Clubiona lamellaris, Zhang & Yu & Zhong, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4415.2.10 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:10DC7DC7-0619-49C8-8FD8-E0BB27990626 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5963073 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8A1F8797-CE31-EE55-8EF5-FA183D96FB8F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Clubiona lamellaris |
| status |
sp. nov. |
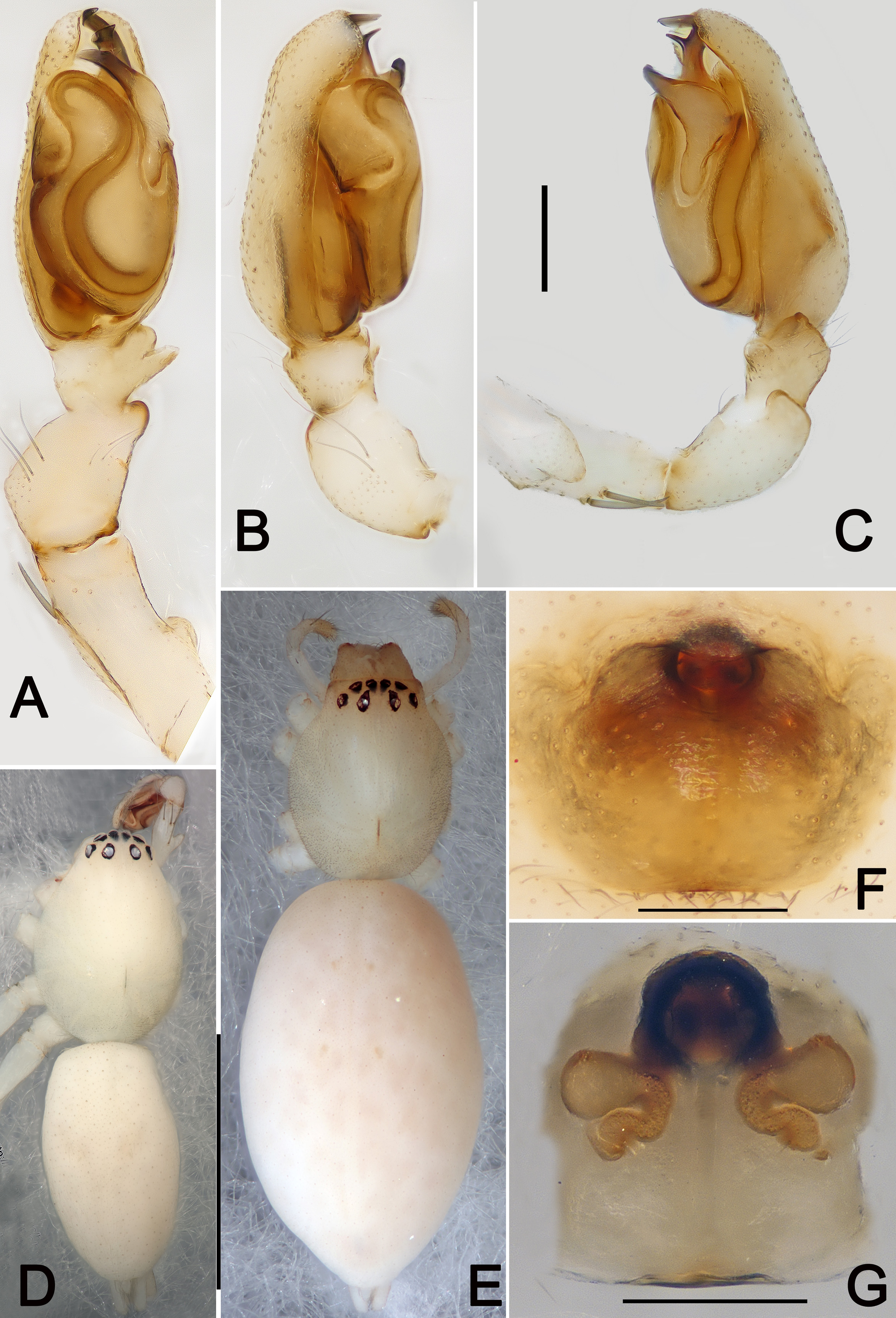
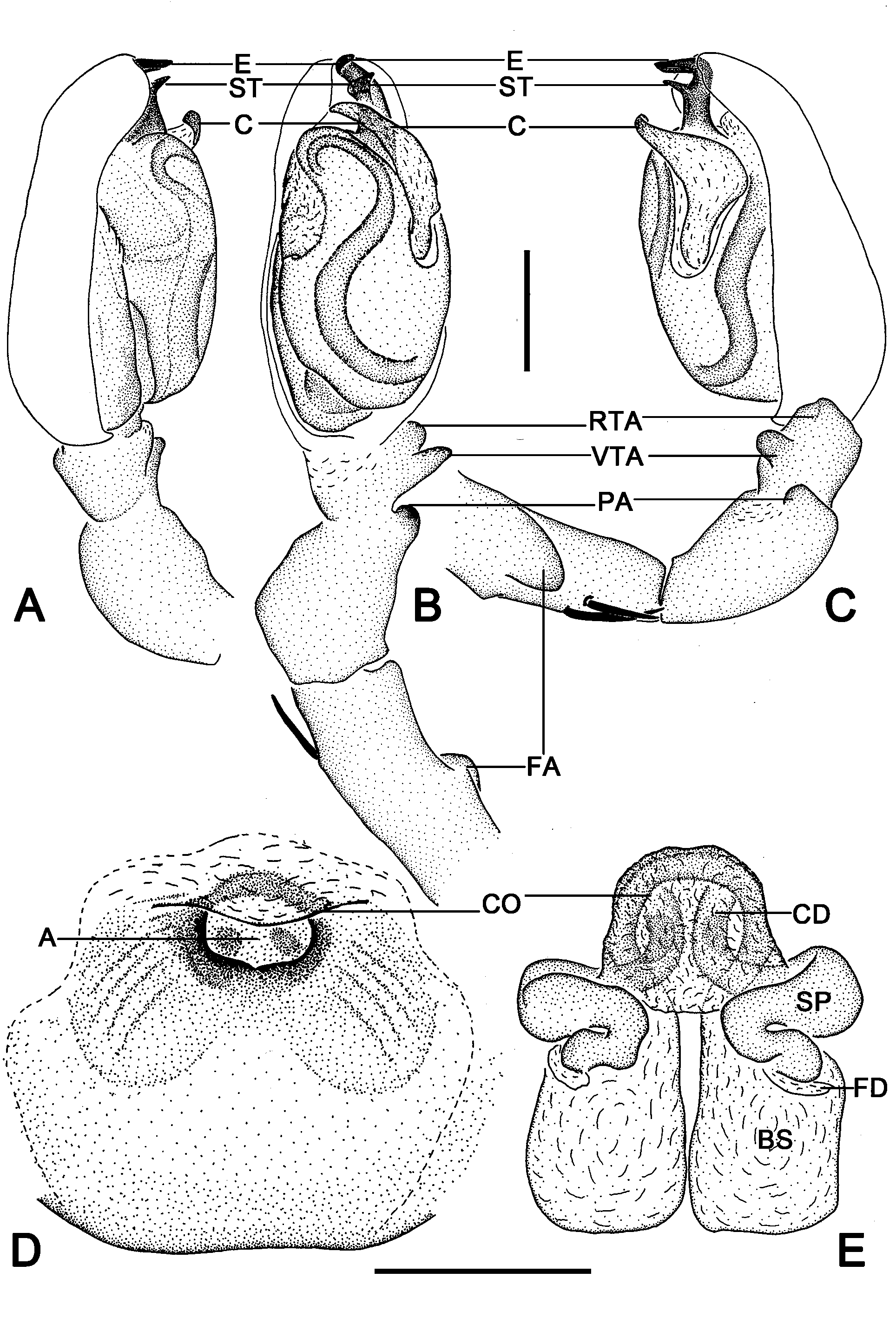
Clubiona lamellaris View in CoL sp. nov. ( Figs. 3–5 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURES 4 View FIGURE 5 )
Type material. Holotype ♂ (MGEU-CLU-16-027) from Gaofeng Villiage , Siping Township, Yangxi Town (29°8'15.40"N, 107°34'12.14"E, 1790 m), Dashahe Nature Reserve, Guizhou Province, China, 4 July 2016, Cong Leng and Changjiang Li leg. GoogleMaps ; Paratypes: 1 ♂, 3 ♀ (MGEU-CLU-16-028~031), same data as holotype GoogleMaps
Etymology. The species epithet is taken from the Latin adjective “lamellae” and refers to the sheet-shaped subapical tooth of embolus.
Diagnosis. Males of Clubiona lamellaris sp. nov. resemble those of Clubiona applanata Liu, Yan, Griswold & Ubick, 2007 ( Liu et al., 2007: figs 1–5) in having similar RTA and VTA, strong embolus with a curved tip and enlarged bulb with S-shaped sperm duct, but differ by: (1) body almost pure white ( Figs 3D–E View FIGURE 3 ) (predominantly yellow in C. applanata ); (2) embolus with subapical tooth ( Figs 4A–C View FIGURES 4 ); (3) palpal patella and femur with apophyses ( Figs 4B–C View FIGURES 4 ); (4) conductor with dagger-shaped tip extending to prolateral side of embolus ( Figs 4A–C View FIGURES 4 ) (relatively short tip in C. applanata ); Females also resemble those of Clubiona applanata in having a subovate atrium but can be recognized by the atrium nearly peach-shaped ( Fig. 4D View FIGURES 4 ) (upright oblate in C. applanata ), brim-shaped anterior atrial membrane ( Fig. 4D View FIGURES 4 ) (thick membrane surrounding the atrium in C. applanata ); spermathecae subtriangular ( Fig. 4E View FIGURES 4 ) (globular in C. applanata ).
Description. Male (holotype): Total length 3.51. prosoma 1.62 long, 1.22 wide; opisthosoma 1.93 long, 1.07 wide. Prosoma ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ). Ovoid in dorsal view, ocular region distinctly narrowed, widest between coxae II and III; in profile highest just behind longitudinal fovea; integument smooth, clothed with short fine hairs. Carapace nearly pure white, without distinctive color pattern; fovea dark. Chelicerae white except brown fang, promarginal and retromarginal both with 4 teeth. Labium and endites white. Sternum oval, white. Eyes. AER slightly recurved, PER slightly wider than AER and procurved when seen from above. AME dark, other eyes light; with black rings. Eye sizes and interdistances: AME 0.05, ALE 0.10, PME 0.09, PLE 0.06. AME–AME 0.04, AME–ALE 0.04, PME–PME 0.13, PME–PLE 0.09, MOQL 0.22, MOQA 0.04, MOQP 0.31. Legs. White, without distinct color markings. Leg formula: IV, II, I, III; leg measurements: I 3.64 (1.03, 1.39, 0.69, 0.53), II 4.12 (1.23, 1.62, 0.71, 0.56), III 3.43 (1.15, 1.16, 0.82, 0.30), IV 5.02 (1.53, 1.62, 1.39, 0.48). Opisthosoma ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ). Elongate-oval, white, with inconspicuous anterior tufts of hairs, dorsum with two pairs of inconspicuous muscular depressions; venter white. Palp ( Figs 3A–C View FIGURE 3 , 4A–C View FIGURES 4 ). Femur with short, thick retrolateral apophysis originating proximally; patella twice longer than tibia, with blunt, round apophysis; tibia short, with two apophyses, VTA short with blunt, partly membranous tip, RTA broad, flat and triangular; genital bulb elongated, sperm duct S-shaped in venter view; subtegulum visible prolaterally; embolus strong, with a beak-shaped tip and a sheet-shaped subapical tooth, the embolic base situated retrolateral on the tegulum and toward prolaterally but the curved tip point retrolaterally; conductor originating from retrolateral side of tegulum, with a membranous, daggershaped distal part.
Female (paratype: MGEU-CLU-16-029): Total length 5.31. prosoma 1.65 long, 1.25 wide; opisthosoma 3.51 long, 1.93 wide. General color darker than in male ( Fig. 3E View FIGURE 3 ). Eye sizes and interdistances: AME 0.07, ALE 0.08, PME 0.08, PLE 0.06. AME–AME 0.03, AME–ALE 0.03, PME–PME 0.18, PME–PLE 0.12, MOQL 0.22, MOQA 0.20, MOQP 0.34. Leg formula: IV, II, I, III. Leg measurements: I 3.34 (0.97, 1.31, 0.63, 0.44), II 3.82 (1.16, 1.54; 0.64; 0.50), III 3.2 2 (0.94, 1.12, 0.73, 0.44), IV 4.84 (1.37, 1.63, 1.36, 0.48). Epigyne ( Figs 3F–G View FIGURE 3 , 4D–E View FIGURES 4 ). Epigynal plate slightly shorter than wide, margin not rebordered; atrium approximately peach-shaped, with brim-shaped membrane on anterior margin; copulatory openings small, located anteriorly on atrium. Copulatory ducts dark descending posteriorly to connect with spermathecae; spermathecae situated anteriorly, with subtriangular proximal part and tubular distal part; reniform bursae situated posteriorly, translucent, surface wrinkled and ribbed; fertilization ducts short, acicular.
Natural history. The holotype of C. lamellaris spec. nov. was obtained from foliage in bush close to a small stream in the center of the Dashahe Nature Reserve.
Distribution. Know only from the type locality, Dashahe Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |