Empidideicus variegatus, Greathead & Evenhuis, 2001
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.4620128 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4620132 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B526FE1F-FFC9-F12D-733C-F9311F95D9B1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Empidideicus variegatus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Empidideicus variegatus sp.nov.
This species is easily separated from the only other Sokotran species of Empidideicus ( E. socotrae ) by the presence of longitudinal vittae on the mesonotum.
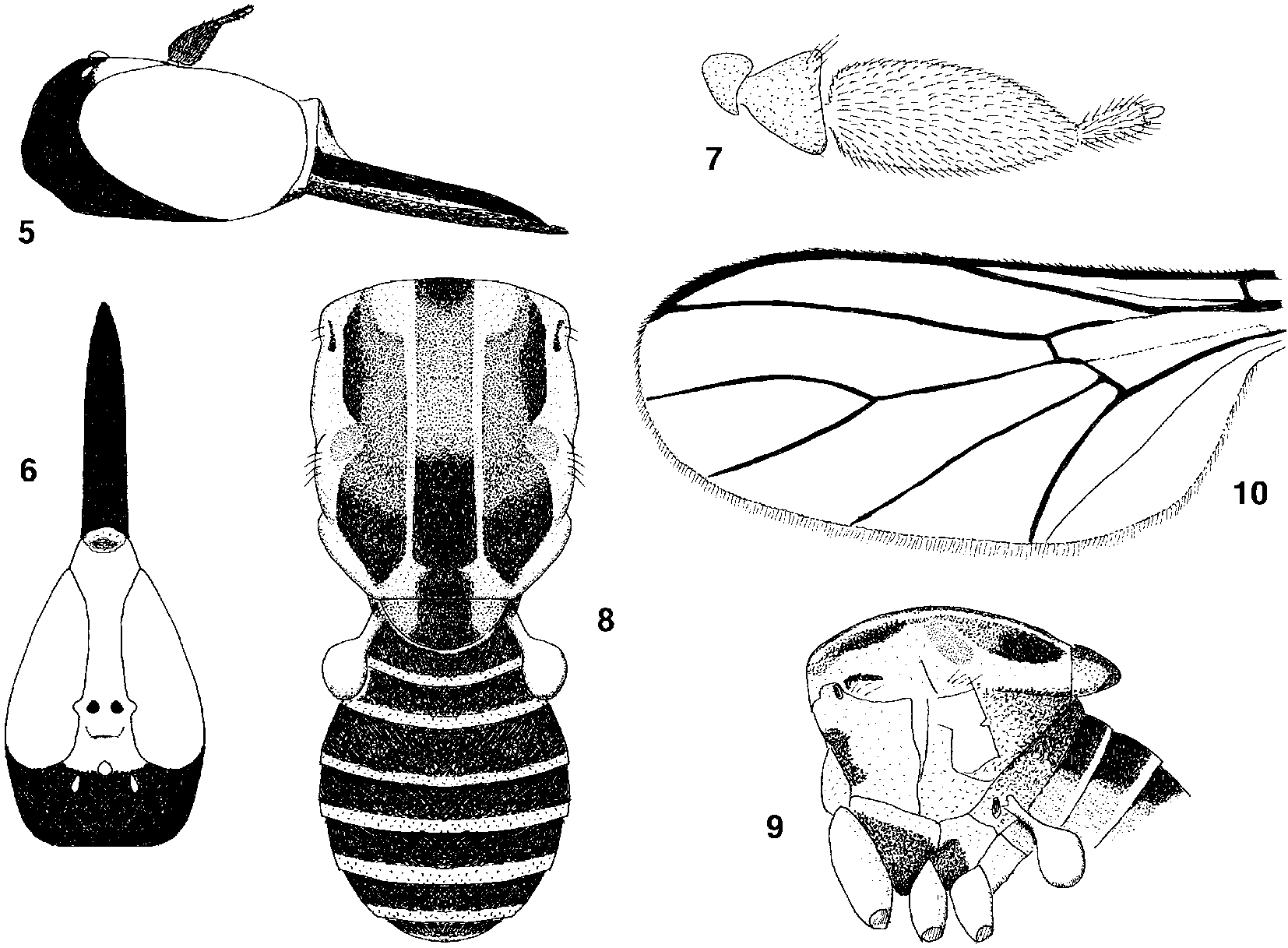
Female. Length: 1.021.23 mm. Head ( Figs. 56 View FIGURES 5 10 ) longer than high, occiput well developed posteriorly; eyes dichoptic, separated at vertex by 1.5 x distance between lateral ocelli; occiput and postgena black; front slightly depressed medially, white; face and tip of oral margin white; antennae ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 5 10 ) black; scape short, subtrapezoidal; pedicel subconical, wider than long; first flagellomere ovoidlanceolate, length ca. 2 x width; length of second flagellomere 1/4 that of first flagellomere, slightly wider apically than basally, with small transparent apical style; mentum black; proboscis black, length slightly longer than head length; labrum sclerotised, stiff, pointed apically; palpus not evident.
Thorax ( Figs. 89 View FIGURES 5 10 ). Mesonotum pale yellowish white to white, dorsum with admedian whitish longitudinal vittae and pattern of brown, dark brown and black pattern medially and dorsolaterally; scutellum black medially, brown to yellowish brown laterally; humeral callus, notopleural area, postalar callus, and admedial triangular prescutellar areas whitish; pleura white except black areas on extreme anterior portion of anepisternum, lower 3/4 of katepisternum, and lower half of meron; coxae and legs yellow; halter stem and knob white.
Wing ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 5 10 ). Subhyaline; veins brown, all well sclerotised except evanescent vein separating basal cells; costa ends slightly beyond end of R4+5; vein Sc incomplete; Rs evanescent at connection with R1; R4+5 slightly curved to wing margin; vein M1 curved toward wing margin; M2 fairly straight to wing margin; length of M2 shorter than M1+2; crossvein dmcu closing cell dm absent; A1 slightly sinuous to wing margin; fringe of hair on posterior margin of wing well developed
Abdomen. Dorsum black, posterior margins of tergites white, dorsal black colour of tergites gradating to pale yellowish white laterally; tergites with sparsely scattered minute hairs; venter yellowish white.
Genitalia ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11 12 ). Spermatheca obconical with typical indentation apically, sclerotised brown; apical spermathecal duct thin, transparent, length ca. 3 x length of spermatheca; sperm pump long, transparent, length ca. 3 x length of apical spermathecal duct, without sclerotised valves apically.
Male. Length: 1.00 1.18 mm. Same as female except as follows: Brown to dark brown areas in female all black in male; admedian vittae thin, white. Hypopygium brown; genitalia not dissected.
Types. Holotype female and 3 male and 8 female paratypes from SOKOTRA: Noghed , cca. 13°N 54°E, 27.ii–1.iii.2000, K. Stástny & V. Bejcek. Holotype in NMSA. Paratypes in MBC, NLE, NMSA, and USNM GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The specific epithet derives from the variegated pattern of the female mesonotum.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |