Isostenosmylus julianae U. Aspöck, Martins & Ardila-Camacho, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4149.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3C009047-18B7-4C79-9C22-6D7659AA533B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6053619 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A94487F7-E15E-FFAA-FF68-2A8AFE7959EC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Isostenosmylus julianae U. Aspöck, Martins & Ardila-Camacho |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Isostenosmylus julianae U. Aspöck, Martins & Ardila-Camacho View in CoL n. sp.
( Figs. 10–12 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 11 View FIGURE 12 )
Holotype, ♂, Peru: Pasco, Villa Rica, ZA. Bosque de Protección, San Matías, San Carlos , 10°38’36’’N − 75°12’55’’W, 674 m, 3~ 5.v.2012, V. Borda and L. Figuova, Malaise trap ( MHNL); Paratype, ♀, Peru, Pasco, Villa Rica, ZA. Bosque de Protección, San Matías, San Carlos , 10°38’36’’N GoogleMaps −75°12’55’’W, 674 m, 3~ 5.v.2012, V. Borda and L. Figuova, Malaise trap (MHNL).
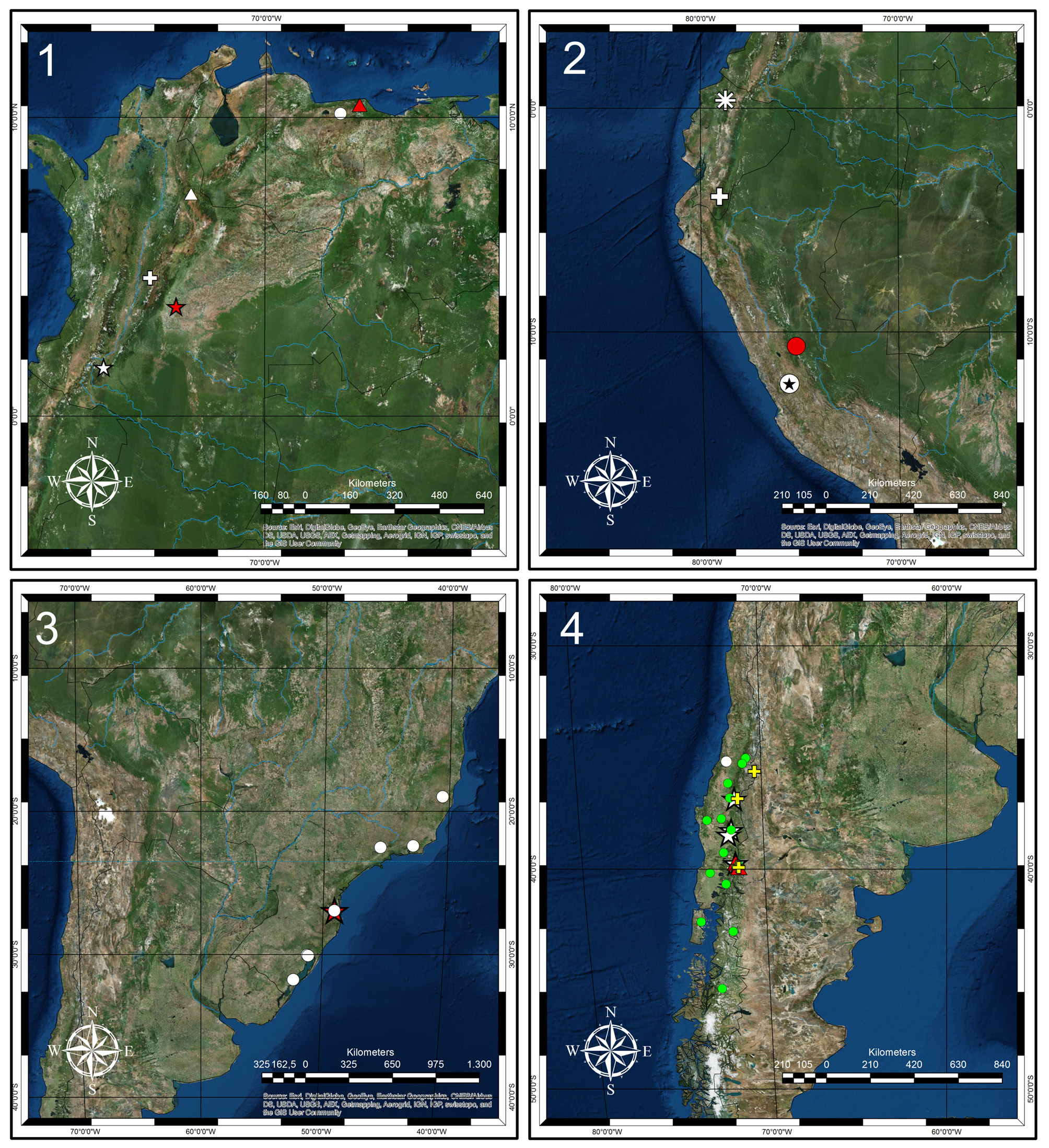
Distribution ( Fig. 43 View FIGURE 43 ). Peru ( Pasco).
Diagnosis. Isostenosmylus julianae presents a wing pigmentation pattern similar to I. contrerasi , with numerous small amber spots at distal half of forewing, but it lacks the distinctive spot located between MP and posterior wing margin of I. contrerasi . The pterostigma is well marked, and its color pattern varies from a mixture of light greyish brown and very pale yellow to light brown and pale yellow. This species is distinguished from other species in the genus by the following combination of genital characters: male terminalia has ectoproct with a prominent beak-like process. Anterolateral branches of ninth gonocoxite are prominent and widened in lateral view, while posteromedial lobe is rounded in ventral view. Another distinctive characteristic of this species is the ventral branch of tenth gonocoxite, which is prominent and acuminate. Female genitalia has the ninth gonapophysis short, with basal half widened, medially it is constrained, and distal half is short and bilobate.
Description. Head ( Figs. 10 View FIGURE 10 A, C). Labrum pale yellow, covered with setae of same color; clypeus pale yellow; frons yellowish brown. Maxillae light brown, maxillary palpi five-segmented, apical one with brown ring; labial palpi yellowish brown. Scape and pedicel light brown. Vertex slightly elevated, with black line laterally, peripheral surface of ocelli light brown. Antennae filiform, with 32 articles left (apex missing), all light brown, and densely covered with setae of the same color as cuticle. Occiput brownish. Genae and postgenae brownish. Eyes damaged.
Thorax ( Figs. 10 View FIGURE 10 A, C). Prothorax, length 1.8 mm; pronotum yellowish brown, with a pair of brownish spots distally, entire surface with numerous setae arising from protuberant bases, most of these dark brown pigmented. Pleural region of prothorax dark brown, densely covered with long setae. Pterothorax, length 2.5 mm. Mesonotum damaged. Metanotum greyish brown, scutum with brown spots. Pteropleura yellowish, with brown spots, entire surface densely covered with yellowish setae.
Legs ( Figs. 10 View FIGURE 10 A, C). Foreleg with elongated coxa, in mid- and hindlegs short. Femora and tibiae mainly yellowish and covered with setae of the same color as cuticle, first and second femora with brown spot basally, tibiae with several brown spots. Apex of tibiae amber. Tibial spurs short, light amber. Tarsi light brown covered with yellowish brown setae, five-segmented, the first tarsomere as long as the following three together, the fifth as long as the second and third together. Tarsal claws light amber, arolium present.
Wings ( Figs 10 View FIGURE 10 A, C). Forewing length 26 mm, maximum width 8.9 mm; wing veins alternating light brown and pale yellow, and covered with setae of the same color as the cuticle. Wing margin with trichosors. Costal field wide, about 65 costal cross-veins before pterostigma, some of these forked near to Sc. Pterostigma, length 3 mm, slightly marked with brownish and yellowish parts. Seven crossveins in the costal field beyond the pterostigma. Subcostal field hyaline with single crossvein basally. Radial field with 27 crossveins. Rs with 11 branches. Wing membrane mostly hyaline, with maculae on crossveins of radial field, Rs, MP and between CuA and CuP. Nygmata barely perceptible. CuP abruptly curved posterad. Hindwing, length 23 mm, maximum width 6.6 mm; wing membrane hyaline, veins mainly pale yellow. Radial field possessing 21 crossveins. CuP pectinate, with most branches forked, not sinuate. Pterostigma weakly marked with color pattern similar to forewing.
Abdomen ( Figs 10 View FIGURE 10 A, 11A–D). Tergites mainly brown, sternites yellowish brown, all segments covered with long yellowish setae.
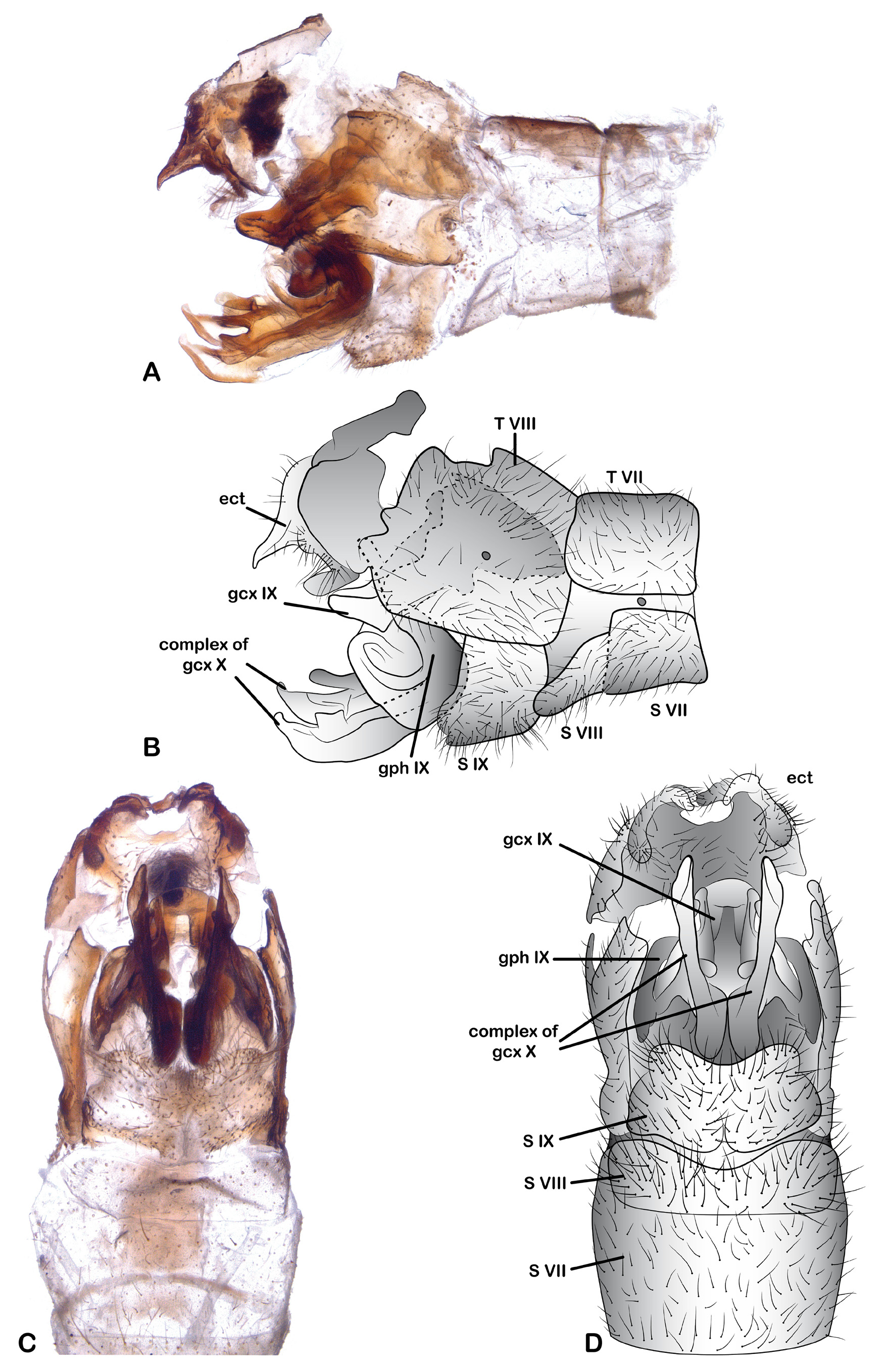
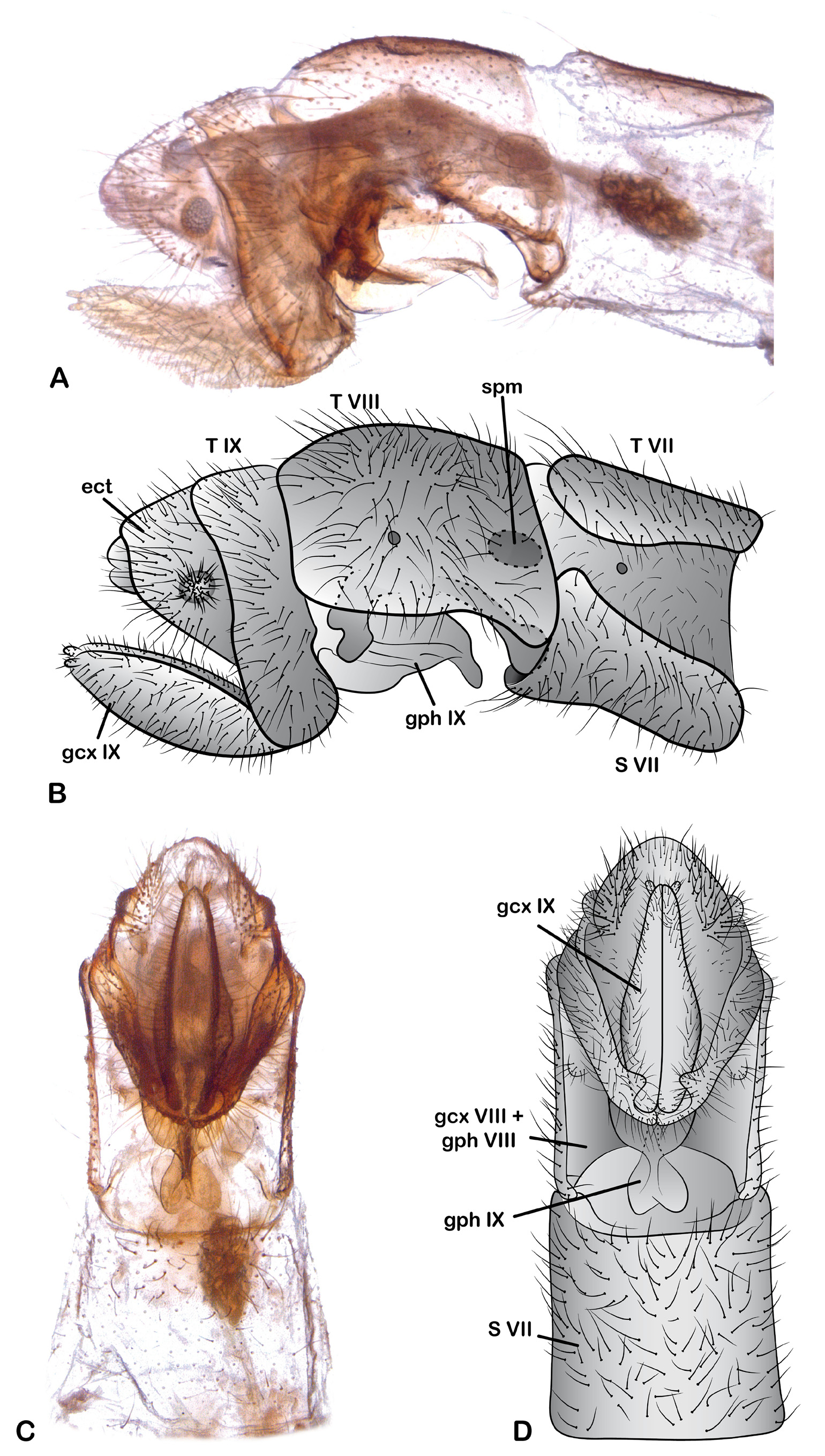
Male genitalia ( Figs. 11 View FIGURE 11 A–D). Eighth and ninth tergites fused. Ectoproct (partly destroyed) posterodorsally with a beak-like acute prominent process; ectoproct caudally with an unpaired bar. Ninth sternite densely setose; in ventral view posteromedially slightly concave. Ninth gonocoxites paired rod-like sclerites, broadened cephally, caudally fused. Ninth gonapophysis U-shaped in lateral view. Complex of tenth gonocoxites strongly curved in lateral view, posteriorly widened and with two subapical processes. Hypandrium internum triangular in ventral view, weakly tender.
Female genitalia ( Figs. 12 View FIGURE 12 A–D). Seventh sternite, in lateral view, posteroventrally produced, posteriorly connected with the fused eighth gonocoxites + gonapophyses. This sclerite is plate shaped, elongated posterodorsally with a lobe moderately developed, covered with long setae. Fused ninth gonapophyses elongated, in lateral view medially slightly curved dorsad, apex with two lobes slightly developed, the dorsal one anteriorly projected, the ventral one anteroventrally projected; in ventral view medially constrained, cephal half heart-shaped. Eighth tergite laterally enclosing spiracle of eighth abdominal segment, anteroventral corner slightly ventrally projected. Ninth tergite laterally elongate, ventrally projected. Ectoproct in lateral view semicircular, posterior margin with numerous long setae, callus cerci with trichobothria arranged in a rosette. Ninth gonocoxites acuminate, with ventral margin straight, densely covered with numerous setae; ninth gonostylus ovoid, equipped with small setae. Spermathecae ellipsoid in lateral view.
Etymology. The specific name is a noun in the genitive singular, feminine, derived from the latinized form of Juliane.
The species is named in honour of Dr. Juliane Diller. On Christmas Eve 1971, when she was a girl of 17, at that time named Juliane Koepcke, daughter of the famous German biologists Hans-Wilhelm and Maria Koepcke, founders of the research station in Panguana in the Amazonas basin in Peru, she flew together with her mother from Lima to Pucallpa. When the airplane crossed the Andes it was hit by a lightning and crashed from an altitude of 3000 m. Juliane was the only survivor of this accident. After fighting her way through the tropical forest she was finally rescued after ten days. Later she studied Zoology and devoted her life to the protection of the tropical forest around the research station of Panguana. She is highly respected in Peru as an authority in strategies for environmental protection. In April and May 2015, we had the opportunity to accompany her to Panguana and to visit the Natural History Museum of Lima where we (Horst and Ulrike Aspöck ) received the two osmylid specimens from Juan Grados, M. Sc., biologist and from Professor Dr. Gerardo Lamas Müller. The two specimens turned out to be the species described here.
Remarks. Isostenosmylus julianae seems to belong to a species group together with I. contrerasi and I. fusciceps . This species group is distinguished by the presence of an elongate and prominent process of ectoproct, pointed or spatulate at the apex. In I. julianae , this process is elongated, ventromedially curved, beak shaped in lateral view. In comparison it is sharply pointed and straigth in I. fusciceps . Moreover, I. contrerasi presents this structure spatulate, straight, slightly pointed in lateral view, and somewhat shorter than in the other two species. Among female genitalia, the ninth gonapophyses of I. julianae are similar to that of I. contrerasi where this structure is short and widened in the basal half. On the basis of the morphology of the genital structures and the distribution of these species, I. julianae may be the sister species of I. fusciceps , and I. contrerasi could be the sister taxon of both species.
| MHNL |
Musee Guimet d'Histoire Naturelle de Lyon |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |