Demicryptochironomus (Irmakia) dividuus Mukherjee et Hazra, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5175.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E2F427A6-B045-4FBC-A565-B96AAEEFF7A5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7003189 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/860D8812-98E8-4B14-ADBB-9E15BF1BFE63 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:860D8812-98E8-4B14-ADBB-9E15BF1BFE63 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Demicryptochironomus (Irmakia) dividuus Mukherjee et Hazra |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Demicryptochironomus (Irmakia) dividuus Mukherjee et Hazra View in CoL , sp. n.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
GenBank Accession No. ON881144 View Materials
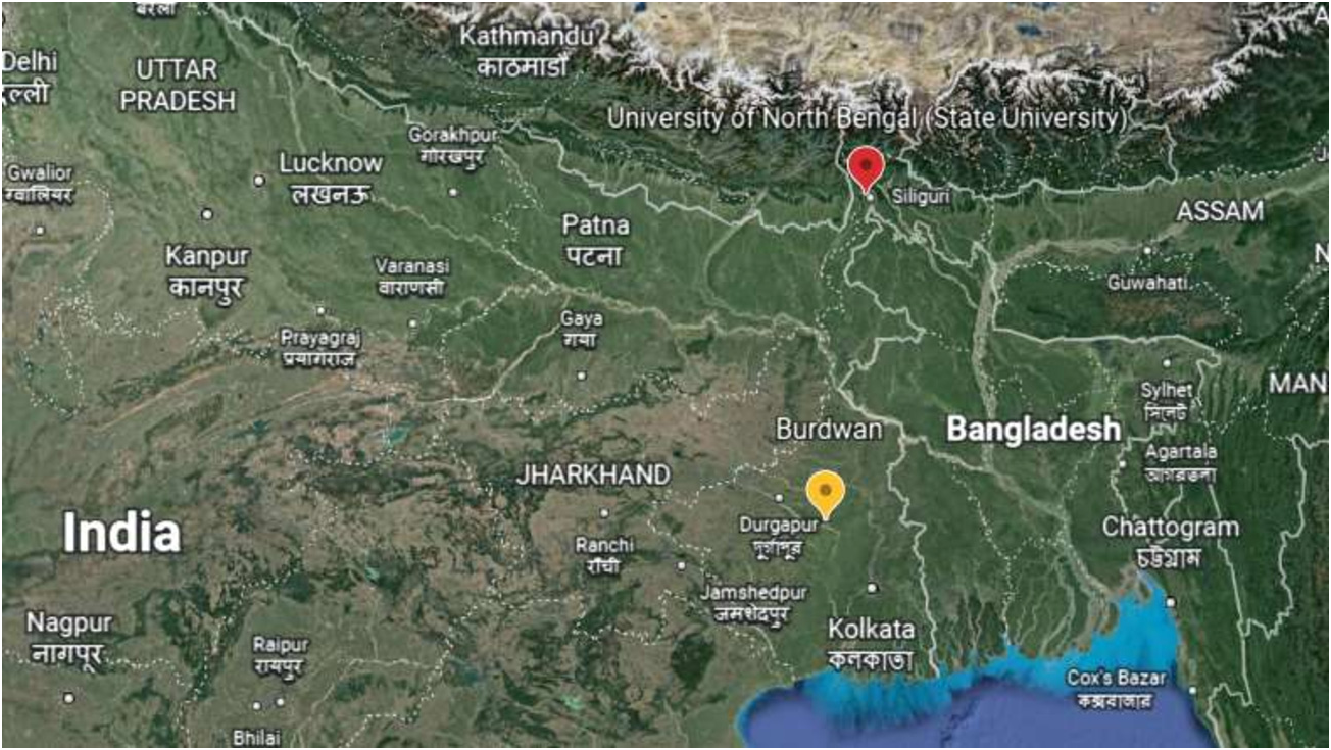
Material examined. Holotype male, labelled ‘ Holotype Demicryptochironomus (Irmakia) dividuus sp. n., India, West Bengal, Darjeeling [ 26.7095° N, 88.3542° E], 04.ix.2021, Coll. G. Pal’ GoogleMaps . Paratype 1 male, labelled ‘ Paratype Demicryptochironomus (Irmakia) dividuus sp. n., India, West Bengal, Burdwan [ 23.2393° N, 87.8512° E], 26.ii.2021, Coll. N. Hazra’ GoogleMaps .
Diagnostic characters. The species can be separated from other species of the genus Demicryptochironomus (Irmakia) by the following combinations of features: partially divided superior volsella at apex, and apically pointed gonostylus with strong concavity.
Etymology. The name “ dividuus ’’, a Latin word, refers to the partly divided superior volsella at apex.
Male (n=2)
Total length 2.4–3, 2.7 mm. Wing length 1.85–1.87 mm. Costal length 1.78 mm. Antennal length 0.8 mm.
Colouration. Thorax yellowish brown, leg colour light brown, abdomen yellow to light brown.
Head. Head width 500–540 µm. Temporal setae 8–10 (IV 1, OV 6–7, Po 0–2). Clypeal setae 9–10. Frontal tubercles present, 4.6–5 µm long. Eyes bare with dorsomedial extension of 115–130 µm. Ultimate flagellomere 490 µm long; AR 1.58. Length of palpomeres (I–V) (µm): 23: 46: 92: 105: 149. CA 0.63–0.68.
Thorax. Acrostichals 4, dorsocentrals 12–14, prealars 3, supraalars 1–2 and scutellars 6–8.
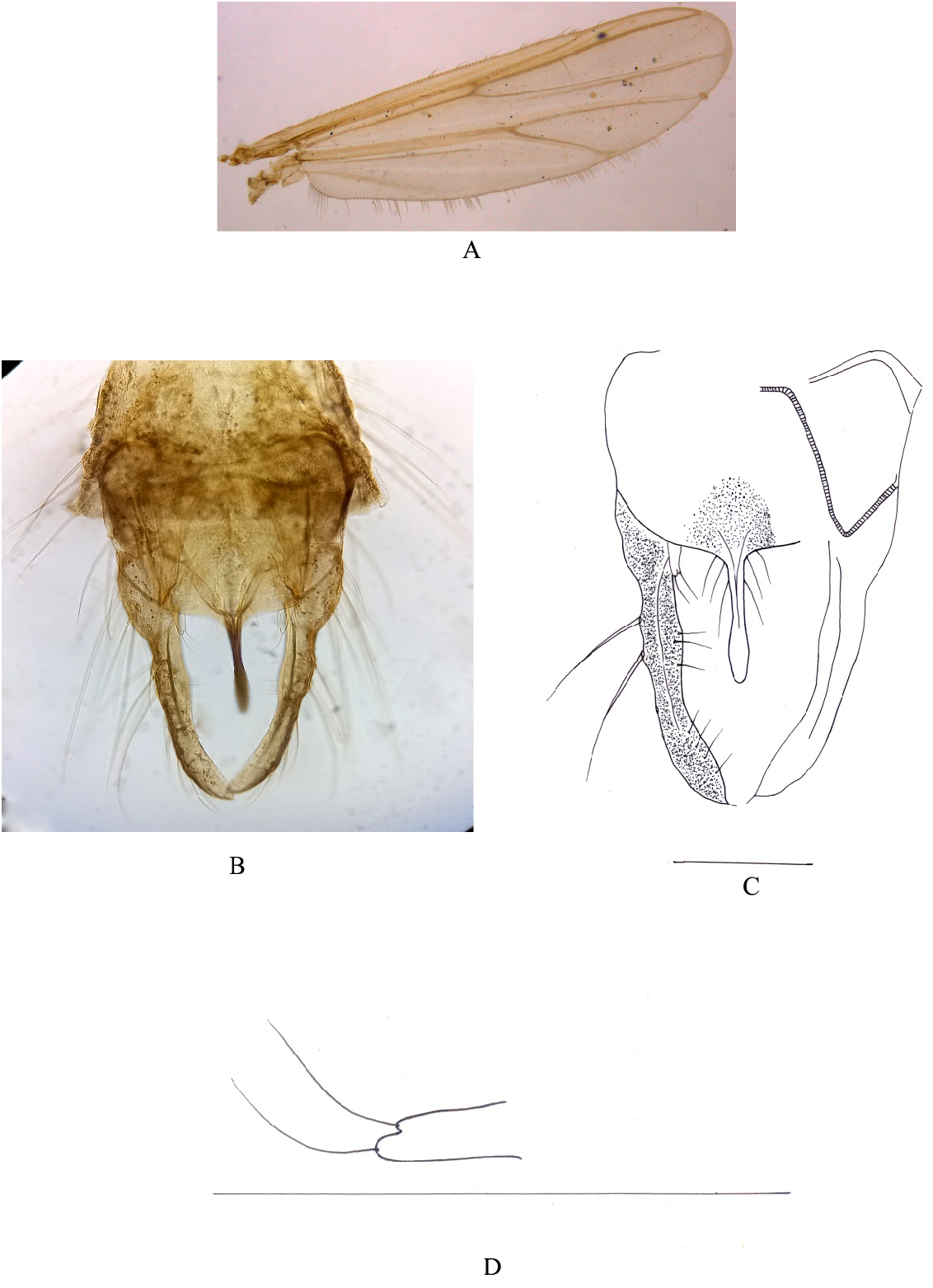
Wing ( Fig. 3A View FIGURES 3 ). VR 1.14. R with 17 setae, R 4+5 with 18 setae. Brachiolum with 2 setae. Squama with 4 fringed setae. FCu distinctly distal to RM. Anal lobe moderately developed.
Legs. Fore tibia with 2–3 setae. Mid legs with 2 tibial spurs; 16–18.4 and 20.7 µm long, comb with 36–40 teeth. Hind leg with 2 tibial spurs; 23 µm and 25.3 µm long, comb with 48–50 teeth. Lengths (µm) and proportions of legs shown in table 2.
Hypopygium ( Figs. 3B–D View FIGURES 3 ).Anal tergite band Y shaped.Anal point 76–80.5 µm long, 9.2–11.5 µm wide, slightly widened sub apically, apically rounded, bearing 3–4 lateral setae on each side. Transverse sternapodeme 23–30 µm long. Digitiform superior volsella 18.34–20.7 µm long, 6.9–9.2 µm wide ( Fig. 3D View FIGURES 3 ), partially bifurcated apex bearing 2 setae. Inferior volsella absent. Gonocoxite 138 µm long. Gonostylus 156–166 µm long, widest medially, apically pointed and strongly curved in middle with strong longitudinal keel. HR 0.84–0.88; HV 2.17.
Distribution ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ). West Bengal, India (present record).
Remarks. The new species shows closeness with D. (I). concavus Yan, Tang et Wang, 2005 in having somewhat similar shaped gonostylus but differs in the shape of superior volsella. Small thumb–like superior volsella is possessed by the new species and D. (I). fastigatus ( Townes, 1945) , but superior volsella is apically bisected in the new species while it is undivided apically in the latter species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |