Chironomus (Chironomus) acidophilus Keyl, 1960
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3981.2.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7BE7922E-5340-4F5C-81B3-A31178E5A1C0 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5587270 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8C3C87D0-FF87-5422-12E5-58F05C2FFCBC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chironomus (Chironomus) acidophilus Keyl, 1960 |
| status |
|
Chironomus (Chironomus) acidophilus Keyl, 1960 View in CoL
( Figs 2–36 View FIGURES 2 – 9 View FIGURES 10 – 19 View FIGURES 20 – 29 View FIGURES 30 – 36 )
Chironomus meigeni Kieffer sensu Thienemann & Strenzke (1951: 8, fig. 1) View in CoL —misidentification. Chironomus acidophilus Keyl, 1960: 191 View in CoL ; Webb & Scholl (1990: 1, fig. 1 A, B, E, F, fig. 2 A, B, fig. 4 A, fig. 5 A, C, E, fig. 6 A, C, E, fig. 7 A), Wülker (1999: 431); Martin 2015b.
Material. Male, pupa, larva, Russia, Kamchatka Peninsula, Kronotsky Reserve, the Uzon volcanic caldera, Vosmerka Lake, 13.VIII.2010, leg. L. Lobkova (rearing); female, pupa, larva, the same location, 17–24.VII.2009, leg. L. Lobkova (rearing); female, pupa, larva, the same location, 03–13.VIII.2010, leg. L. Lobkova (rearing); male, pupa, larva, the same location, 07.VIII.2011, leg. L. Lobkova (rearing); male, pupa, larva, the same location, 08.VIII.2012, leg. L. Lobkova (rearing); male, pupa, larva, the same location, 16.VI.2013, leg. L. Lobkova (rearing); larvae, the same location, 05–09.VIII.2013, leg. L. Lobkova (for karyological research).
Diagnostic characters. The imago males of C. acidophilus Keyl 4.5–6.0 mm long, wing length 2.7–3.0 mm; flagellum dark brown, AR 2.81–3.06; ground color of thorax and scutellum yellowish, mesonotal stripes and postnotum dark brown, Aps 1 (rarely 0), Ac 15–21, Dc 18–29, Pa 4–6, Scts 27–42, Sq 12–26; abdomen and legs brown or dark brown, sternite II with 12–14 median and 0–4 lateral setae, LRP1 1.33–1.51, BRP1 2.78–3.89; tergite IX with 9–14 median setae, anal point expanded in the apical 1/3, sometimes widest at about middle, superior volsella S– type, gonostylus widest at proximal 1/3. The pupa length 5.8–7.5 mm; tergite VI with X-shaped shagreen, tergite VII with two patches of shagreen in proximal part, tergite VIII with two bands of shagreen laterally; pleura of segment III with several posterolateral spines, pleura of segment IV with longitudinal rows of spinules; paratergites V–VI with a band of spinules; hook row with 53–77 hooks; conjunctives IV/V, V/VI and VI– VII with small spinules, sometimes on conjunctives IV–V spinules absent; sternites II–IV covered with median shagreen, sternite V in distal part with median path of shagreen; anal comb with 2–4 teeth; anal lobe with 70–87 lamelliform setae. The larva has a yellowish brown head, AR 1.63–1.95, L1 107–144 µm, L 2 27–37 µm, L1/ W1 4.2 –4.5, L1/L2 3.5–4.7, blade 61–65 µm long, reached to the segment 5; 3rd mandibular tooth usually brown, rarely pale, type mandible IIB/IIC, anterior margin of the base maxilla slightly convex, type of mentum by the characters of the median trifid tooth—III/IV; type of mentum by the degree of development of the 4th lateral teeth—I/II, ventromental plate 173–184 µm wide, distance between ventromental plates 58–61 µm, ventromental plates with 40–45 striae, VmPR 0.47–0.56, VmPSR 1.47–1.61, lateral tubules on segment VII absent; ventral tubules present.
Male (n=4). Total length 4.5–6.0 mm; wing length 2.7–3.0 mm. Total length / wing length 1.5–2.2.
Coloration. Antenna dark brown; ground color of thorax and scutellum yellowish; mesonotal stripes and postnotum dark brown; abdomen and legs brown or dark brown.
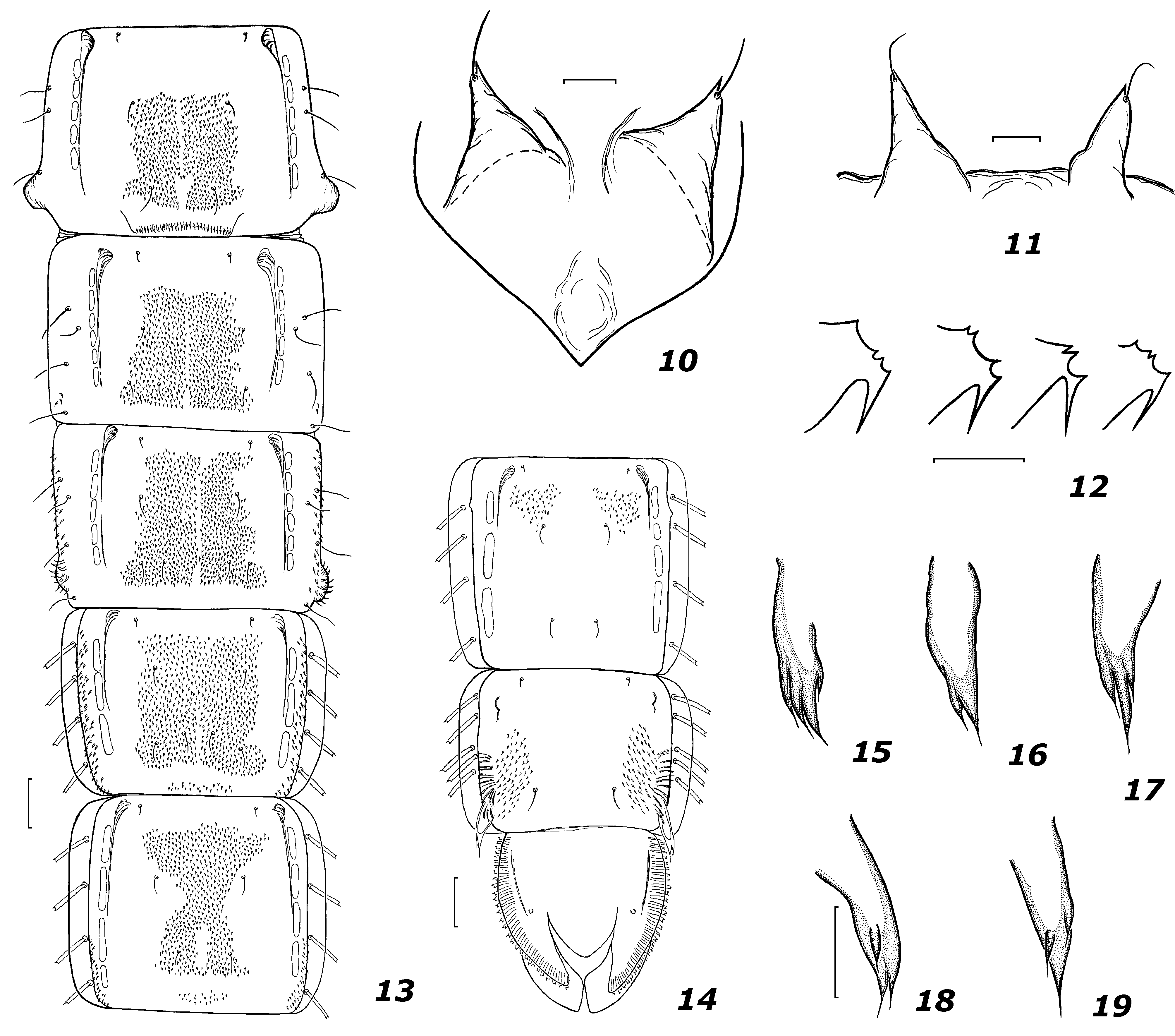
Head. Head width 624–640 µm. Height of eyes 376–408 µm. Frontal tubercles finger-shaped, length 24–34 µm, and width 10–17 µm ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 2 – 9 ). Antenna 1281–1449 µm long. Ultimate flagellomere 945–1092 µm long. AR 2.81–3.06. Verticals 25–28. Clypeus with 35–38 setae. Cibarial pump 136–143 µm long, 95–99 µm wide. Maxillary palp 736–800 µm long, lengths of last 4 palpomeres (in µm): 56–72; 216–240; 192–208; 264–296. CP 0.80–0.84; Al/Pl 1.81–1.91.
Thorax. Antepronotals 1 (rarely 0); acrostichals 15–21; dorsocentrals 18–29; prealars 4–6; supraalars 1. Scutellum with 27–42 setae.
Wing. Length 2.7–3.0 mm, width 0.60–0.68 mm. Veins R, R1 with 64–83 setae, R4+5 with 24–42 setae. Squama with 12–26 setae; brachiolum with 2–3 setae. VR 1.05.
Legs. Spurs of middle tibia 27 µm, of hind tibia 34 µm long. TiR 2.04–2.33. Lengths and proportions of legs as in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Abdomen. Sternite II with 12–14 median and 0–4 lateral setae.
Hypopygium ( Figs 3–9 View FIGURES 2 – 9 ). Tergite IX with 9–14 median setae. Laterosternite IX with 4–5 setae. Anal point 92– 102 µm long, 24–27 µm wide, expanded in the apical 1/3, sometimes widest at about middle (depends on the position of hypopygium). Transverse sternapodeme 102–136 µm long, without oral projections. Phallapodeme 170–204 µm long. Gonocoxite 197–204 µm long, with 4 inner setae. Total length of superior volsella (S– type) 85 µm; height of apical finger-shaped part 58–68 µm, width—27–44 µm, sometimes with 1–2 setae; base 17–27 µm high, 58–68 µm wide, with 5–8 basal setae and with cover microtrichia ( Figs 5–9 View FIGURES 2 – 9 ). Inferior volsella 160–170 µm long, with 12 strong dorsal and 14–16 weak ventral setae. Gonostylus 187–204 µm long, 37–48 µm wide, widest at proximal 1/3, with 1 apical seta and 4–6 subapical inner setae. GsR 3.0–5.0. HR 1.00–1.09.
Pupa (n =7, males). Total length 5.8–7.5 mm.
Cephalothorax. Cephalic tubercles conical 92–119 µm long, 65–119 µm wide; frontal setae 41–51 µm long ( Figs 10–11 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ). Base of thoracic horn 102–133 long µm, 41–54 µm wide. Thorax granulose. Prealar tubercle absent. Pc1 and Pc2 50 µm long; MAps 102–136 µm long; LAps absent; Dc1 34–92 µm long, Dc2 85–119 µm long, Dc3 51– 102 µm long, Dc4 34–58 µm long; distance between setae Dc1–Dc2 51–92 µm, Dc3–Dc4 41–61 µm, Dc2–Dc3 68– 119 µm. Wing sheath length 313–340 µm, width 78–85 µm.
Abdomen ( Figs 12–19 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ) length 5.0– 6.5 mm. Tergites II–V covered by square shagreen; tergite VI with Xshaped shagreen; tergite VII with two patches of shagreen in proximal part; tergite VIII with two bands of shagreen laterally. Pleura of segment III with several posterolateral spines, pleura of segment IV with longitudinal rows of spinules. Paratergites V–VI with a band of spinules ( Figs 13–14 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ). Anal segment without shagreen, but in posterior part granulose. Hook row with 53–77 hooks; tips of median hooks with 3–5 small teeth ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ). Conjunctives IV/ V, V/VI and VI–VII with small spinules, sometimes on conjunctives IV–V spinules absent. Sternites II–IV covered with median shagreen, sternite V in distal part with median path of shagreen. Segment I with anterior pedes spurii B. Dark brown anal comb of segment VIII with 2–4 elongated teeth, dorsal spines absent ( Figs 15–19 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ). Segment II with 3 L setae, III–IV each with 4 L setae (1 seta always situated intersegmentally), and V–VII each with 4 LS setae, VIII with 4–5 LS setae. Anal lobe with 70–87 lamelliform setae; length of anal lobe 464–496 µm, width 432–560 µm. ALR 0.87–1.07.
Fourth instar larva (n=5).
Coloration. Body blood red. Head capsule uniformly yellowish brown; gular region and frontoclypeus unpigmented.
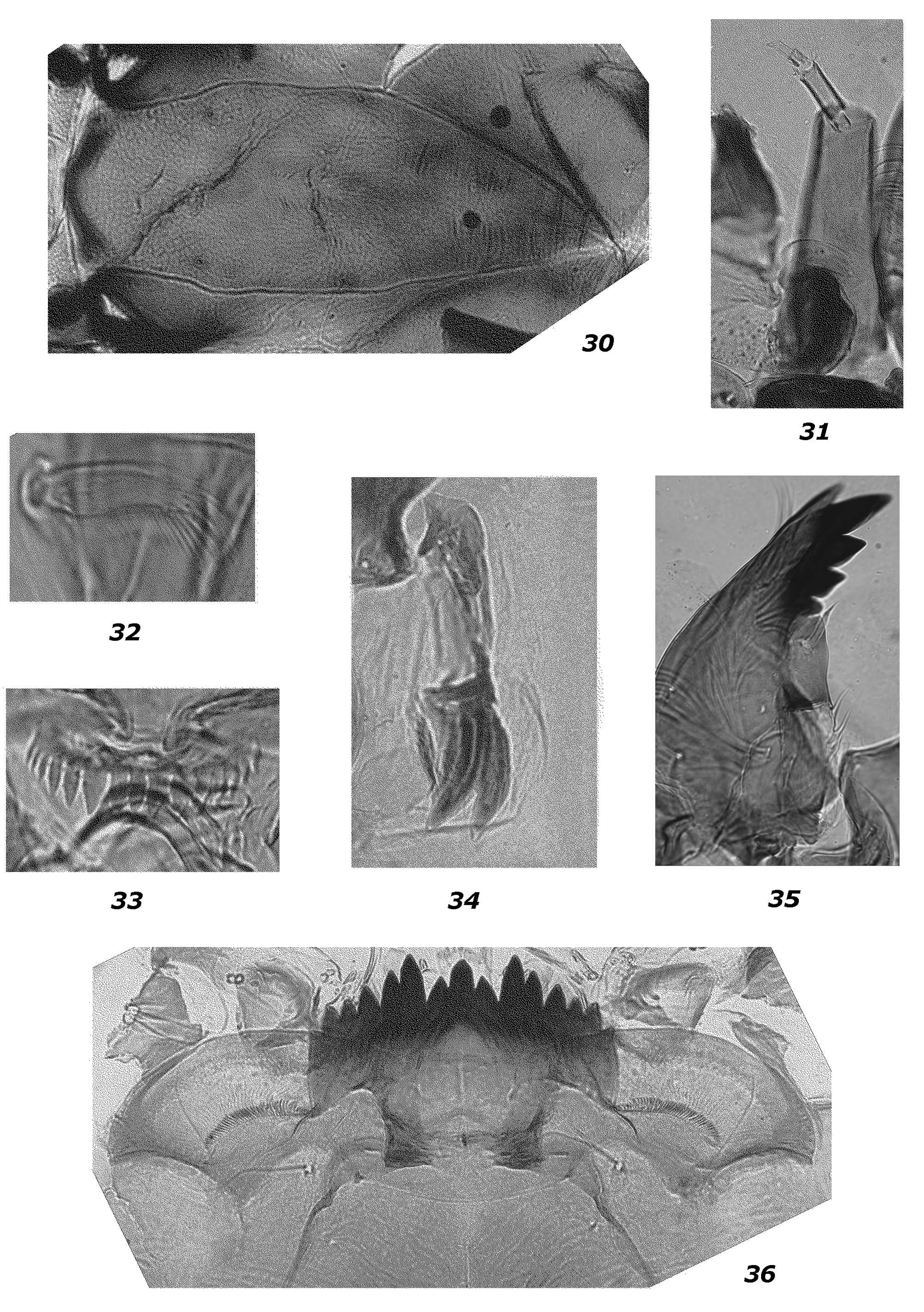
Head ( Figs 20–29 View FIGURES 20 – 29 , 30–36 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ) yellowish brown, length 0.65 mm, width 0.50 mm, cephalic index (W/L) 0.77. Frontoclypeal apotome 536 µm long, 168–184 µm wide ( Fig. 30 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ). Distance between setae S1– S1 75 –85 µm, S2–S2 119–129 µm, S3–S3 133–143 µm, S4–S4 126–143 µm, S5–S5 156–167 µm. Antenna 192–207 µm ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 20 – 29 , 31 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ), length of each segment (in µm): 119–133; 31–37; 8.5–10.2; 10.9–13.6; 8.5. AR 1.63–1.95. Maximal width of basal segment 34–40.8 µm. Ring organ distribute in the proximal 2/3 basal segment; distance from ring organ to base of antenna 44–61 µm; ROR 2.1–2.9. Blade 61–65 µm long, reached to the segment 5; accessory blade 13.6 µm. S I 31–44 µm long ( Fig. 32 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ), S II 68 µm long, S III 14–17 µm long, S IV 11.9–13.6 µm long. Labral chaetae consist of 3 pairs of well-developed pectinated chaetae and 2 pairs of shorter chaetae. Pecten epipharyngis 51–61 µm long, with 14–18 teeth ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ). Premandible 136–154 µm long, with 2 teeth about equally long, inner tooth about 1.2– 1.5 times wider than the outer; premandibular seta simple 24–27 µm long ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 20 – 29 , 34 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ). Mandible (length 221–145 µm, width 112–136 µm) with 2 yellowish dorsal teeth length (14–17 µm and 10–20 µm respectively), dark brown apical (length 31–34 µm) and 3 inner teeth; 3rd tooth usually brown, rarely pale ( Figs 22–26 View FIGURES 20 – 29 , 35 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ). Type mandible IIB (tooth partly free on lower margin and some degree of pigmentation present on 3rd tooth) or IIC (3td tooth as dark as other teeth). Seta subdentalis 27 µm long. Pecten mandiblaris with 10–14 setae. Mola with 3–4 spines. Maxillary palp 27–34 µm long, 24–27 µm wide ( Fig. 27 View FIGURES 20 – 29 ). Anterior margin of the base maxilla slightly convex ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 20 – 29 ). Mentum 177–180 µm wide, central tooth conical 17–18.7 µm wide, median trifid tooth 42.5–47.6 µm wide, distance between first lateral teeth 71.4–78.2 µm, distance between second lateral teeth 92–102 µm; distance between the top of first lateral teeth 61.2–64.6 µm. Type of mentum by the characters of the median trifid tooth— III/IV; type of mentum by the degree of development of the 4th lateral teeth—I/II. Ventromental plate 173.4–183.6 µm wide and 85–98.6 µm height ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 20 – 29 , 36 View FIGURES 30 – 36 ). Distance between ventromental plates 57.8–61.2 µm. Ventromental plates with 40–45 striae. VmPR 0.47–0.56. VmPSR 1.47–1.61.
Body. Lateral tubules absent on abdominal segment VII; ventral tubules present on segment VIII (thummi type). Procercus 32–64 µm height and 40–48 µm wide.
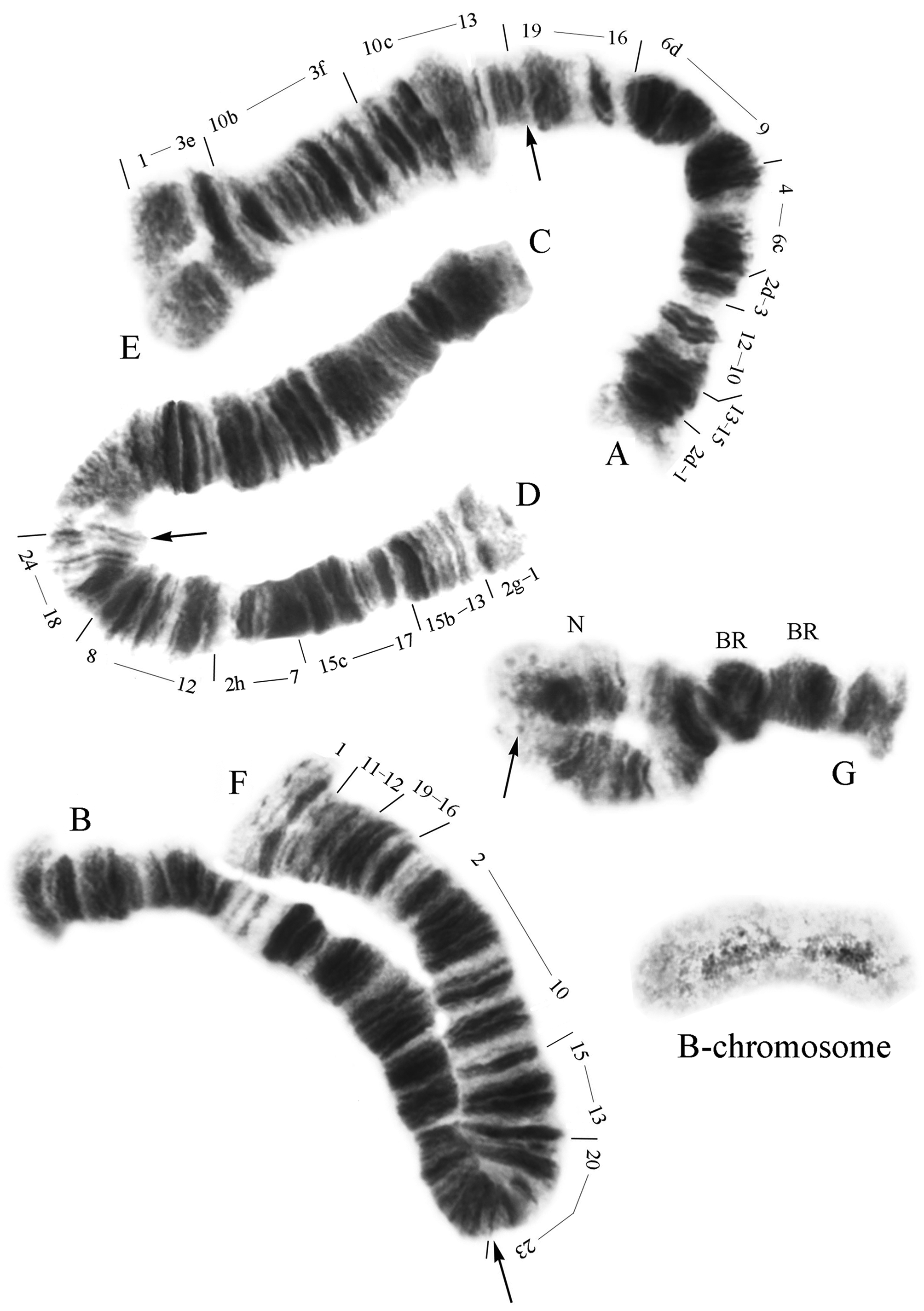
Karyotype. The karyotype is 2n=8, 2n=8+B ( Fig. 37 View FIGURE 37 ). The chromosome arm combination is AE, CD, BF, G (pseudothummi-cytocomplex). Chromosomes CD and BF are metacentric, AE is submetacentric, G is acrocentric. The centromeric bands are thin and do not differ visually from other bands in the chromosome; these bands were identified in C. acidophilus by comparison with C. pseudothummi . The karyotype is usually characterized by one permanent nucleolus (N) and two Balbiani rings (BR) in chromosome IV. In addition, some larvae revealed a puffed region in the near-telomere part of arm E; the end of the chromosome was fan-shaped. This puffed region, and also the segment of chromosome IV between the N and the dark heterochromatin band are almost always asynaptic. B-chromosomes are present sometimes. In the banding pattern, C. acidophilus most closely resembles Chironomus sp. Ya4 and C. pseudothummi .
Since arms B, C, D were mapped by Devai et al. (1989) much later than the original description of the karyotype was made ( Keyl 1962), and arm G were not mapped, we estimated only the degree of their polymorphism.
TABLE 1. Lengths (in µm) and proportion of legs C. acidophilus Keyl.
| P | fe | ti | ta1 | ta2 | ta3 | ta4 | ta5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1176–1302 | 1029–1218 | 1512–1743 | 777–945 | 630–714 | 441–567 | 252–315 |
| P2 | 1260–1386 | 1155–1302 | 693–756 | 420–441 | 315–336 | 210–231 | 147–168 |
| P3 | 1428–1575 | 1428–1617 | 1008–1134 | 588–693 | 441–525 | 294–315 | 189–210 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Chironomus (Chironomus) acidophilus Keyl, 1960
| Orel, Oksana V., Lobkova, Ludmila E., Zhirov, Sergey V. & Petrova, Ninel A. 2015 |
Chironomus acidophilus
| Keyl 1960: 191 |
Chironomus meigeni
| Kieffer sensu Thienemann & Strenzke 1951 |