Hydroides dianthus ( Verrill, 1873 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2017.344 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:27AA4538-407D-470A-8141-365124193D85 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3851375 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/794587B2-FFD9-FFA7-FD81-FD5FFC1AFAD2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Hydroides dianthus ( Verrill, 1873 ) |
| status |
|
Hydroides dianthus ( Verrill, 1873) View in CoL
Serpula dianthus Verrill, 1873: 620 View in CoL ( type locality: New Jersey to Massachusetts, United States).
Serpula hexagona Bosc, 1801: 205 ( type locality: Charleston, South Carolina, United States; on oyster shells). — Zibrowius 1971: 697, 699 (name indeterminable; the tube description does not match H. dianthus View in CoL , but records on the US east coast are misidentified and really belong to H. dianthus View in CoL ). — Read et al. 2016: 22–23 (name no longer in use and representing a species inquirenda).
Hydroides (Eupomatus) dianthoides Augener, 1922: 49–50 View in CoL (specimens from Veracruz, eastern Mexico; partial synonymy).
Serpula dianthus View in CoL – Treadwell 1891: 276 –280 ( Long Island, New York; anatomy and histology). — Wilson 1905: 119 and table (fossil records from Pleistocene of Sankaty Head, Nantucket, Massachusetts; abundant tubes). — Oldale et al. 1982: fig. 5 (same).
Eupomatus dianthus View in CoL – Richards 1933: 198 and table (fossil records from Cape May Formation, an interglacial warm stage from New Jersey). — Hartman 1945: 48, pl. 10, fig. 1 (North Carolina; under stones, shell fragments); 1951: 118–119 (Southwestern Florida, Louisiana, South Texas; intertidal, snail shell, rocks). — Rioja 1958: 260 –262 (Sacrificios and Verde Islands, Veracruz, eastern Mexico; on rocks, mollusk shells, corals and ship hulls). — Wells & Wells 1961: 152, 154–155, Beaufort, off Portsmouth Island and Pamlico Sound, North Carolina; 3.5–11 m, salinity 15–25‰; associated with the gastropod Fargoa dianthophila ( Wells & Wells, 1961) View in CoL (previously in the genus Odostomia View in CoL ). — Wells & Gray 1964: 74 (Cape Hatteras, North Carolina; hard substrates). — Wells & Wells 1969: 109 – 110 (North Carolina; Buzzard’s Bay, Massachusetts; Panama City, Alligator Harbor and Cedar Key, Florida; associated with F. dianthophila View in CoL ).
Hydroides dianthus View in CoL – Webster & Benedict 1884: 737 ( Massachusetts; intertidal, on shells). — Benedict 1887: 549, pl. 20, fig. 10 (Chesapeake Bay; on living oysters, shells and stones). — Cushman 1906: 9 (fossil records from Pleistocene of Sankoty Head, Nantucket).— Roberge 1968:145 (Buzzard’s Bay, Massachusetts; subtidal rocks; as host of parasite gastropod F. dianthophila View in CoL ). — Zibrowius 1971: 697 –705 (east coast of United States, Atlantic France, Mediterranean and Senegal, Western Africa; 1–189 m, salinity 18–50‰, temperature 5–30°C; on sand and the seagrass Posidonia View in CoL , bryozoan nodules and oysters). — Day 1973: 132 (Cape Hatteras to South Carolina; intertidal to 30 m). — Robertson & Mau-Lastovicka 1979: 323 (Woods Hole; “host” of Fargoa bartschi (Winkley, 1909)) View in CoL . — Haines & Maurer 1980a: 646 –647 (Delaware Bay; 6 m, salinity 23.3–28.3‰, temperature 3–25.4°C, on muddy sand); 1980b: 44–46 (Delaware Bay; invertebrates associated with H. dianthus View in CoL ; same data as 1980a). — ten Hove & Wolf 1984: 55 -21, figs 55-15, 55-16a–j (western Florida; 22 m, medium sand). — ten Hove & van den Hurk 1993: 41 –42, fig. 4B, D (Baffin Bay and Corpus Christi, Texas; 0.6–2.4 m and in concrete tunnels supplying cooling water to a power station; salinity average 51.7‰). — Perkins 1998: 95 (checklist of shallow-water polychaetes of Florida). — Bastida-Zavala & Salazar-Vallejo 2000b: 845, fig. 1m–u (eastern Mexico: San Juan de Ulúa, Veracruz; Champotón, Campeche; Celestún Beach, Ría Lagartos and San Felipe, Yucatán; Contoy Island, Nichupté Lagoon and Yalahau Lagoon, Quintana Roo; 0.5–4 m; on seagrass, algae, sponges, rocks, fort wall covered with vermetids, oysters and ascidians, wood dock pilings). — Sun &Yang 2000: 120 –121,fig. 2e–k ( China).— Bianchi & Morri 2001: 216 –218(Orbetello Lagoon, Italy; reef-builders, competitor with Ficopomatus enigmaticus View in CoL ; salinity 13–48‰, temperature 7–30°C). — Toonen & Pawlik 2001: 104 –112 (Wrightsville Beach, North Carolina; gregarious and non-gregarious settlement; intertidal). — Bastida-Zavala & ten Hove 2002: 143 –146, figs 23A–M, 24A–K, 28 (Connecticut, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and eastern Mexico: Veracruz, Yucatán and Quintana Roo; 0.6–28 m, salinity 1–34‰,on oysters, rocks and wooden pier). — Link et al. 2009: 1 –6, figs 1a–g, 2 ( Tokyo Bay, Japan, as NIS; 0.8 m, on PVC plates). — Otani & Yamanishi 2010: 63 –64, fig. 3a–g ( Osaka Bay, Japan, as NIS; seasonal change in densities; intertidal to 4 m, salinity 26.5– 32.3‰, temperature 17.7–19.1°C; on concrete blocks). — Ben-Eliahu & ten Hove 2011: 14 –16 ( Cyprus; 0.3 m, from ship propeller). — Boltachova et al. 2011: 34 –38 (Crimea, Black Sea). — Sun et al. 2016a: poster (discussion as global invader or a complex of species).
Hydroides (Eupomatus) dianthoides View in CoL – Bastida-Zavala & ten Hove 2002: 143 (partial synonymy).
Material examined
1787 specimens: RI (108) Sep. 2001, CB (352) Sep. 2000 and Aug. 2012, CH (117) Sep. 2004, JX (99) Aug. 2001, IR (99) Aug. 2005, BB (78) Aug. 2004, TB (38) Jun. 2012, PB (323) Aug. 2002, GB (356) Sep. 2002, CC (217) Sep. 2002.
Diagnosis
This species is gregarious and can form small colonies. Tube white, with two longitudinal ridges; lacks peristomes, transverse ridges or alveoli. Opercular peduncle smooth, white. Opercular funnel with 24– 37 radii with pointed tips ( Fig. 4C View Fig ); verticil with 8–13 spines, all curving ventrally, with one basal internal spinule, without external and lateral spinules or wings ( Fig. 4C View Fig ). Special collar chaetae with two blunt, short teeth and smooth distal blade.
Taxonomic remarks
Hartman (1945, 1951) mentioned that the distribution of Hydroides dianthus includes the West Indies; the only record of this subtropical species, in the Caribbean Sea, is from Weisbord (1964: 158), who collected several empty tubes from northern Venezuela, as H. cf. dianthus , but species identification with only the tube in the genus Hydroides , is doubtful.
Hydroides dianthus was recorded, as Eupomatus , by Holguín-Quiñones (1994) from Socorro Island, in the Mexican Pacific; however, the record is indeterminable because it lacks a description and figures, and the specimens were not deposited in a collection (Holguín-Quiñones, pers. comm. 2011; Bastida-Zavala et al. 2016: 418).
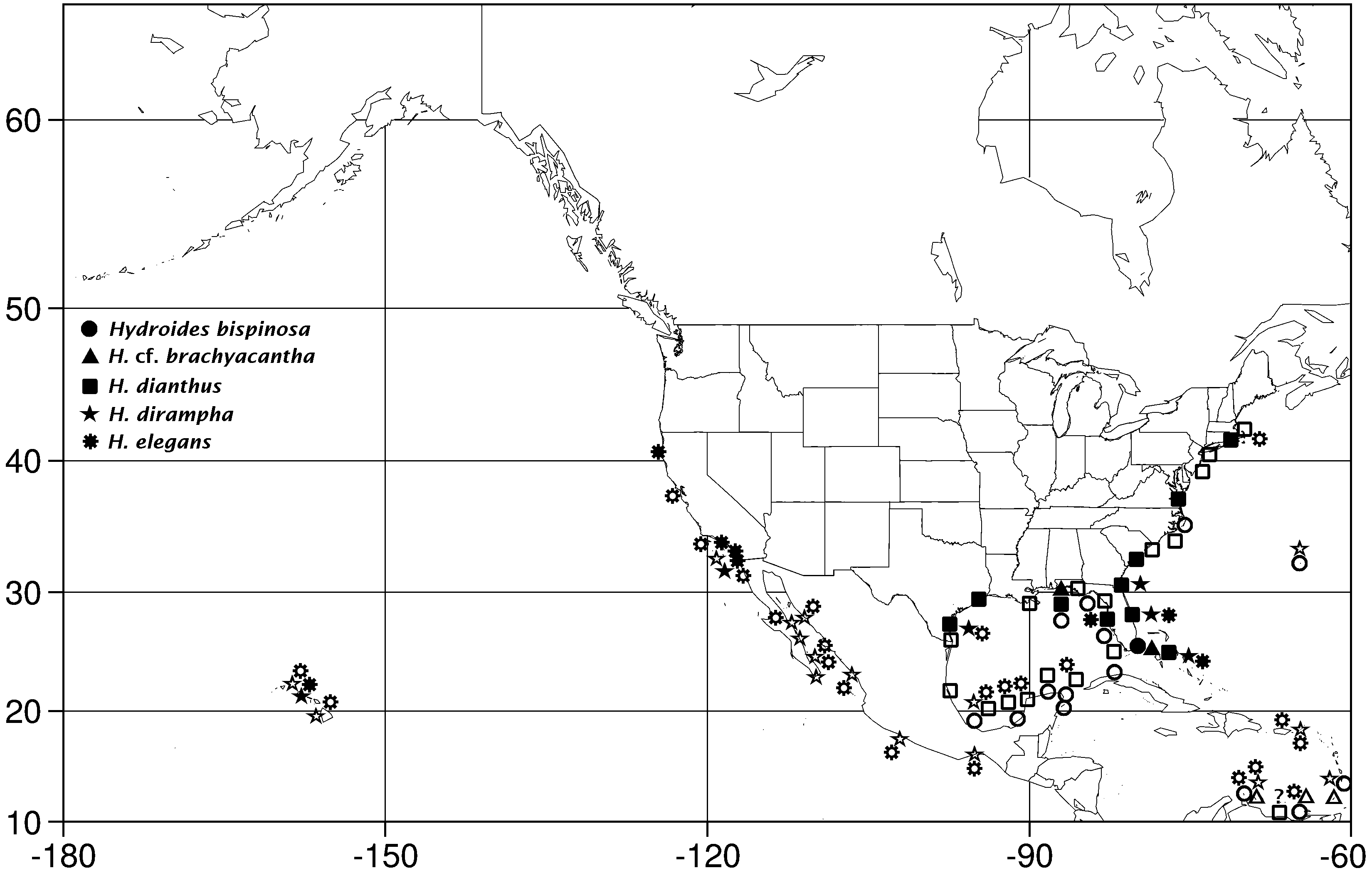
By far, Hydroides dianthus is the most abundant species (1787 specimens) on fouling plates from the 10 localities on the east coast of the United States and northern Gulf of Mexico ( Table 1 View Table 1 ). In one sample from the northern Gulf of Mexico, two of four specimens had an operculum with red verticil spines (see also H. floridana ( Bush, 1910)) , a character never seen before.
In Delaware Bay and Virginia’s coastal lagoons ( Haines & Maurer 1980a: 647), H. dianthus builds tube clusters ( 10–400 cm 3) and at the former site the clusters harbor up to 54 invertebrate species ( Haines & Maurer 1980b). The gregarious settlement of this species was studied in North Carolina ( Toonen & Pawlik 2001) and the Mediterranean, where H. dianthus builds large reefs in coastal lagoons ( Bianchi & Morri 2001). It competes with other NIS, such as Ficopomatus enigmaticus , at several sites in the Mediterranean ( Zibrowius 1973; Bianchi & Morri 2001).
Due to its euryhaline (1–51.7‰) and eurythermic (3–30°C) tolerances, H. dianthus has successfully invaded many harbors around the world. However, in Osaka Bay Otani & Yamanishi (2010) found that salinities above 30‰, combined with biological interactions with macroalgae or mussels, may be limiting the distribution of H. dianthus .
Hydroides dianthus , previously considered native to the US east coast ( Bosc 1801; Verrill 1873), should be considered cryptogenic (see the 'Cryptogenic species' section in the Discussion below).
Ecology
Intertidal to sublittoral ( 189 m). In subtropical and tropical marine and brackish waters; salinities of 1–51.7‰, temperature 3–30°C ( Zibrowius 1971; Haines & Maurer 1980a; Bianchi & Morri 2001); on rocks, mollusk shells, corals, seagrass, algae, sponges and artificial substrates ( Rioja 1958; Zibrowius 1971; Bastida-Zavala & Salazar-Vallejo 2000b; Bastida-Zavala & ten Hove 2002; Ben-Eliahu & ten Hove 2011); also associated with the gastropods Fargoa dianthophila and F. bartschi ( Robertson & Mau-Lastovicka 1979; Wells & Wells 1969). Fargoa dianthophila was considered a parasite of Hydroides dianthus by Roberge (1968).
Distribution
East coast of United States, Bermuda, Gulf of Mexico, Mexican Caribbean, Mediterranean, European Atlantic, Senegal (western Africa), Japan ( Zibrowius 1971; Bastida-Zavala & ten Hove 2002; Link et al. 2009; Otani & Yamanishi 2010), China, Brazil and Black Sea ( Sun & Yang 2000; Boltachova et al. 2011; Sun et al. 2016a). In this work, Hydroides dianthus was found abundantly and frequently on fouling plates from Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island; Chesapeake Bay, Virginia; Charleston, South Carolina; Jacksonville, Indian River, Biscayne Bay, Tampa Bay and Pensacola Bay, Florida; and Galveston Bay and Corpus Christi, Texas ( Fig. 5 View Fig ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hydroides dianthus ( Verrill, 1873 )
| Bastida-Zavala, J. Rolando, McCANN, Linda D., Keppel, Erica & Ruiz, Gregory M. 2017 |
Hydroides (Eupomatus) dianthoides
| Bastida-Zavala J. R. & ten Hove H. A. 2002: 143 |
Hydroides (Eupomatus) dianthoides
| Augener H. 1922: 50 |
Serpula dianthus
| Verrill A. E. 1873: 620 |
Serpula hexagona
| Read G. 2016: 22 |
| Zibrowius H. 1971: 697 |
| Bosc L. A. G. 1801: 205 |
Serpula dianthus
| Treadwell 1891: 276 |
| Wilson 1905: 119 |
| Oldale et al. 1982 |
Eupomatus dianthus
| Richards 1933: 198 |
| Hartman 1945: 48 |
| Rioja 1958: 260 |
| Wells & Wells 1961: 152 |
| Wells & Gray 1964: 74 |
| Wells & Wells 1969: 109 |
| Webster & Benedict 1884: 737 |
| Benedict 1887: 549 |
| Cushman 1906: 9 |
| Roberge 1968:145 |
| Zibrowius 1971: 697 |
| Day 1973: 132 |
| Robertson & Mau-Lastovicka 1979: 323 |
| Haines & Maurer 1980a: 646 |
| ten Hove & Wolf 1984: 55 |
| ten Hove & van den Hurk 1993: 41 |
| Perkins 1998: 95 |
| Bastida-Zavala & Salazar-Vallejo 2000b: 845 |
| Sun &Yang 2000: 120 |
| Bianchi & Morri 2001: 216 |
| Toonen & Pawlik 2001: 104 |
| Bastida-Zavala & ten Hove 2002: 143 |
| Link et al. 2009: 1 |
| Otani & Yamanishi 2010: 63 |
| Ben-Eliahu & ten Hove 2011: 14 |
| Boltachova et al. 2011: 34 |
| Sun et al. 2016a |