 (larval description; 3 spec. from Suruga Bay and adjacent water); Shinohara et al. 2005:418 (12 spec. listed from Ryukyu Islands); Senou et al. 2006:421 (listed; Sagami Sea); Shao et al. 2008b: table 2 (2 spec. listed from southwestern Taiwan); Shinohara et al. 2009:709 (listed; Pacific off Tohoku); Furuhashi et al. 2010: table 2 (217 spec. listed from northern Okinawa Trough); Jeong et al. 2010:317, fig. 1 (first record from Korea; brief description; 1 spec. from Ulsan); Nakabo & Kai 2013:499 (in key; Japan); Fukui et al. 2015:182, fig. 12 (4 spec. from off Kuro-shima Island, Kagoshima Pref., East China Sea); Ikeda & Nakabo 2015:320, pl. 65, figs. 6–8 (brief description; 2 spec. from Wakayama Pref.); Iwamoto et al. 2015:109, fig. 28 (brief description; 8 spec. from southwestern Taiwan and Japan); Iwatsuki et al. 2017:32 (listed; Hyuga-nada); Sonoyama et al. 2020:30, fig. 4G (1 spec. listed from Yamaguchi Pref., Sea of Japan); Motomura 2020:39 (listed; Japan).
[?] Lionurus darus (not Gilbert & Hubbs 1916): Kuroda 1941:80, fig. 10 (brief description; 2 spec. from Suruga Bay) [reidentified here from figure].
[?] Malacocephalus nipponensis View in CoL (not Gilbert & Hubbs 1916): Suzuki & Kataoka 1997:82, pl. 32, fig. 175 (brief description; 1 spec. from Kumano-nada) [re-identified here from figure].
Diagnosis. Second spinous ray of first dorsal fin finely serrated along its leading edge; first dorsal and anal fins uniformly pale to dusky; anal fin uniformly dusky; prominent black spot absent on front of premaxillary ascending process; oral cavity pale; median rostral ridge lacking narrow blackish streak; leading edges of snout, supranarial ridges, and suborbital shelves only faintly marked with black; dorsal parts of trunk and tail dark, sharply demarcated from paler lateral and ventral parts of body (especially prominent in fresh specimens); snout low, slightly protruding beyond upper jaw, preoral length 14–22% HL; no scute-like scale at snout tip; body scales covered with short, moderately erect, broadly triangular spinules in quincunx order; spinules on scales along second dorsal-fin base not enlarged; body scales moderately small, transverse scale rows below midbase of first dorsal fin 5.5–7.5, below second dorsal-fin origin 5.5–7; longitudinal scales 35–44; area of spinuleless scales posterior to first dorsal-fin base almost absent or only narrowly developed; outer series of premaxillary teeth slightly enlarged; mandibular teeth arranged in narrow tapered band; suborbital shelf not greatly constricted anteriorly; inner gill rakers on first arch 16–19, outer gill rakers on second arch 15–18; orbit large, greatest diameter 32–38% HL; suborbital width 11–13%; upper-jaw length 41–47% HL; interorbital space broad, width 27–33% HL; barbel moderately long, length 20–33% HL; pectoral-fin length 52–66% HL.
Material examined. 40 specimens. Holotype of Coryphaenoides garmani: USNM 50933 (51.7 mm HL, 285+ mm TL), off Chigasaki, Kanagawa Pref., Sagami Bay, Japan , 35.2500ºN, 139.4167ºE, 110–259 ftm (202– 474 m), Albatross sta. 3695, 8-ft Tanner beam trawl, 4 Mar. 1900 GoogleMaps . Paratypes of C. garmani: CAS-SU 8548 (5, 30.6–47.1 mm HL, 191+–279+mm TL), southeast of Cape Manazurumisaki, Sagami Bay , 35.1333ºN, 139.1667ºE, 120–153 ftm (220–280 m), Albatross sta. 3697 or 3698, 8-ft Tanner beam trawl, 5 Mar. 1905 GoogleMaps ; * USNM 51415 About USNM (9, 20.4–45.7 mm HL, 83+–249+ mm TL), off Heta, Suruga Bay , 34.9667ºN, 138.7667ºE, 161–167 ftm (295–306 m), Albatross sta. 3737, tangles, 17 Mar. 1900 GoogleMaps . Non-types : Japan : BSKU 106845 View Materials (1, 42.0 mm HL, 225+ mm TL), southeast of Shimokoshiki-jima Island, East China Sea , 31.5675ºN, 129.8930ºE, 393 m, F/ V Maruko-maru, tr. 2, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 24 Apr. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 106763 View Materials (1, 39.7 mm HL, 212+ mm TL) , BSKU 106764 View Materials (1, 33.9 mm HL, 187+ mm TL), southeast of Shimokoshiki-jima Island, East China Sea , 31.5658ºN, 129.8915ºE, 380 m, F/ V Maruko-maru, tr. 1, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 24 Apr. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 106820 View Materials (1, 37.6 mm HL, 199+ mm TL), southeast of Shimokoshikijima Island, East China Sea , 31.5652ºN, 129.8878ºE, 407 m, F/ V Maruko-maru, tr. 3, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 24 Apr. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 50878 View Materials (1, 32.5 mm HL, 160+ mm TL), off Nomaike, Kagoshima, East China Sea , F/ V Maruko-maru, bottom trawl, coll. M. Yamashita and Y. Ohashi, 10 Sept. 2010 ; BSKU 109054 View Materials (1, 49.3 mm HL, 286+ mm TL), west of Sanpo-sone , 32.2872ºN, 129.0732ºE, 351–389 m, T/ V Nagasaki-maru, cr. N365, sta. B4, 3-m ORE beam trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 19 Nov. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 109053 View Materials (1, 18.0 mm HL, 108+ mm TL), east of Kasayama Bank , 32.3884ºN, 129.0505ºE, 304–312 m, T/ V Nagasaki-maru, cr. N365, sta. A3, 3- m ORE beam trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 19 Nov. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 109020 View Materials (1, 51.4 mm HL, 300+ mm TL), west of Okikasayama Bank , 32.1503ºN, 129.0072ºE, 499–504 m, T/ V Nagasaki-maru, cr. N365, sta. C5, 3-m ORE beam trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 19 Nov. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 27287 View Materials (1, 58.8 mm HL, 325+ mm TL) , BSKU 27290 View Materials (1, 53.7 mm HL, 314+ mm TL), west-northwest of Amami-oshima Island, Okinawa Trough , 28.8033ºN, 127.0617ºE, 425 m, F/ V Yuryo-maru, No. 8, tr. 25, bottom trawl, coll. Y. Kinoshita and S. Hagino, 6 Feb. 1978 GoogleMaps ; * BSKU 101604 View Materials (1, 41.8 mm HL), south of Muroto , 33.0790ºN, 134.1645ºE, 414–513 m, R/ V Tansei-maru, cr. KT-05-29, sta. K-500, beam trawl, coll. H. Endo et al., 17 Nov. 2005 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 71693 View Materials (1, 24.8 mm HL, 153+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, bottom trawl, 13 Feb. 2004 ; BSKU 72788 View Materials (1, 27.4 mm HL, 166+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, bottom trawl, 20 Feb. 2004 ; BSKU 112435 View Materials (1, 51.2 mm HL, 292+ mm TL) , BSKU 112453 View Materials (1, 54.6 mm HL, 306+ mm TL) , BSKU 112454 View Materials (1, 44.9 mm HL, 260+ mm TL) , BSKU 112456 View Materials (1, 37.4 mm HL, 182+ mm TL) , BSKU 112459 View Materials (1, 47.8 mm HL, 271+ mm TL), off Susaki, Tosa Bay , 320–380 m, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 9 Mar. 2014 ; BSKU 113653 View Materials (1, 40.5 mm HL, 249+ mm TL) , BSKU 113654 View Materials (1, 47.0 mm HL, 283+ mm TL), off Okitsu, Tosa Bay , 380 m, F/ V Koseimaru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 11 Mar. 2014 ; BSKU 113667 View Materials (1, 33.5 mm HL, 196+ mm TL), Numazu fish market, coll. S. Ohashi and M. Takami, 16 Feb. 2010 ; BSKU 110089 View Materials (1, 40.4 mm HL, 219+ mm TL) , BSKU 110434 View Materials (1, 35.1 mm HL, 212+ mm TL) , BSKU 110435 View Materials (1, 42.3 mm HL, 253+ mm TL), Suruga Bay , 34.7489ºN, 138.4664ºE, 200–450 m, F/ V Hinode-maru, sta. 6, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama and R. Misawa, 23 Apr. 2013 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 110016 View Materials (1, 45.1 mm HL, 258+ mm TL), Suruga Bay , 34.7080ºN, 138.4587ºE, 200–450 m, F/ V Hinode-maru, sta. 2, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama and R. Misawa, 23 Apr. 2013 GoogleMaps .
Counts and measurements. Based on 30 specimens (18–58.8 mm HL, 108+–325+ mm TL). Counts: first dorsal-fin rays II,9–12; pectoral-fin rays i17–i23; pelvicfin rays 8–9; gill rakers on first arch (outer/inner) 9– 14/16–19, on second arch 15–18/14–18; longitudinal scales 35–44; transverse scale rows below first dorsal-fin origin 7.5–11, below first dorsal-fin midbase 5.5–7.5, below second dorsal-fin origin 5.5–7, above anal-fin origin 21.5.
The following measurements are in % of HL, followed by those in % of PRL in parentheses: snout length 26–29 (32–39); orbit diameter 32–38 (42–49); postorbital length 41–46 (52–61); postrostral length 74– 80; orbit–preopercle distance 40–45 (52–60); suborbital width 11–13 (15–18); upper-jaw length 41–47 (55–62); length of rictus 35–39 (46–52); length of premaxillary tooth band 30–34 (38–46); preoral length 14–22 (18–27); distance between tip and lateral angle of snout 15–18 (19–23); snout width 25–29 (33–39); internasal width 20– 25 (26–33); interorbital width 27–33 (35–43); occipital width 14–19 (18–25); body width over pectoral-fin bases 38–61 (49–78); body depth at first dorsal-fin origin 79–99 (100–129); body depth at anal-fin origin 50–89 (63–116); prepelvic length 101–123 (131–159); preanus length 109–129 (144–171); preanal length 129–148 (165–196); isthmus–pelvic distance 41–58 (54–77); isthmus–anus distance 47–68 (62–90); isthmus–anal distance 67–90 (87–119); pelvic–anal distance 22–38 (28–49); anus–anal distance 12–26 (16–34); pelvic-fin length 38–44 (50–57); pectoral-fin length 52–66 (69–87); predorsal length 103– 118 (136–154); height of first dorsal fin 70–87 (95–113); length of first dorsal-fin base 26–35 (34–46); interdorsal length 50–81 (65–108); length of gill slit 24–30 (31–39); length of posterior nostril 3–6 (5–7); barbel length 20–33 (27–43).
Size. To about 33 cm TL ( BSKU 27287 View Materials , 325 View Materials + mm TL, Okinawa Trough , Japan).
Development. Larval morphology was described by Fukui & Tsuchiya (2005).
Distribution. Restricted to Japan, Korea, and Taiwan. Known from off the Pacific coasts of Japan northward to Rikuzen-Takata (39.03ºN; Iwate Pref.), Okinawa Trough, northern South China Sea, and Sea of Japan off Hagi (Yamaguchi Pref.) as well as the Korean Peninsula, at depths of 110‾ 980 m ( Shao et al. 2008a, 2008b; Jeong et al. 2010; Sonoyama et al. 2020; this study; Appendix 3-12C). A dominant species of Ventrifossa found along the Pacific coasts of southern Japan as well as in the East China Sea (but rare in Taiwanese and Korean waters).
Remarks. For a full description see Okamura (1970a). Ventrifossa garmani was originally described by Jordan & Gilbert (in Jordan & Starks 1904; as a species of Coryphaenoides Gunnerus, 1765 ) based on specimens collected from Sagami Bay, Japan ( Fig. 197 View FIGURE 197 ). This is by far the most common species of Ventrifossa at upper slope depths in the Pacific off southern Japan and the Okinawa Trough in the East China Sea ( Horikawa 2009: table 1; Furuhashi et al. 2010: table 2; author’s pers. observ.).
Relationships and comparisons. Ventrifossa garmani belongs to the subgenus Ventrifossa as redefined by Iwamoto (1979), and is unlikely to be mistaken for any other congeners, if body scales are available for identification. In V. garmani , spinules on the body scales are broadly triangular ( Fig. 198 View FIGURE 198 ), whereas those of other species are needle-like (see Figs.201 View FIGURE 201 , 205 View FIGURE 205 , 208 View FIGURE 208 ).Among other Japanese congers of the subgenus Ventrifossa , this species is readily distinguished from V. longibarbata Okamura, 1982 and V. rhipidodorsalis Okamura, 1984 by having a broader interorbital space (27–33% HL vs. 21–26% and 20–27% in V. longibarbata and V. rhipidodorsalis respectively). It further differs from V. longibarbata in having much larger scales on the body (scale rows below the first dorsal-fin midbase 5.5–7.5 vs. 8.5–11.5; below the second dorsal-fin origin 5.5–7 vs. 7–9.5) and a shorter chin barbel (20–33% HL vs. 31–38%); and from V. rhipidodorsalis by lacking a prominent black spot on the first dorsal fin (vs. present). Ventrifossa garmani is distinguished from V. saikaiensis Okamura, 1984 by having a paler suborbital shelf (vs. blackish), a narrower snout (snout width 25–29% HL vs. 30–40%), and a shallower suborbital space (11–13% HL vs. 13–17%).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Ventrifossa garmani
| Nakayama, Naohide 2020 |
Ventrifossa garmani
| : Okada & Matsubara 1938: 452 |
Lionurus garmani:
| Gilbert & Hubbs 1916: 193 |
Coryphaenoides garmani
| Jordan & Gilbert 1904 |