Streblocera (Eutanycerus) trangana Long & Pham, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4767.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:91221D05-77DA-4883-A301-96607B86302C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3797092 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/960887D4-6935-FF8F-FF06-F126FDFE1AD1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Streblocera (Eutanycerus) trangana Long & Pham |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Streblocera (Eutanycerus) trangana Long & Pham , sp. n.
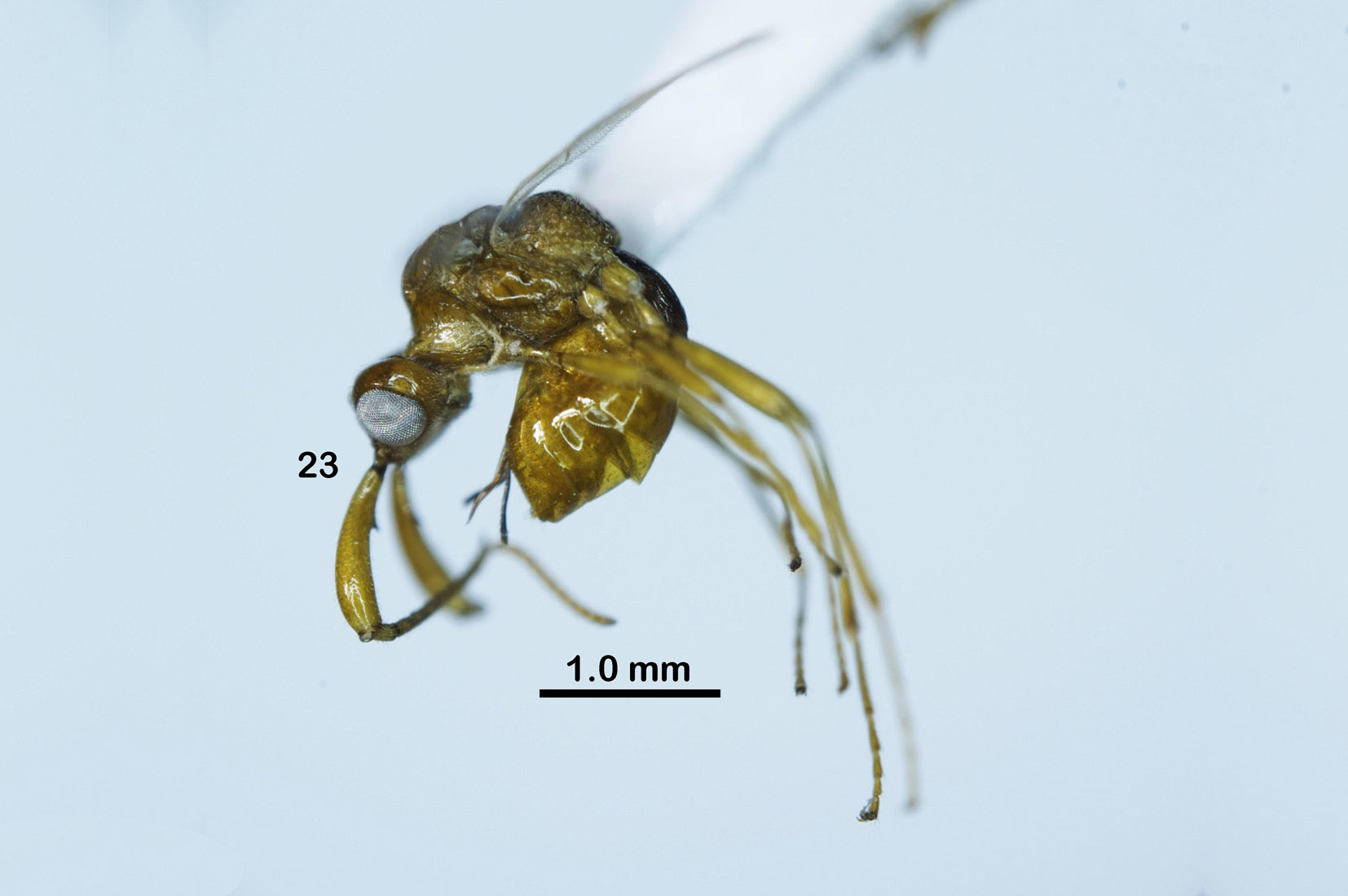
( Figs 23–33 View FIGURE 23 View FIGURES 24–33 )
Material examined. Holotype, ♀, “Euph. 347 ” ( IEBR), N Vietnam: Ninh Binh, Trang An, Den Tran, limestone forest, light trap, 11.vi.2018, Pham, T.N . Paratype 1 ♀, “Euph. 348 ” ( IEBR), locality as holotype.
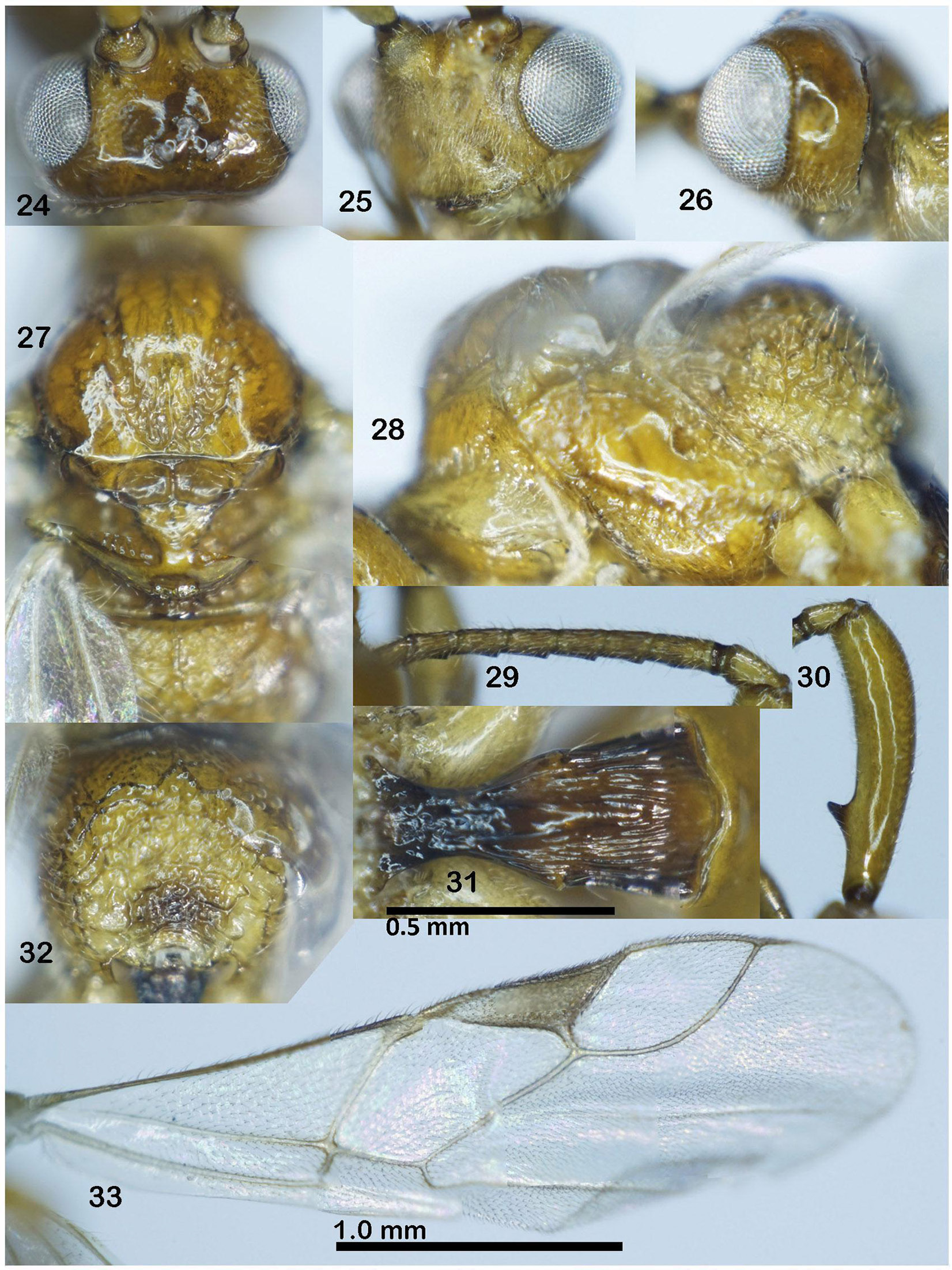
Diagnosis. Antenna with 19 antennomeres; scapus robust, with tooth-shaped horn in basal 0.3 of scapus ( Fig. 30 View FIGURES 24–33 ); length of scapus 4.7 × its maximum width, and 1.7 × of head height (in dorsal view); second-seventh flagellomeres serrate ventrally; tentorial pits below lower level of eyes ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 24–33 ); malar space 1.4 × as long as basal width of mandible; temple wide, in lateral view, transverse diameter of eye 2.3 × temple; mesosoma 1.6 × as long as its height; propodeum distinctly convex anteriorly higher upper level of scutellum; propodeum largely rugose; first metasomal indistinctly narrowed behind spiracle, 2.0 × as long as its apical width; first tergite almost smooth medially and apically, rugose basally, striate laterally and subapically ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 24–33 ).
Description. Holotype, ♀, body length 3.3 mm, fore wing length 2.9 mm, ovipositor sheath 0.4 mm ( Fig. 23 View FIGURE 23 ).
Head. Antenna with 19 antennomeres; scapus robust, length of scapus 4.7 × its maximum width (42: 9); with tooth-shaped horn in basal 0.3 of scapus (14: 42); scapus 1.7 × of head height (42: 25); third antennomere 1.4 × fourth (7: 5); second-seventh flagellomeres serrate ventrally ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 24–33 ); length from eighth flagellomere to apex of antenna 0.9 × scapus (37: 42); in dorsal view, temple roundly narrowed behind eye; width of head 1.6 × its median length (39: 25), 1.5 × width of mesoscutum (without tegulae) (39: 26); ocelli small, POL: OD: OOL = 5: 2: 8 ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 24–33 ); in lateral view, transverse diameter of eye 2.3 × temple (14: 6); length of eye 1.75 × as long as broad (14: 8); in frontal view, diameter of antennal socket 2.0 × distance between sockets (8: 4); face width subequal to length of face and clypeus combined (20: 21), and 1.3 × height of eye (20: 15); clypeus margin straight; malar space 1.4 × as long as basal width of mandible (7: 5), and 0.5 × as long as eye height (7: 15); distance between tentorial pits 1.3 × distance from pit to eye margin (8: 6); face setose, rugo-punctate ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 24–33 ); frons and vertex sparsely punctate ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 24–33 ); temple smooth ( Fig. 26 View FIGURES 24–33 ).
Mesosoma. Mesosoma highly convex, length of mesosoma 1.6 × as long as its height (55: 34) ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 24–33 ); notauli wide, sparsely crenulated anteriorly, rugose posteriorly, fused with largely rugose area of mesoscutum close to scutellar sulcus ( Fig. 27 View FIGURES 24–33 ); prescutellar sulcus rather wide, smooth, with one carina, and 0.6 × as long as scutellum (4: 7) ( Fig. 27 View FIGURES 24–33 ); mesoscutum and scutellum almost smooth, with finely scattered punctures; subalar depression rugose; pronotal side almost smooth ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 24–33 ); precoxal sulcus wide, sparsely crenulated ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 24–33 ); mesopleuron smooth medially; metapleuron rugose; propodeum with short basal carina, coarsely rugose entirely ( Fig. 32 View FIGURES 24–33 ).
Wings. Length of fore wing 2.7 × its width (118: 43); length of pterostigma 3.4 × its width (27: 8), and 1.6 × vein 1-R1 (27: 17) ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 24–33 ); vein r arising distinctly behind middle of pterostigma, and 0.1 × as long as width of pterostigma (3: 27), and 0.2 × vein 1-R1 (3: 17); vein 1-CU1 short and thick, near quadrate ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 24–33 ); vein cu-a 0.33 × vein 2-CU1 (4: 12); length of hind wing 4.1 × its width (90: 22); vein 1-M: 1r-m: 2-SC+R = 2: 6: 5.
Legs. Length of hind femur, tibia and basitarsus 6.2, 12.5 and 10.0 × as long as their width, respectively; hind basitarsus 0.4 × hind tibia (20: 50); hind basitarsus 2.85 × second-fifth tarsus (20: 27); fourth hind tarsus 0.8 × fifth tarsus without pretarsus (5: 6).
Metasoma. Length of first tergite 2.0 × its apical width (30: 15); apical width of first tergite 3.0 × its minimum width (15: 5); ovipositor sheath 0.2 × fore wing (19: 118), and 6.3 × first tergite (19: 30); first tergite almost smooth medially and apically, rugose basally, striate laterally and subapically ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 24–33 ); ovipositor sheath 0.1 × as long as fore wing; ovipositor sinuate.
Colour. Body yellow, except first metasomal tergite and ovipositor sheath yellowish-brown; eyes silver-grey; wing veins pale yellow; wing membrane hyaline.
Male. Unknown.
Host: Unknown.
Etymology. Named after type locality, Trang An Scenic Landscape Complex, Ninh Binh Province, Northern Vietnam.
Variation. Paratype, female, body length 3.1 mm, fore wing length 2.6 mm; ovipositor sheath 0.4 mm.
Distribution. N Vietnam: Ninh Binh.
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |