Lygosoma schneideri Werner, 1900
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4438.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:595B1D22-58CF-4142-9268-9F92DD8A4FD5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5988922 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AA2B87D3-D914-FF85-8682-F936FB0FFF04 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lygosoma schneideri Werner, 1900 |
| status |
|
Lygosoma schneideri Werner, 1900
Sumatran Supple Skink
Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 & 5 View FIGURE 5
Lygosoma bampfyldii Boulenger, 1912:93 ; Smith, 1930:36
Lygosoma bampfyldei de Rooji, 1915:263 ; Greer, 1977:915; Welch et al., 1990:83; Das & Yaakob, 2007:78; Das, 2010:238; Grismer, 2011:613.
Riopa bampfyldei Smith 1937:228 ; Manthey & Grossmann 1997:275; Chan-ard et al., 1999:27.
Mochlus bampfyledei Mittleman, 1952:22
Riopa bampfyldii Denzer & Manthey, 1991:317
Holotype. Adult male (BM 4743) from “Indragiri, Djapura”, Sumatra, Indonesia and accessioned into the Naturhistorischen Museum Basel by G. Schneider on 1 January 1900.
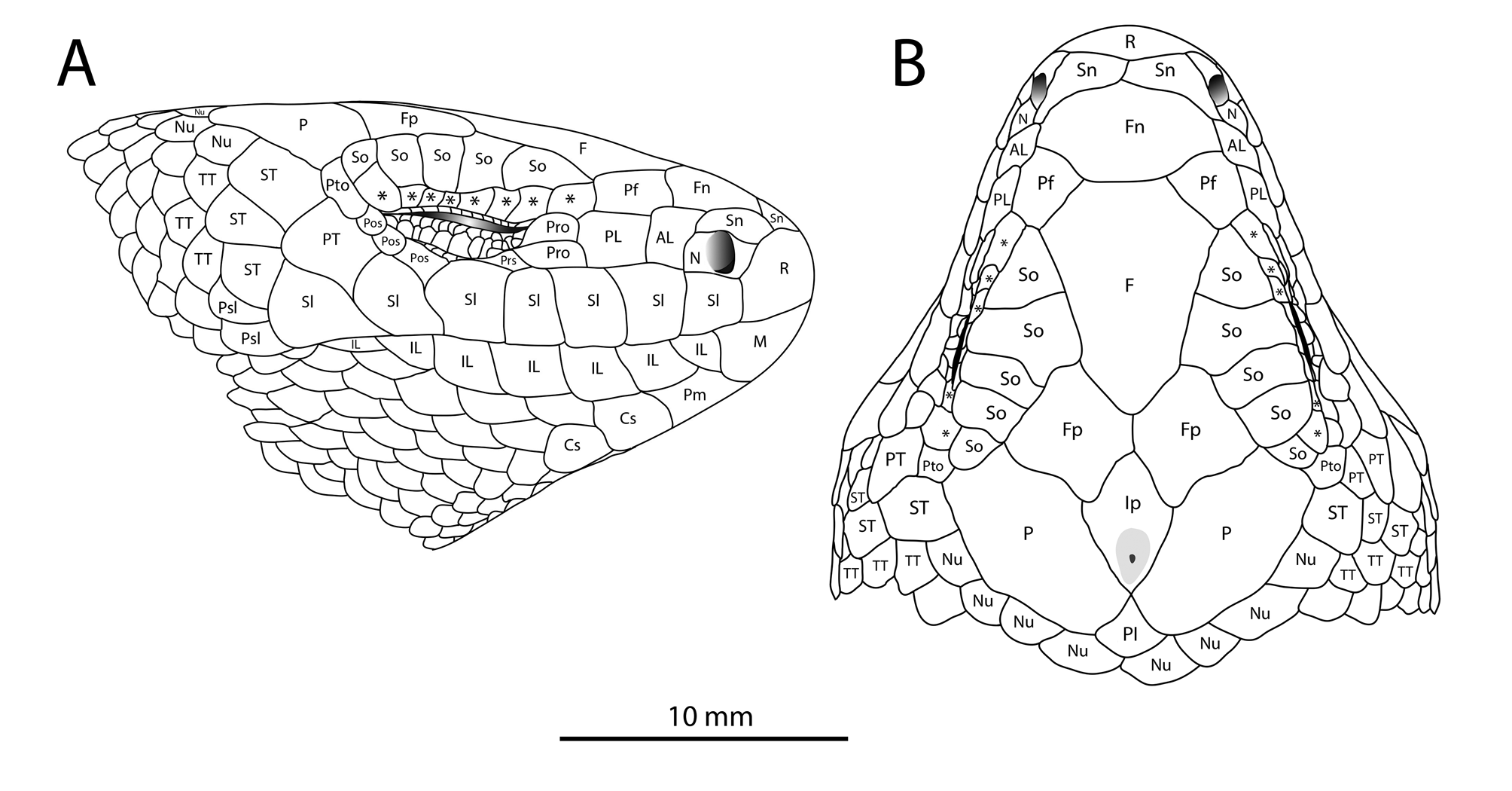
Diagnosis. Lygosoma schneideri can be differentiated from all other Lygosoma by having the combination of a relatively large (SVL = 129 mm) robust body (PEC/SVL = 0.15); seven supralabials and infralabials; midline contact of the supranasals; prefrontals not in contact; frontoparietal contacting three supraoculars; large postinterparietal present; eight superciliaries; two postsuboculars, the first being small; one or two primary and three secondary and tertiary temporals; eight nuchal scales; a deep postnasal groove extending from the nasal scale to below the anterior portion of the eye and lying below the anterior loreals and lower preocular and above the second and third supralabials; scaly lower eyelid, no window; 45 midbody scale rows; 95 paravertebral scale rows; 98 ventral scale rows; 34 caudal scale rows at the tenth subcaudal; eight large precloacal scales; smooth to weakly keeled subdigital finger lamellae, 10 lamellae on third finger; keeled subdigital toe lamellae, 16 lamellae on fourth toe; low, round, small, palmar scales numbering seven across the base of the palm; head pattern consisting of a dark, continuous frontal and occipital band separated by a yellowish band; dark occipital band not confluent with lighter color of dorsum and tail. These characters are scored across all species in the L. bampfyldei group in Table 2.
Distribution. Lygosoma schneideri is known only from the type locality. Das (2010) reports this species from “north-western Sumatra (Indrajiri, Riau Province)” however the type locality listed by Werner (1910) “Indragiri, Djapura” is in southeastern Sumatra ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
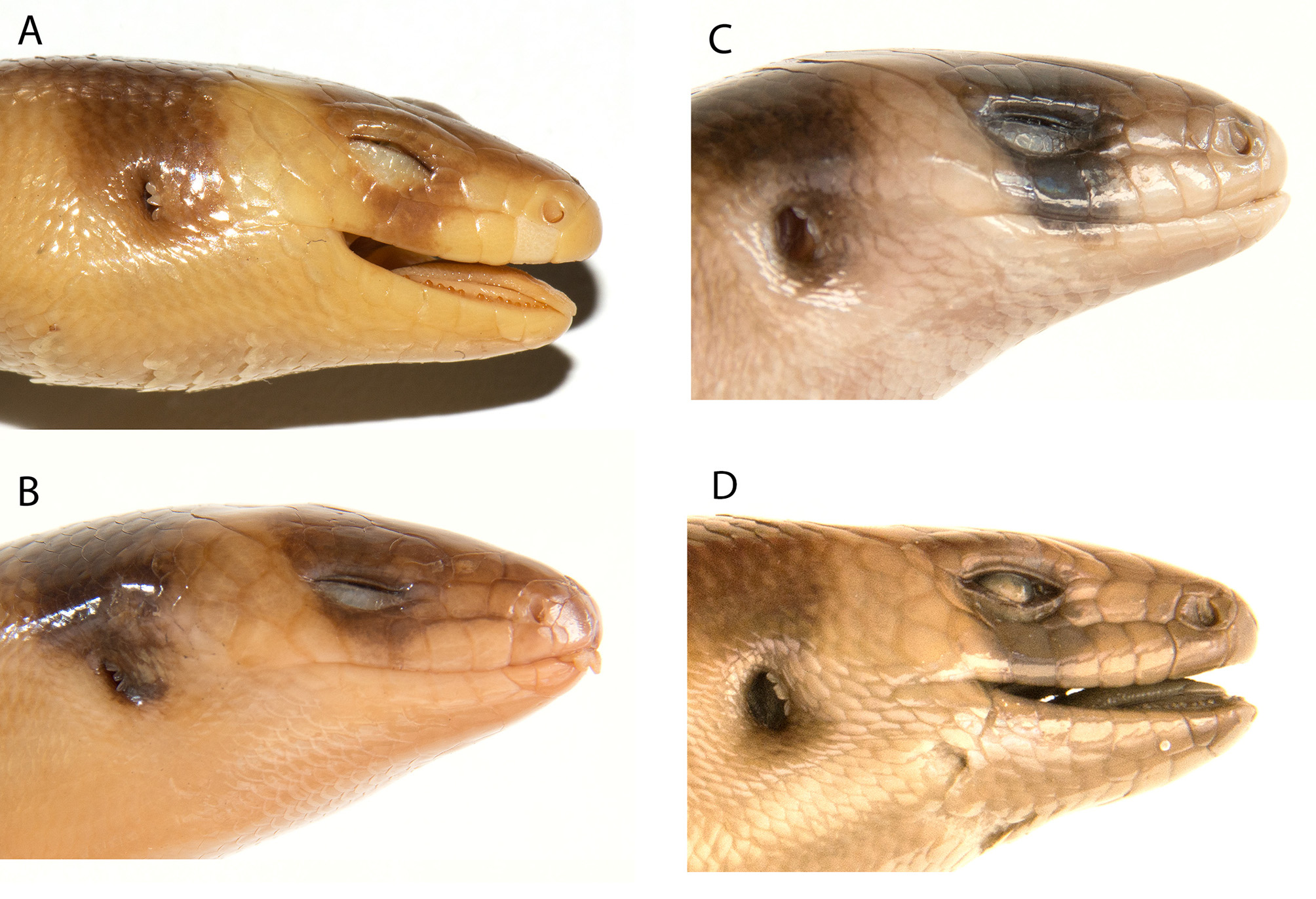
Remarks. Boulenger (1912) placed Lygosoma schneideri in the synonymy of L. bampfyldei in his redescription of the latter. Our analyses indicate that L. schneideri is considerably different from L. bampfyldei in having two vs. three suboculars, a postparietal scale ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ), 45 vs. 36–40 midbody scale rows, 95 vs. 82–85 paravertebral scale rows, 34 vs. 28–30 scale rows around the tail at the 10th subcaudal, and a significantly (t = -6, p = 0.004) more robust (PEC/SVL = 0.15) vs. a slender (PEC/SVL = 0.12–0.13) body ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Lygosoma schneideri Werner, 1900
| Grismer, L. Lee, Quah, Evan S. H., Duzulkafly, Zaharil & Yambun, Paul 2018 |
Lygosoma bampfyldii
| Boulenger, 1912 :93 |
| Smith, 1930 :36 |
Lygosoma bampfyldei
| Greer, 1977 :915 |
| Welch et al., 1990 :83 |
| Das & Yaakob, 2007 :78 |
| Das, 2010 :238 |
| Grismer, 2011 :613 |
Riopa bampfyldei
| Smith 1937 :228 |
| Manthey & Grossmann 1997 :275 |
| Chan-ard et al., 1999 :27 |
Mochlus bampfyledei
| Mittleman, 1952 :22 |
Riopa bampfyldii
| Denzer & Manthey, 1991 :317 |