Stylopoma variabilis, Ramalho & Taylor & Moraes & Moura & Amado-Filho & Bastos, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4483.1.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:05A08470-9473-4147-B54B-AB0C90173572 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5952380 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6C3EF226-FFA9-7903-FF43-FBD5FC43FB7A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stylopoma variabilis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stylopoma variabilis n. sp.
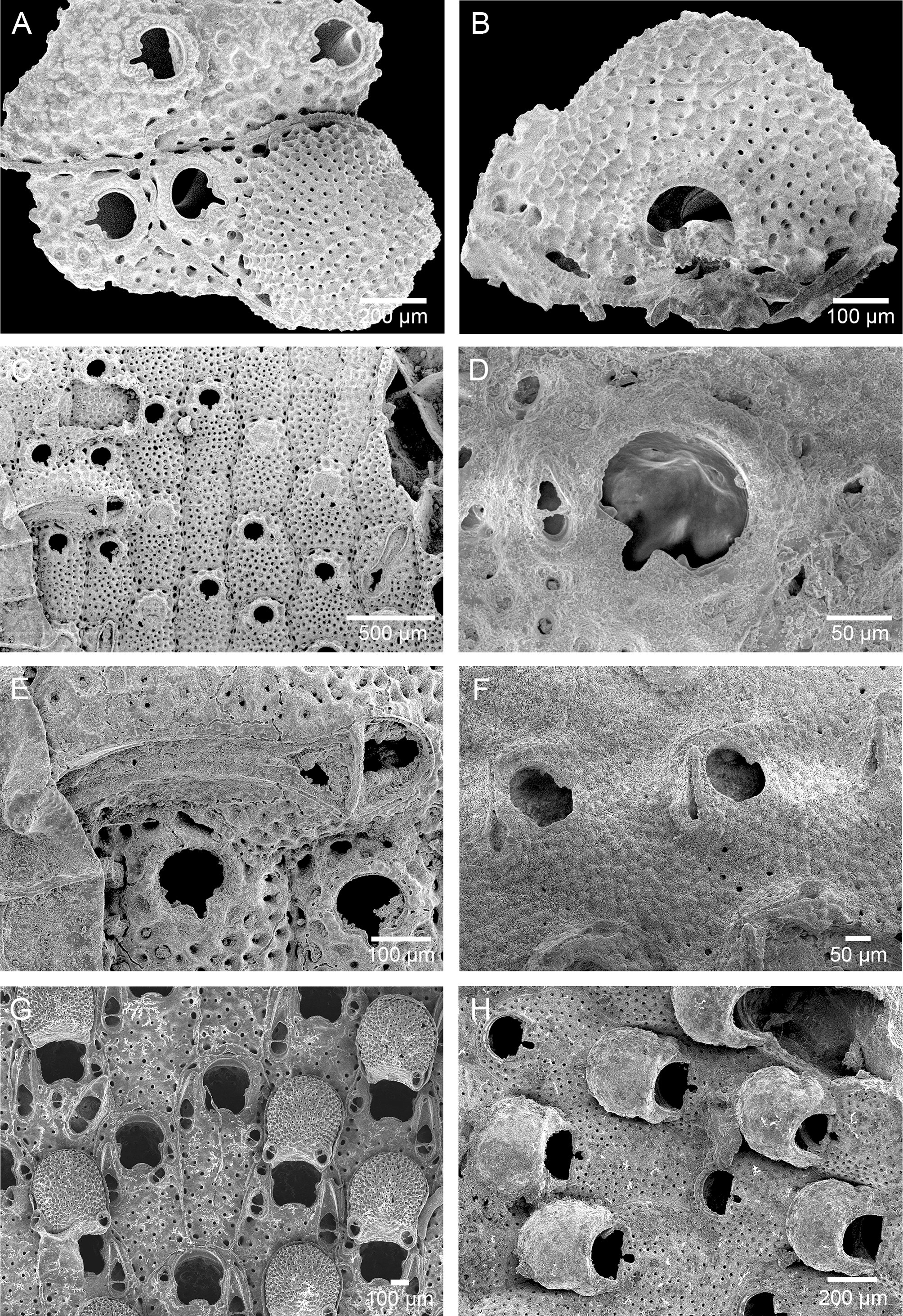
( Figs 4G, H View FIGURE 4 , 5A, B View FIGURE 5 , 7E View FIGURE 7 )
Stylopoma View in CoL sp. 1 Reis et al., 2016: Supplementary table; Bastos et al., 2018: table 1.
Material examined. Abrolhos Bank, Bahia State, Brazil. Holotype: MNRJ-Bry1356, Parcel dos Abrolhos, 4 m depth, February 2014, col. R. Moura, G. Amado-Filho & A . Bastos ; Paratype: MNRJ-Bry1354, Parcel dos Abrolhos, 15 m depth, February 2014, col. R. Moura, G. Amado-Filho & A. Bastos.
Etymology. From the Latin ' variabilis ', meaning 'variable, changeable', referring to the variability of the sinus shape (U- to funnel-shaped).
Diagnosis. Orifice wider than long with a narrow U- to funnel-shaped sinus; tab-like condyles extending almost to the sinus and ending in a downwardly curved rounded tip; lateral oral avicularia triangular with rostrum raised from the frontal surface; very frequent spatulate vicarious avicularia, variable in size and direction; ovicell globose with some pores on the ooecial surface.
Description. Encrusting colonies, multilamellar. Red in vivo ( Fig. 7E View FIGURE 7 ). Autozooids rectangular to irregularly polygonal (471–646–862 µm long x 333–419–497 µm wide), initially disposed in quincunx but with the age the growth becomes irregular by frontal budding; frontal wall perforated by small circular pores inside depressions ( Fig. 4G View FIGURE 4 ). Orifice wider than long (96–111–123 µm long x 128–147–163 µm wide), anter circular and poster almost straight, narrow U- to funnel-shaped sinus; tab-like condyles extending to middle or more of the proximal border and ending in a downwardly curved rounded tip. Peristome low and rough textured ( Figs 4H View FIGURE 4 , 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Single small (68–78–87 µm long) adventitious avicularium (sometimes absent), located laterally and near the proximal border of the orifice, directed latero-distally; rostrum rounded proximally with a short triangular rounded tip, raised above the frontal shield ( Fig. 4G, H View FIGURE 4 ). Vicarious avicularia common, variable in size (315–545 µm long), tip spatulate, directed randomly; crossbar complete ( Fig. 4G View FIGURE 4 ). Ovicell globose (470 µm long x 640 µm wide), with ooecial surface similar to frontal shield of the autozooid, some pores present and lacking avicularia; crescentic opening guarded by asymmetrical ‘crab claw-like’ extensions (one thin and the other thick) from either side of the base towards the midline of the aperture but not completely fused in the center, just touching each other ( Fig. 5A, B View FIGURE 5 ).
Geographic distribution. Abrolhos Bank, Bahia State, Brazil ( Reis et al. 2016; Bastos et al. 2018; present study).
Remarks. Four species of Stylopoma have been recorded from Brazil: S. carioca Winston et al., 2014 , S. rotundum Winston et al., 2014 , S. aurantiacum Canu & Bassler, 1928a and S. spongites ( Pallas, 1766) ( Tilbrook 2001; Winston et al. 2014; Almeida et al. 2017).
Stylopoma carioca has a frontal shield with a porous, rough texture, ribbed calcification and an umbo at the centre of the zooid, an orifice almost as long as wide with a small tab-like condyle, small funnel-shaped median sinus, frontal avicularia which lie flat against the frontal shield surface, and an ooecium with ribs between the marginal pores. Stylopoma rotundum differs from the Abrolhos specimens in the rounded frontal avicularia and orifice with thick condyles ending in blunt, downwardly curved hooks. Stylopoma spongites has smaller zooids (510 µm long x 360 µm wide), an orifice almost as long as wide (100 µm long x 120 µm wide), an anter with sparsely denticulate inner rim, and tall condyles covering a small portion of the proximal margin. There are two kinds of vicarious avicularia: one with a spatulate mandible and the other with a pointed mandible. The labellum is fused to the ooecium leaving a crescent lumen. Stylopoma aurantiacum is the most similar species, but it has smaller autozooids (501 µm long x 423 µm wide) with slightly ribbed calcification and a raised umbo at the centre of the zooid, an orifice as long as wide (120 µm long x 128 µm wide) with a funnel-shaped sinus and commashaped condyles, and lacks interzooidal avicularia; the ovicell is large (581 µm long x 648 µm wide), covering parts of several zooids, with ribs between the marginal pores on the ooecial surface.
Stylopoma haywardi Winston & Woollacott, 2009 , described from Barbados, has a triangular oral avicularium but with a rostrum ending in a hooked tip, and broad straight condyles occupying almost the entire inner edges of the sinus. Stylopoma smitti Winston, 2005 View in CoL , described from Florida, shares with S. variabilis n. sp. a similar-shaped orifice and triangular avicularia but can be distinguished by the deeply slit, round-bottomed, almost tear-drop shaped sinus, broad condyles extending almost to the sinus and occasional thickened denticles or tabs on the inner edges of the spatulate avicularia, as well as triangular avicularia on the frontal shield or below the orifice.
According to bryozoa.net (accessed 01.03.2018) there are almost 40 species of Stylopoma View in CoL . Most are extinct and from the Caribbean and Indo-Pacific. The characteristics of S. variabilis n. sp., orifice wider than long with a U- to funnel-shaped sinus, tab-like condyles ending in a downwardly curved tip, single triangular, lateral oral avicularium, vicarious avicularia variable in size with spatulate tip and ovicell globose with ooecial surface perforate and lacking avicularia, distinguish it from other Stylopoma View in CoL species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Neocheilostomina |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Stylopoma variabilis
| Ramalho, Laís V., Taylor, Paul D., Moraes, Fernando Coreixas, Moura, Rodrigo, Amado-Filho, Gilberto M. & Bastos, Alex C. 2018 |
Stylopoma
| Ramalho & Taylor & Moraes & Moura & Amado-Filho & Bastos 2018 |
S. variabilis
| Ramalho & Taylor & Moraes & Moura & Amado-Filho & Bastos 2018 |
Stylopoma
| Ramalho & Taylor & Moraes & Moura & Amado-Filho & Bastos 2018 |
S. variabilis
| Ramalho & Taylor & Moraes & Moura & Amado-Filho & Bastos 2018 |
Stylopoma
| Ramalho & Taylor & Moraes & Moura & Amado-Filho & Bastos 2018 |
Stylopoma haywardi
| Winston & Woollacott 2009 |
Stylopoma smitti
| Winston 2005 |