Cyamophiliopsis zaisani (Klimaszewski, 1963)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3936.3.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EE3C6346-4A91-48ED-862C-3CBC8558BAA0 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6103296 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AD2A9F1B-FFB9-FFF3-FF4A-FA034D41AB60 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cyamophiliopsis zaisani (Klimaszewski, 1963) |
| status |
|
Cyamophiliopsis zaisani (Klimaszewski, 1963) View in CoL
( Figs 2 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ‒15, 45)
Psylla zaisani Klimaszewski, 1963: 68, 1973: 229 View in CoL ; Loginova, 1972: 294; Gegechkori & Loginova, 1990: 80. Cyamophiliopsis zaisani: Li, 2011: 676 View in CoL .
Redescription. Adults: Seasonally dimorphic. Winter form slightly smaller in body size ( Table 1), darker in coloration, and with relatively broader forewing ( Table 1).
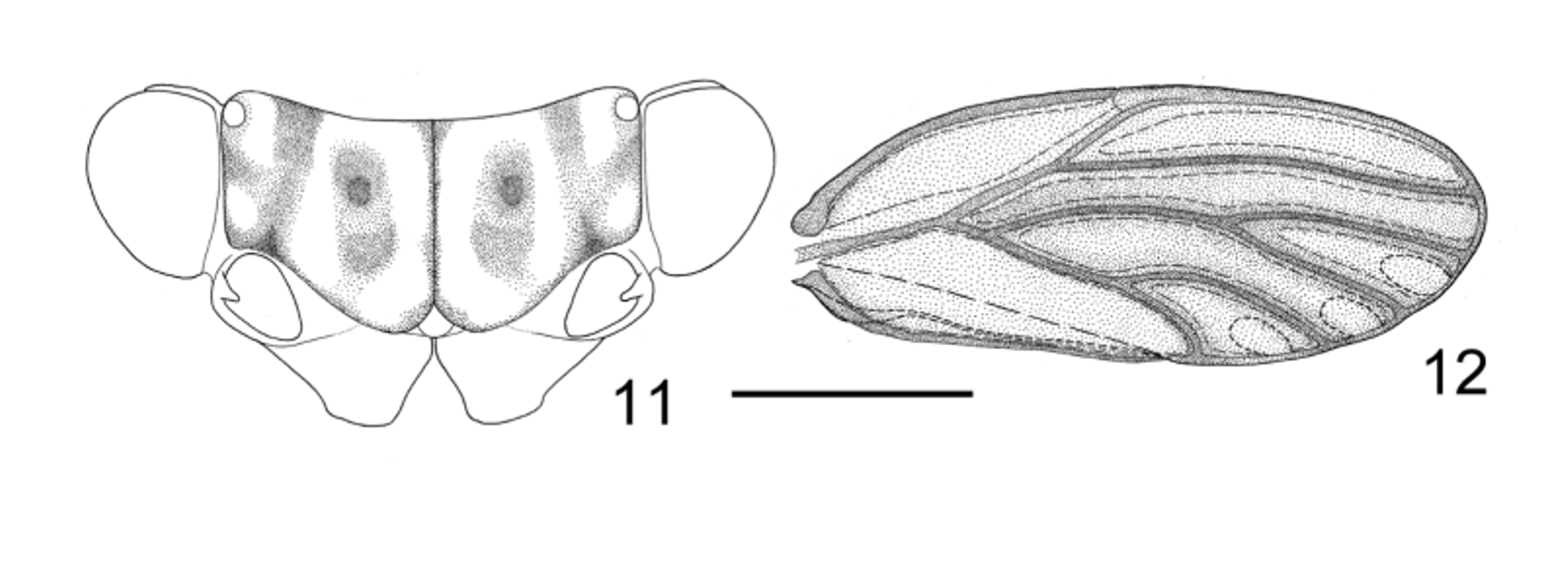
Coloration. Summer form: Body usually bicolor in overall view. Thorax and head orange in general, occasionally green. Vertex with darker orange pattern as shown in Fig. 2 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 . Compound eyes dark grey, ocelli orange. Antenna orange, with black apices on segments IV, VI and VIII, brown apices of segments V and VII, and segments IX‒X entirely black. Dorsal aspect of thorax with normally arranged darker orange pattern, pronotum with three incomplete medial patches. Legs yellow, claws black. Forewing membrane ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ) translucent, slightly yellowish; margin from apical 1/3 of pterostigma to anal break, and area along Cu2 yellowish brown or grey, gradually fading towards the base and anterior margin; narrow bands along M1+2, M3+4, Cu1a and Cu1b brown, darker than color previously described; veins yellow. Abdomen green, light green or beige. Apex of paramere black. Tip of female subgenital plate black.
Winter form: Body dark brown in general view. Thorax and head yellow in ground color, with dark brown patterns arranged in the same manner as in summer form ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 ‒ 12 ). Pro- and mesopleuron black. Metapleuron and metacoxa orange to light brown. Legs yellow, femora black in basal 4/5. Forewing ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11 ‒ 12 ) translucent, slightly brownish; narrow bands along R, Rs, M+Cu1, M, M1+2, M3+4, Cu1, Cu1a and Cu1b brown. Abdomen black, leaving a narrow band along posterior margin of each segment and peritremes orange. Male and female terminalia black, lateral margin of apical process of female proctiger yellow.
Structures: Head ( Figs 2 & 4 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ) inclined from longitudinal body axis in about 70°, wider than mesoscutum. Vertex clearly demarcated from gena by being much higher and a well-developed gap, area above antennal insertion depressed. Genal process short, apex blunt, obliquely truncate.
Pronotum arched, and deflexed as head. Propleural suture ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ) basically vertical; dorsal end reaching middle of lateral margin of pronotum, unclearly bi-forked at joint, with both branches short and obscure. Proepisternum and proepimeron subequal in size. Metatibia with blunt basal spine. Fore wing ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 & 12 View FIGURES 11 ‒ 12 ) membranous, oblong oval, widest in middle; m1 about as wide as m2 apically; cu1 relatively long, strongly leaned backwards; fields of surface spinules and radular spinules as in Fig. 8 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 .
Male terminalia: Proctiger ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ) tubular, moderately curved caudad, covered with evenly lengthed short setae which are denser apically. Paramere ( Figs 4 & 6 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ) shorter than proctiger, apical part of the main part relatively broad and strongly curved cephalad; posterior margin near apex emarginated; lateral lobe small and narrow, knifeshaped, inner surface with a cluster of about 10 acute or subacute spines in apical portion. Distal segment of aedeagus ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ) long and slender, apical dilatation small, apex blunt; end tube of ductus ejaculatorius curved dorsally-posteriorly. Anterior margin of subgenital plate ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ) nearly straight, dorsal margin with a cluster of several setae, ventral surface with evenly spaced setae.
Female terminalia ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 2 ‒ 10 ): Apex of proctiger slightly raised; apical process of proctiger with 1+1 longitudinal rows of relatively long setae and dozens of peg setae near lateral margins. Subgenital plate with peg setae bilaterally, and short setae on ventral surface.
Fifth instar immature (Figs 13‒15): Coloration: Body completely yellow. Compound eyes reddish black.
Structures: Body oval, forewing pad without produced humeral lobe; dorsal aspect uniformly covered with long, short or minute capitate setae; ventral surface and appendages with capitate setae and simple setae.
Cephaloprothorax dorsally fused into one large sclerite, indistinctly demarcated with compound eye, leaving 2+2 small free sclerites posteriorly. All setae in anterior margin of head capitate, ventral sclerites of head with several simple setae, ocular- and post ocular setae capitate. Clypeus pyriform, with a pair of simple setae anteriorly. Antenna 7-segmented, with a single rhinarium on apices of segments 3 and 5, and two rhinaria in middle section of segment 7, and with scattered simple setae; segments 2, 4 and 5 with one apically, segment 3 with two (one medially and one apically) capitate setae, together forming a row on the opposite side of the rhinaria; for segments 3 and 5, one extra capitate seta present near each rhinarium.
Dorsal aspect of meso- and metathorax composed of 2+2 longitudinally oblong lateral sclerites and shattered small medial sclerites, covered with sparse capitate setae, setae based in sclerites conspicuously longer, thicker and symmetrical than the ones in membrane. Forewing pad oval, unevenly covered with dozens of minute or short capitate setae on dorsal surface, and about ten long capitate setae along outer margin; one pore present in anterior part medially. Hindwing pad blade-shaped, sparsely covered with capitate setae which are longer basally on dorsal surface, apex with two thick capitate setae. Legs with mixed setation: Each coxa with several simple setae; each femur with a short capitate seta in dorsal surface subapically; ventral surface of prefemur with two capitate setae; meso- and metafemur with two closely packed minute simple setae right dorsal to pore row; each tibia with capitate setae dorsally, and simple setae ventrally. Tarsal arolium (Fig. 14) fan-shaped and petiolate, with rather long unguitractor.
Dorsal aspect of abdomen composed of 5+5 main free sclerites, several small free sclerites, and large caudal plate, with minute or short capitate setae arranged in bands, indicating future division of segments. Ventral aspect of abdomen with 3+3 free lateral sclerites with one spiracle each, none fusing with caudal plate; long, short or minute capitate setae present laterally, and simple setae of varying sizes present medially. Anus (Fig. 15) ventral, circum-anal pore field formed by complete outer circum-anal pore ring and complete inner circum-anal pore ring; outer circum-anal pore ring formed by a single row of slit-shaped pores, strongly emarginated anteriorly, and slightly emarginated laterally and posteriorly; inner circum-anal pore ring formed by a moderately jagged row of small oval pores, following the same shape as the outer ring. Abdominal margin of caudal plate with 6+6 long capitate setae, with caudal-most pair based in dorsal submargin; posterior margin of caudal plate (Fig. 15) with 2+2 sectasetae; slightly lateral-cephalad to the outer pair of sectasetae, 1+1 setae present in ventral submargin, long, smoothly tapered yet truncate apically.
Material examined. China: Inner Mongolia: 88 ♂, 101 ♀, Ewenki, Honghuaerji, 780 m, 21.viii.1986, Li Fasheng, on Spiraea aquilegifolia ; 36 ♂, 29 ♀, numerous nymphs, same locality, 48.24219°N, 119.99327°E, 3.vii.2013, Luo Xinyu, on Spiraea aquilegifolia ; 2 ♂, 33 ♀, winter form, numerous immature, same locality, 11.vi.2012, Luo Xinyu & Wang Jianyun, on Spiraea aquilegifolia .
Host plant. Spiraea aquilegifolia (Li 2011) , S. hypericifolia (Loginova 1972) , S. media (Loginova 1972) .
Distribution. China: Inner Mongolia; Kazakhstan (Gegechkori & Loginova 1990); Mongolia (Klimaszewski 1963; Loginova 1972); Russia: Transbaikal (Loginova 1972).
Remarks. This is the type species of the genus, however, a relatively special one. The pattern on dorsum and head are generally lighter than in other species, especially in dry mounted specimens. The rather narrow lateral lobe of paramere and the trait that sclerotised spines only exist in the medial and apical portions of it makes C. zaisani really easily distinguished. The immature characters can fit in the greatly diverse genus Cacopsylla .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Psylloidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Cyamophiliopsis zaisani (Klimaszewski, 1963)
| Luo, Xinyu, Li, Fasheng & Cai, Wanzhi 2015 |
Cyamophiliopsis zaisani:
| Li 2011: 676 |
Psylla zaisani
| Klimaszewski 1963: 68 |