Lygosoma bampfyldei Bartlett, 1895
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4438.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:595B1D22-58CF-4142-9268-9F92DD8A4FD5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5988920 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AA2B87D3-D91B-FF87-8682-FA15FEF5FD56 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lygosoma bampfyldei Bartlett, 1895 |
| status |
|
Lygosoma bampfyldei Bartlett, 1895
Bampfylde’s Supple Skink
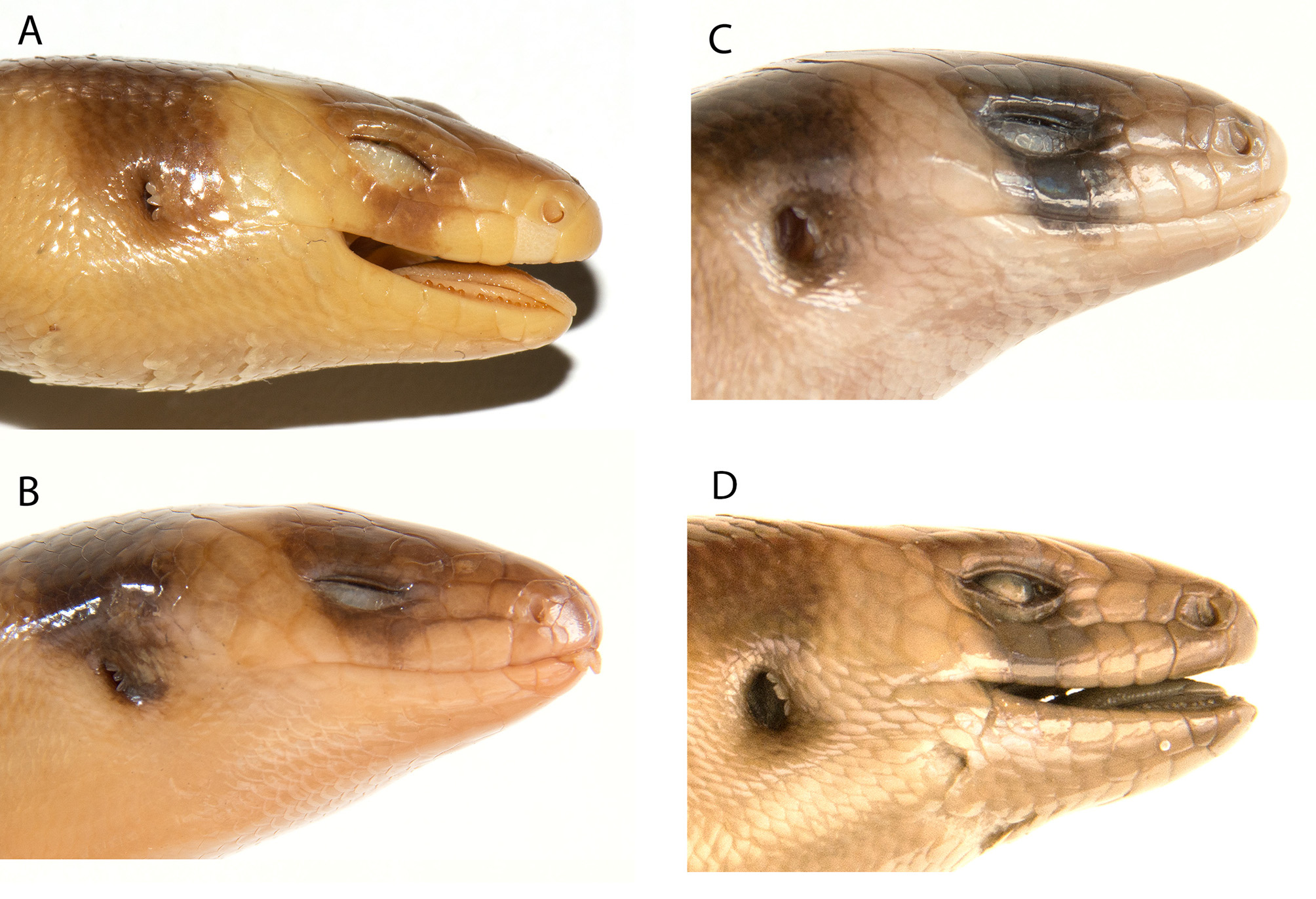
Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 & 5 View FIGURE 5
Lygosoma (Riopa) bampfyldei Bartlett, 1900:96 .
Lygosoma bampfyldii Boulenger, 1912:93 (in part); Smith, 1930:36 (in part).
Lygosoma bampfyldei de Rooji, 1915:263 (in part); Greer, 1977:915; Welch et al., 1990:83; Das & Yaakob, 2007:78; Das, 2010:238 (in part); Geissler et al., 2012:65; Grismer, 2011:613 (in part).
Riopa bampfyldei Manthey & Grossmann 1997:275 (in part); Chan-ard et al., 1999:27 (in part).
Mochlus bampfyledei Mittleman, 1952:22 .
Syntypes. Two male syntypes ( BMNH 1946.8 .64, 1946.8.10.84) collected by C. A. Bampfylde from somewhere along the “Rejang [= Rajang ] River, Sawawak”, East Malaysia .
Diagnosis. Lygosoma bampfyldei can be differentiated from all other Lygosoma by having the combination of relatively large (SVL = 110–119 mm) slender body (PEC/SVL = 0.12–0.13); seven supralabials; six or seven infralabials; midline contact of the supranasals; prefrontals not in contact; frontoparietal contacting three supraoculars; postinterparietal absent; eight superciliaries; three postsuboculars, the first being the largest; one primary and two or three secondary temporals; three tertiary temporals; seven or eight nuchal scales; a deep postnasal groove extending from the nasal scale to below the anterior portion of the eye and lying below the loreals and lower preocular and above the second and third supralabials; scaly lower eyelid, no window; 36–40 midbody scale rows; 81–85 paravertebral scale rows; 94–97 ventral scale rows; 28–30 caudal scale rows at the tenth subcaudal; seven or eight small precloacal scales; smooth to weakly keeled subdigital finger lamellae, 10 lamellae on third finger; keeled subdigital toe lamellae, 17 lamellae on fourth toe; low, round, small palmar scales numbering seven or eight across the base of the palm; head pattern consisting of dark, continuous frontal and occipital bands separated by a yellowish band; dark occipital band not confluent with lighter color of dorsum and tail. These characters are scored across all species in the L. bampfyldei group in Table 2.
Distribution. This species in known the from the type locality and the Croker Range, Sabah. Das in Karin et al. (2018) listed this species as occurring at “Sungei Rejang [=Sungai Rajang], Sri Aman Division, Sarawak ”. However, no part of the 563 km long Sungai Rajang passes through the Sri Aman Division as this division lies well south of the river and is not part of the Rajang drainage basin. Therefore, the precise collecting locality along this river is unknown.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Lygosoma bampfyldei Bartlett, 1895
| Grismer, L. Lee, Quah, Evan S. H., Duzulkafly, Zaharil & Yambun, Paul 2018 |
Lygosoma bampfyldii
| Boulenger, 1912 :93 |
| Smith, 1930 :36 |
Lygosoma bampfyldei
| Greer, 1977 :915 |
| Welch et al., 1990 :83 |
| Das & Yaakob, 2007 :78 |
| Das, 2010 :238 |
| Geissler et al., 2012 :65 |
| Grismer, 2011 :613 |
Riopa bampfyldei
| Manthey & Grossmann 1997 :275 |
| Chan-ard et al., 1999 :27 |
Mochlus bampfyledei
| Mittleman, 1952 :22 |