Aegidinus, Arrow, 1904
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2019.1606953 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:09AA5C86-5138-42A7-9646-9FF2A7F46767 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4561501 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/9F138799-E555-B06A-9ABD-5DC5D4A7F9B1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Aegidinus |
| status |
|
Key to Aegidinus species (males)
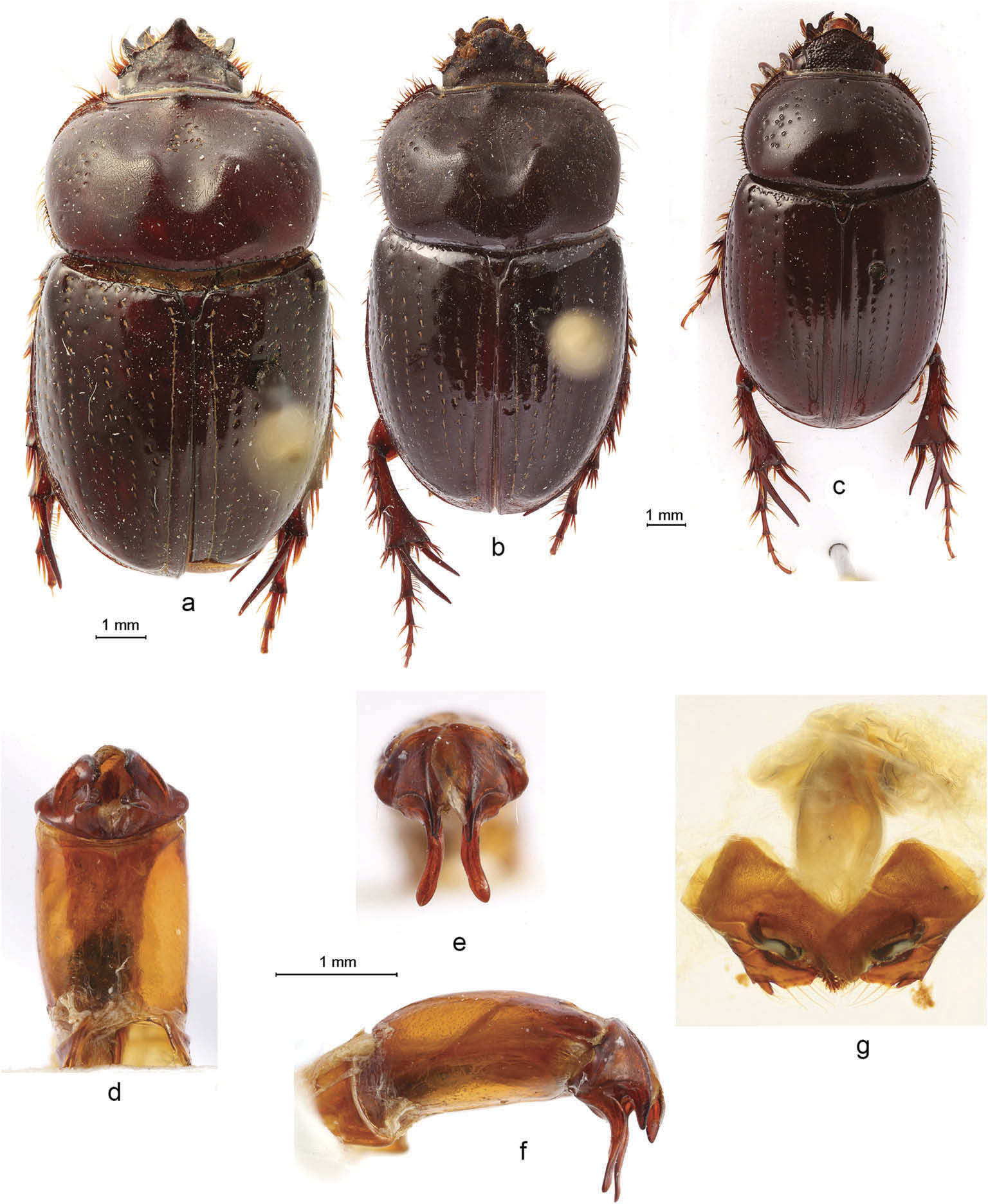
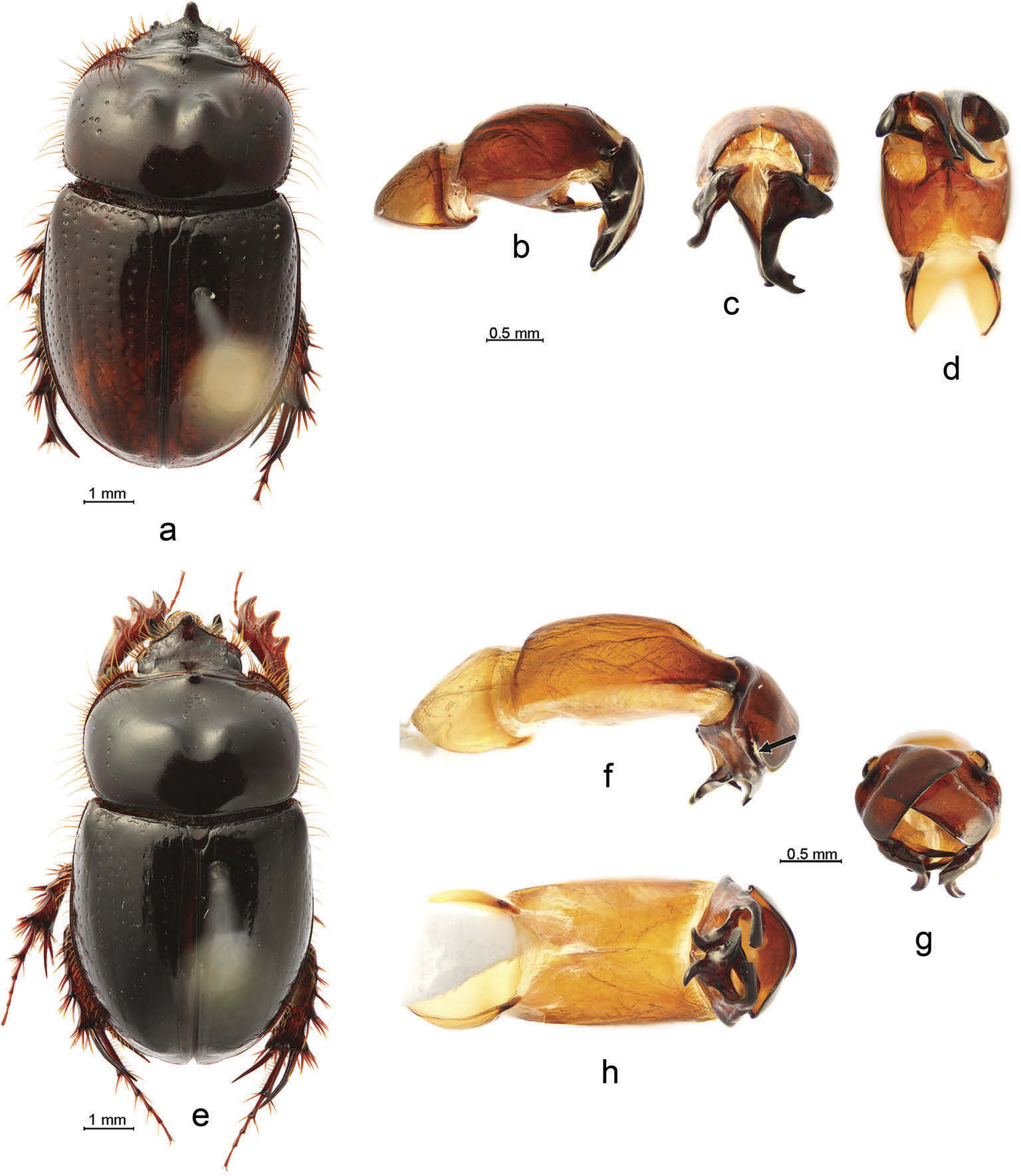
1. Parameres separated into dorsomedial and ventrolateral lobes ( Figures 1 View Figure 1 (h,i), 2(e,f) and 3(b – d))....................................................................................................................................................... 2
- Parameres not separated into dorsomedial and ventrolateral lobes ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (c – e))... ................................................................................................................................ Aegidinus cornutus
2. Phallobase with ventroapical plate ( Figures 1 View Figure 1 (g), 3(c) and 4(d)) ......................................... 3
- Phallobase without ventroapical plate ( Figures 2 View Figure 2 (d), 4(h) and 5(d)).............................. 6
3. Parameres symmetrical .......................................................................................................................... 4
- Parameres asymmetrical .................................................................................................................... 5
4. Ventrolateral lobe of paramere with subapical tooth ( Colby 2009, fig. 55)........................ ............................................................................................................................... Aegidinus howdenorum
- Ventrolateral lobe of paramere without subapical tooth ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 (h)).............................. ............................................................................................................................ Aegidinus guianensis
5. Parameres longer, more asymmetrical ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 (b,c)); ventroapical plate of phallobase longer than wide ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 (d)); protibia without medioapical tooth.......................................... .......................................................................................................................... Aegidinus noriegai sp. nov.
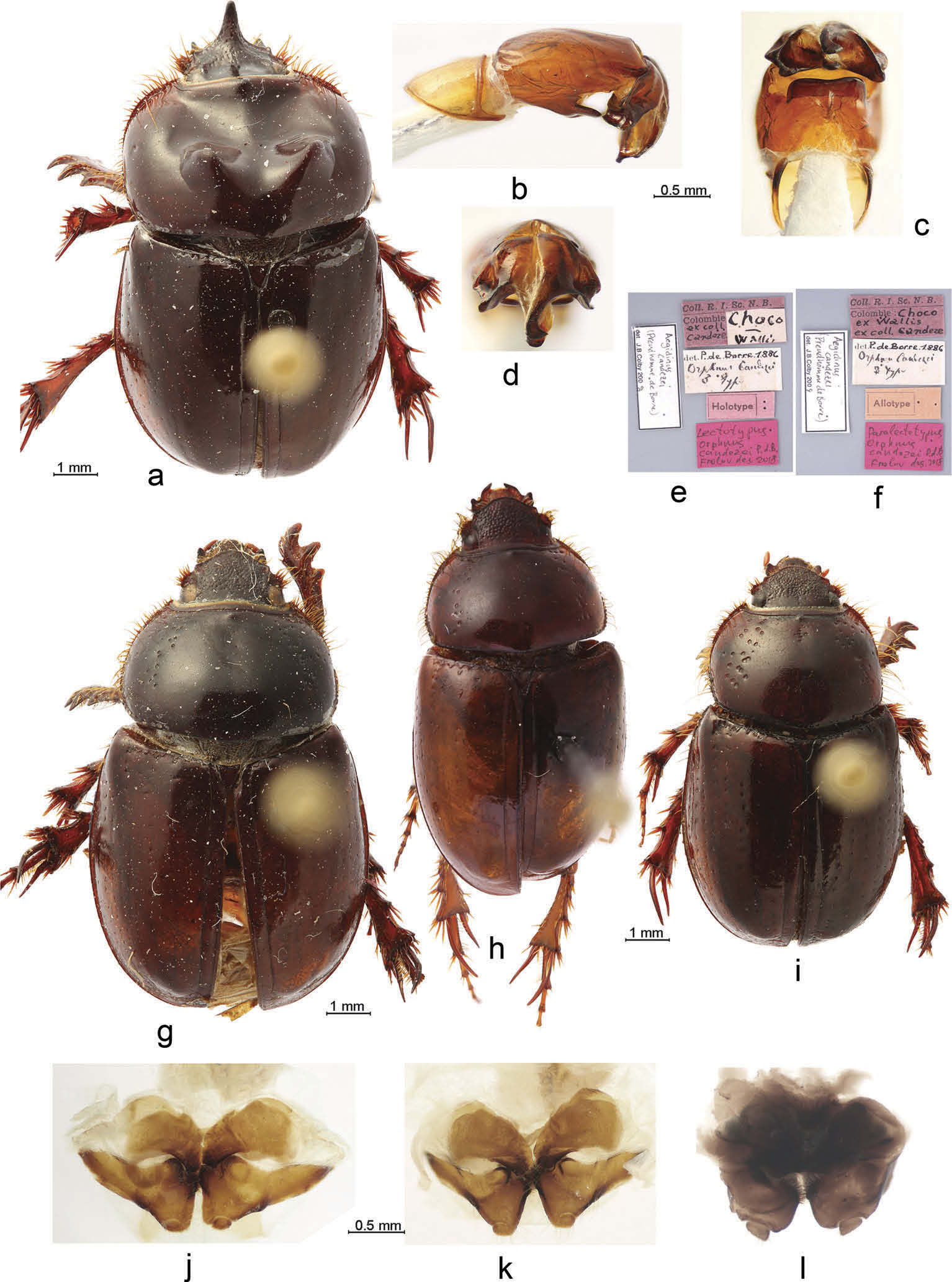
- Parameres shorter, less asymmetrical ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (b,d)); ventroapical plate of phallobase wider than long ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (c)); protibia with medioapical tooth Aegidinus candezei
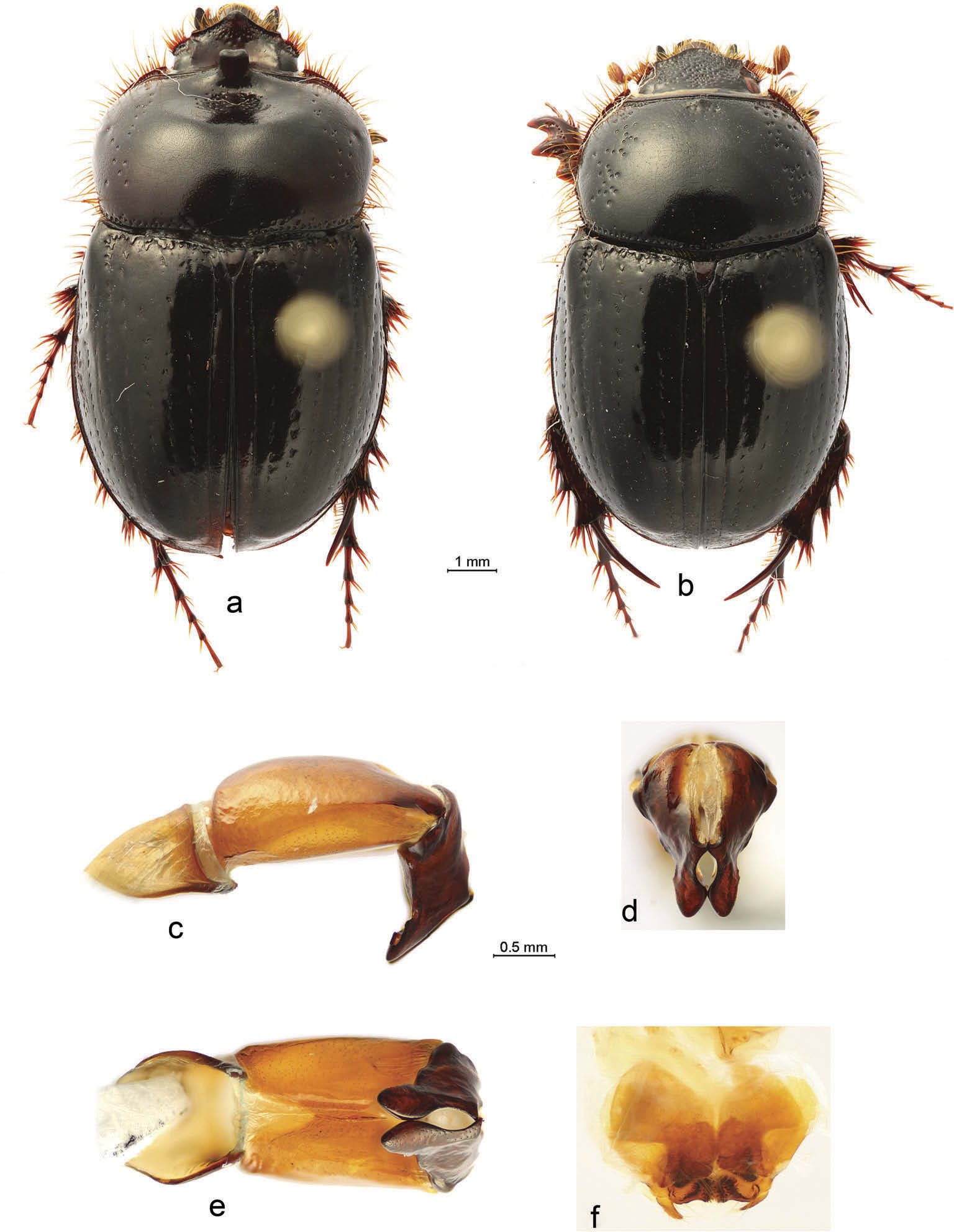
6. Mediobasal margins of dorsomedial lobes of parameres feebly sclerotised, membranous ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (e)); protibia with medioapical tooth...................................................................... 7
- Mediobasal margins of dorsomedial lobes of parameres strongly sclerotised (4G, 5E); protibia without medioapical tooth ............................................................................................. 9
7. Ventrolateral lobes of parameres long and slender (in lateral view), noticeably longer than dorsomedial lobes ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (f)).......................................... .......................................... steinheili
- Ventrolateral lobes of parameres triangular and obtuse in lateral view, not longer than dorsomedial lobes ..................................................................................................................... 8
8. Ventrolateral lobes of parameres as long as dorsomedial lobes...... Aegidinus petrovi
- Ventrolateral lobes of parameres noticeably shorter than dorsomedial lobes............... ............................................................................................................... Aegidinus teamscaraborum 9. Dorsal sides of parameres strongly overlapping and separated by slit ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 (f), arrowed).......................................................... .......................................................... Aegidinus simulatus - Dorsal sides of parameres less overlapping and not separated by slit ( Figure 5 View Figure 5 (f)) 10
10. Dorsal processes of parameres carina shaped ( Figure 5 View Figure 5 (e), arrowed)................................. ........................................................................................................................... Aegidinus colbyae sp. nov.
- Dorsal processes of parameres tooth or spur shaped........................................................ 11
11. Dorsal processes of parameres long, spur shaped........... ........... Aegidinus brasiliensis
- Dorsal processes of parameres short, tooth shaped............ ............ Aegidinus howeae
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Orphninae |