Synosis clepsydra Townes, 1959
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2013.768912 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8E5FA67F-F80A-4D78-8E5E-7CC8D6662396 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/76018791-FFED-D62B-2EA6-FC64FB1EF9B4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Synosis clepsydra Townes, 1959 |
| status |
|
Synosis clepsydra Townes, 1959 View in CoL
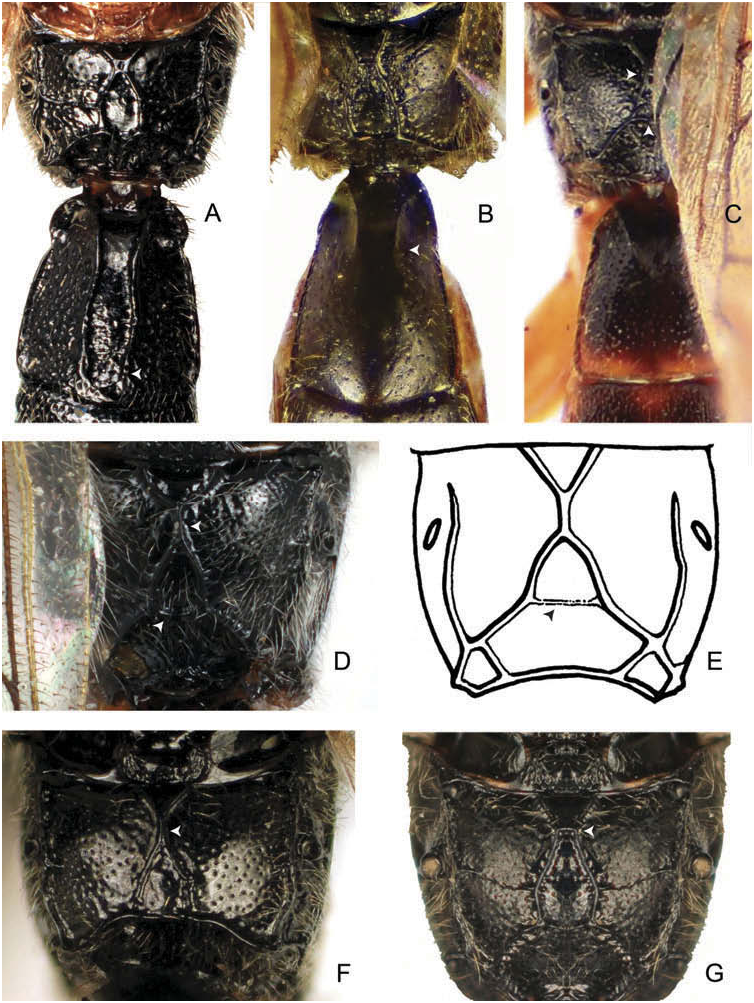
( Figures 5 View Figure 5 , 6C, D View Figure 6 )
Material examined
1♀ ( Holotype), USA: Camino , Califor. [ California] June 27, 1948, MHG & D Townes ( USNM) ; 1 ♀ ( Paratype), Auburndale, Mass., June 17 (Townes) ( AEIC). There is morphological variation in S. clepsydra . The holotype has the lateromedian longitudinal carinae converging to form a single median carina ( Figure 6E View Figure 6 ), but the paratype has the lateromedian longitudinal carinae converging and in contact but not forming a single carina ( Figure 6D View Figure 6 ) as was mentioned when the genus was described ( Townes and Townes 1959) .
Key for identification of New World species of Synosis View in CoL
1. Mesosoma reddish except propodeum and metasoma black ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 ); tergite I with lateromedian carina extending almost to posterior margin; punctures present between lateromedian carina ( Figure 6A View Figure 6 )........... rubinus sp. nov. Mesosoma black, at most with yellowish tegulae and upper area of subalar prominence; tergite I with lateromedian carina extending at most to middle of tergite ( Figure 6B, C View Figure 6 )................................................... 2
2. Propodeum with lateromedian longitudinal carinae approaching closely ( Figure 6C View Figure 6 ) or fused ( Figures 6D–F View Figure 6 ) without transverse carina separating area basalis and superomedia; metacoxa reddish.............................. 3 Propodeum with short transverse carina separating area basalis and superomedia ( Figure 6G View Figure 6 ), if weak or absent, then there is a space present wider than thickness of carinae combined ( Figure 6B View Figure 6 ); metacoxa black............... 5
3. Laterotergites I and II developed, laterotergite II at least 0.4× as wide as long ( Figure 7A View Figure 7 );......................................... cosnipatensis sp. nov. Laterotergites I and II vestigial ( Figure 7C View Figure 7 ), less than 0.3× as wide as long.......................................................................... 4
4. Lower face c.0.9× as broad as long; propodeum with posterior transverse carina present between lateromedian longitudinal carinae ( Figures 6C, D View Figure 6 ); metasomal tergites with reddish borders ( Figure 6C View Figure 6 )...... clepsydra Townes View in CoL Lower face c.1× as broad as long; propodeum with posterior transverse carina between lateromedian longitudinal carinae vestigial ( Figure 6E View Figure 6 ); metasomal tergites with black borders....................... ugaldei Gauld and Sithole View in CoL
5. Submetapleural carina anteriorly expanded into conspicuous triangular lobe ( Figure 7B View Figure 7 ); 36–37 flagellomeres; metatibia yellowish with apical black spot ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 )................................................. townesi sp. nov. Submetapleural carina not anteriorly expanded ( Figure 7C View Figure 7 ); 29 flagellomeres; metatibia yellowish with basal and apical spots ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 ).... gauldi sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.