Asellia arabica, Benda & Vallo & Reiter, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3161/150811011X624749 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4328280 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/87388827-1821-FFC9-CDFE-C316E7BD6AE8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Asellia arabica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Asellia arabica View in CoL View at ENA sp. nov.
Synonymy
Asellia tridens ( Geoffroy, 1813) View in CoL : Pockock, 1935: 442; Harrison, 1964: 98; Harrison, 1980: 390; Kingdon, 1990: 37; Harrison and Bates, 1991: 55.
Asellia tridens tridens ( Geoffroy, 1813) View in CoL : Harrison, 1957: 5; Kock, 1969: 129; Nader, 1990: 340; Al-Jumaily, 1998: 483.
Asellia patrizii De Beaux, 1931 View in CoL : Al-Jumaily, 2004: 60.
Type material
Holotype: adult ♂ ( NMP 92790 [S+A]), Hawf (Al Mahra Prov.), 14 October 2005, leg. P. Benda.
Paratypes (9): 3♂♂, 2♀♀ ( NMP 92791 , 92792– 92794 View Materials [S+A], 92789 [A]), Hawf (Al Mahra Prov.), 14 and 15 October 2005, leg. P. Benda ; – 2♂♂, 2♀♀ ( NMP 92795 , 92796 View Materials , 92798 View Materials [S+A], 92797 [A]), Damqawt (Al Mahra Prov.), 16 October 2005, leg. P. Benda.
Type locality
Republic of Yemen, Province of Al Mahra, oasis of Hawf (easternmost edge of the country), 16°39’N, 53°03’E, 410 m a.s.l.
Description and diagnosis
Small bat and medium-sized to small representative of the genus Asellia Gray, 1838 . It is in most
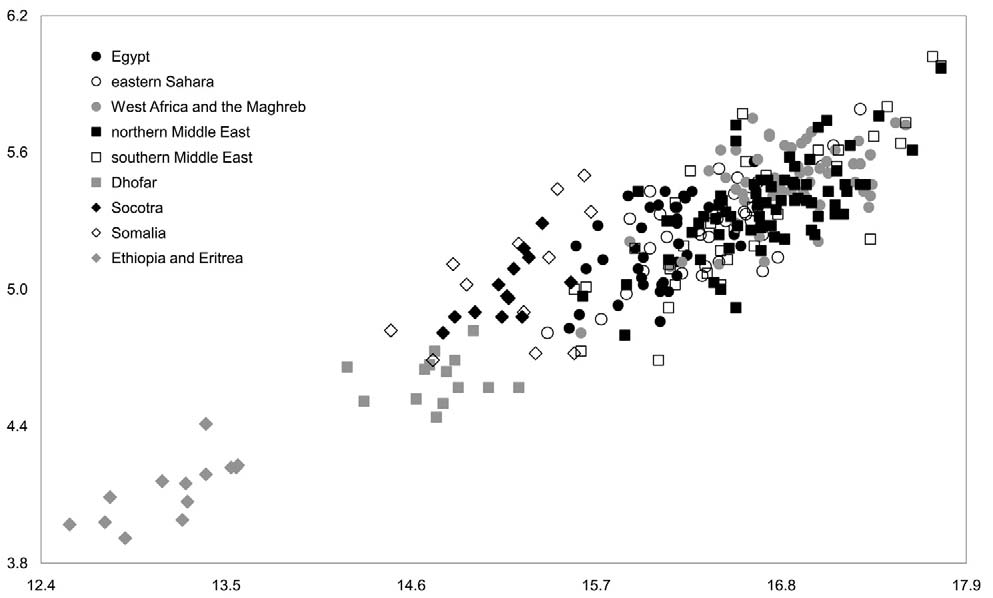
respects very similar to the other species of the genus, including the structure of the nose leaf (Fig. 11). In body and skull size, A. arabica sp. nov. clearly differs from both the largest and the smallest species of the genus, A. tridens ( Geoffroy, 1813) and A. patrizii De Beaux, 1931 , respectively, but it partly overlaps with A. italosomalica De Beaux, 1931 ( Table 1 View TABLE , Figs. 2 View FIG and 4 View FIG ). Forearm length 43.1–46.5 mm, condylocanine length of skull 14.2–15.3 mm, length of the upper tooth-row 5.7–6.1 mm. Asellia arabica sp. nov. has a relatively narrow skull (width across the zygomatic arches 8.7–9.3 mm; relative zygomatic width, LaZ/LCc, 0.589 –0.622) and a relatively narrow and short rostrum (width of rostrum across canines 4.4–4.8 mm; relative width of rostrum across canines, CC/LCc, 0.297 –0.324) in comparison to the other Asellia species; the skull and rostrum of A. arabica sp. nov. are, on average, the narrowest, and the rostrum is the shortest, relatively speaking. The braincase is low (height of braincase 4.7–5.1 mm; relative height of braincase, ANc/LCc, 0.320 –0.342) and the tympanic bullae are rather large (largest horizontal diameter of bulla 2.6–2.9 mm; relative size of bulla, LBT/LCc 0.181 –0.214).
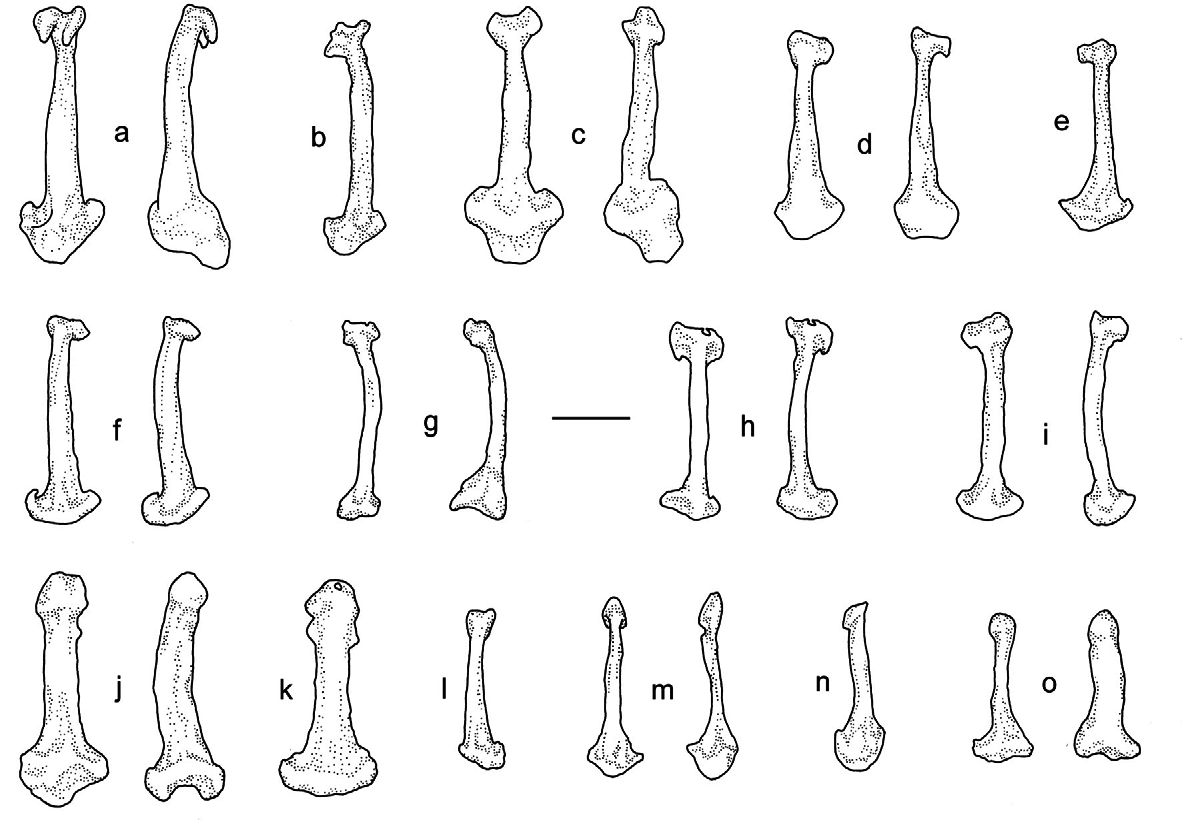
The baculum of A. arabica sp. nov. is a tiny bone, 1.0– 1.3 mm long, with a very narrow distal epiphysis, 0.1–0.2 mm wide (<18% of the baculum length) and a rather narrow proximal epiphysis that is 0.3–0.4 mm wide (<30% of the baculum length) ( Fig. 6 View FIG l–n).
The colouration of the dorsal pelage of A. arabica sp. nov. is beige or pale-brownish grey (Fig. 11) with yellowish or pale rusty tinges; the ventral pelage is somewhat paler than the dorsal colouration. The nose leaf is almost unpigmented to very pale brownish; often the anterior leaf is slightly pigmented while the posterior leaf and supplementary leaflets are unpigmented. The wing membranes are pale brownish-grey.
Dimensions of the holotype: see Table 3 View TABLE .
Genetics: Asellia arabica sp. nov. showed unique base positions within the mitochondrial gene for cytochrome b (1140 bp) at 24 sites: 486, 636, 681, 696, 750 (A→G), 201, 507 (C→A), 1092 (C→G), 145, 282, 492, 504, 690, 915, 958, 963, 1020, 1044 (C→T), 981, 1080, 1093 (T→C), 510, 717 (A/T→C), and 498 (G/T→C). At two sites, 324 and 609, uniquely different positions of G instead of A (A→G, A→A/G, and A→G/A) were present
in three known haplotypes (DF1, DF2, DF3; see Appendix II). Asellia arabica sp. nov. was found to share identical unique base positions within the gene for cytochrome b with A. tridens ( Geoffroy, 1813) at 88 sites: 18, 27, 105, 153, 237, 330, 357, 466, 582, 697, 709, 720, 807, 870, 933, 936, 945, 996, 1038, 1057, 1119 (A), 45, 57, 81, 84, 114, 165, 195, 204, 297, 315, 321, 329, 435, 438, 465, 477, 480, 519, 546, 564, 567, 589, 592, 618, 621, 624, 648, 687, 693, 699, 708, 713, 774, 789, 804, 831, 834, 840, 852, 858, 882, 888, 894, 916, 1126 (C), 129, 178, 372, 476, 591 (G), 66, 121, 126, 246, 285, 288, 345, 351, 399, 474, 528, 792, 897, 906, 999, 1077, and 1122 (T); and with A. italosomalica De Beaux, 1931 at 16 sites: 123, 864, 909, 984, 1023, 1116 (A), 174, 441, 447, 555, 663, 921, 1110 (C), 1017 (G), 684, and 828 (T).
Mitochondrial sequence of holotype and all examined paratypes (NMP 92789–92791, 92793, 92794, 92796–92798) — complete sequence of the mitochondrial gene for cytochrome b (GenBank Accession Number JF439015 View Materials ; haplotype DF1 — Appendix II), 5’ end: atg acc aac atc cga aaa tcc cac cca cta ttc aaa att atc aac gac tca ttc atc gac cta cct gcc ccc tca agc atc tcc tcc tga tga aac ttt ggc tca cta cta ggc gta tgc tta gct gtg caa atc cta aca gga tta ttc cta gcc ata cac tac aca tcc gac aca gcc acc gcc ttc tat tcc gtc aca cac atc tgc cga gac gtt aat tat ggc tga atc cta cgc tac ctt cat gcc aac gga gca tcc ata ttc ttc atc tgc ctt ttt ctt cat gta ggc cga gga att tac tac ggc tcc tac aca ttc aca gaa aca tga aac att ggt att att cta ctt ttc gcc gtc atg gca aca gcc ttc ata ggc tac gtc ctt cca tga gga caa ata tcc ttc tga gga gca aca gtc atc acc aac ctc ctc tca gcc atc cca tac atc gga act agc ctc gta gag tga gtt tga ggc ggc ttt tca gtc gac aaa gcc acc ctc act cga ttc ttc gcc ctc cac ttc ctc ctc cca ttc atc atc gca gcc ata gta ata gtc cac ctg cta ttc cta cat gaa acg ggc tca aac aac ccc aca gga atc ccg tca gac ata gac ata atc ccc ttc cac cca tac tac acc atc aag gat atc ctt ggc ctg atc cta ata atc ata gca ctg cta tcc cta gtc cta ttc gca cca gac ctc ctg gga gac cca gac aac tac act ccc gca aac cca ctc aac act cca ccc cat atc aaa cca gag tga tat ttc cta ttt gcc tac gcc atc cta cgg tca atc cca aac aaa cta gga gga gta gta gcc ctc gtc ctc tca atc ctt atc cta gct gta atc cct cta ctc cac aca tca aaa caa cgc agc ata acc ttc cgc cca tta agt caa tgc tta ttc tga ctc cta gtc gcc gac cta ctt aca cta aca tga atc ggg ggt caa cct gta gaa cac cca ttc att att atc gga caa ata gcc tca atc cta tac ttt ctc atc atc cta gtg ctc ctc cca ctc gca agc atc gca gaa aat cac cta tta aaa tga aga.
Derivatio nominis
The name arabica (Arabian) reflects the area of occurrence of the new species, i.e. the southern part of Arabia.
Distribution
Coastal areas of southern Arabia stretching from the Hadramaut Province in south-eastern Yemen (ca. 49°E) to the Dhofar Province in south-western Oman (ca. 55°E), i.e., ca. 650 km of a narrow coastal strip.
Received 22 July 2010, accepted 23 March 2011
APPENDIX I
List od the specimens examined in morphological analysis
Asellia arabica sp. nov. — Oman (6): 2 ♂♂, 2 ♀♀ ( NMP 92721 – 92724 [S+A]), Ain Jarziz (Dhofar Prov.), 27 October 2009, leg. P. Benda, A. Reiter and M. Uhrin; – 1 ♀ ( NMP 92753 [A]), Ain Tabruq (Dhofar Prov.), 29 October 2009, leg. A. Reiter; – 1 ind. ( BMNH 34.8.4.1 [S+B]), Cave of Sahaur, Qara Mts. , SE Arabia , date unlisted, leg. B. S. Thomas. – Yemen (14): 2 ♂♂, 2 ♀♀ ( NMP 92795 , 92796 , 92798 [S+A], 92797 [A]), Damqawt (Al Mahra Prov.), 16 October 2005, leg. P. Benda; – 4 ♂♂, 2 ♀♀ ( NMP 92790 , 92791 , 92792 – 92794 [S+A], 92789 [A]), Hawf (Al Mahra Prov.), 14 and 15 October 2005, leg. P. Benda; – 1 ♂ ( BCSU 013 [B]), Ryan (Hadramaut Prov.), July 1995, leg. A. Basmaidi; – 2 ♂♂, 1 ♀ ( BCSU 128 , 136 , 195 [S+B]), Shikhawi (Hadramaut Prov.), 12 March 2000, leg. A. K. Nasher.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Asellia arabica
| Benda, Petr, Vallo, Peter & Reiter, Antonín 2011 |
Asellia tridens tridens ( Geoffroy, 1813 )
| NADER, I. A. 1990: 340 |
| KOCK, D. 1969: 129 |
| HARRISON, D. L. 1957: 5 |
| Al-Jumaily, 1998: 483 |
Asellia tridens ( Geoffroy, 1813 )
| HARRISON, D. L. & P. J. J. BATES 1991: 55 |
| KINGDON, J. 1990: 37 |
| HARRISON, D. L. 1980: 390 |
| HARRISON, D. L. 1964: 98 |
| Pockock, 1935: 442 |
Asellia patrizii
| Asellia patrizii De Beaux, 1931 |
| Al-Jumaily, 2004: 60 |