Elisolimax flavescens (Keferstein, 1866)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2462.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6413F378-FFC9-6A54-F28B-76FCFDA8F997 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Elisolimax flavescens (Keferstein, 1866) |
| status |
|
Elisolimax flavescens (Keferstein, 1866) View in CoL
Figures 33E View FIGURE 33 , 34B View FIGURE 34 , 36D–F View FIGURE 36 , 37A–B View FIGURE 37
Synonymy: see van Goethem, 1977.
Material examined. Mozambique: NMSA L5563 About NMSA ( one specimen dissected, radula examined), Inhaca Island , Ponta Terres area ( 26º04.2' S, 32º56.5' E), coastal bush, abundant, 25 Mar. 2001, P. Cairns GoogleMaps .
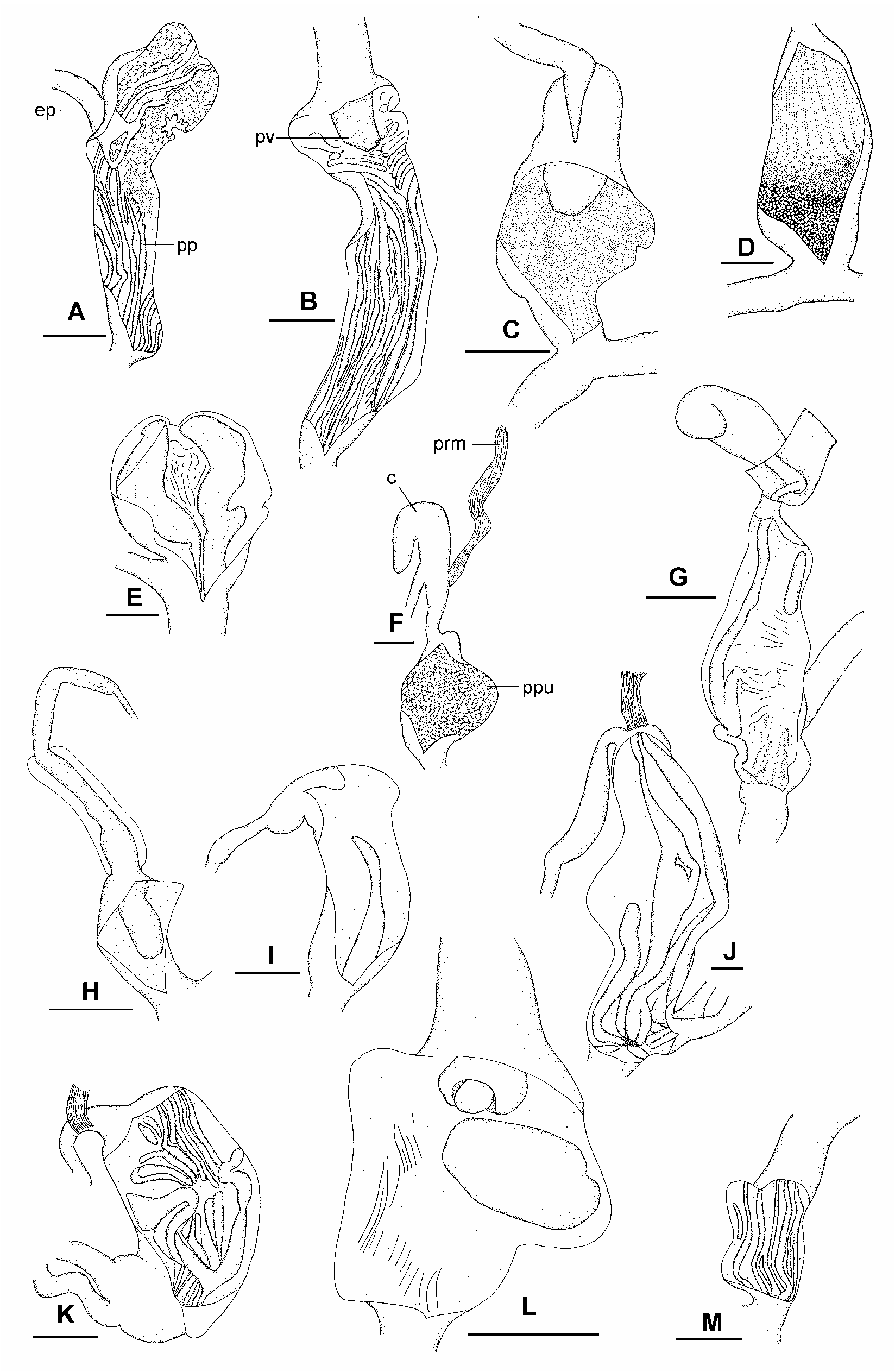
Description. External morphology: Shell highly reduced, glossy. Protoconch smooth; teleoconch sculptured with strong radial growth lines. Animal light yellowish brown. Mantle laps very large, completely fused, uniform in colour. Right mantle lobe small, left and median mantle lobes large, fused to form large lobe over head. Sole of foot and caudal apparatus as for family; caudal horn very small; caudal foss vertical slit in tail.
Mantle cavity: As for family. Mantle with no visible minor blood vessels, pigmentation absent, mantle gland absent.
Digestive system: Oesophageal crop present, extremely large.
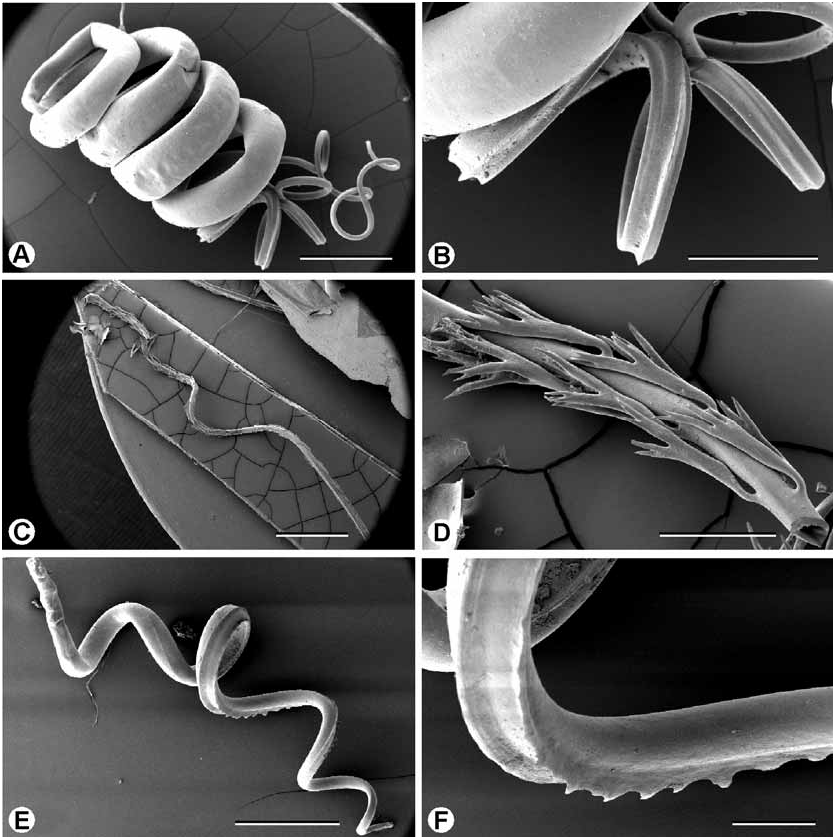
Genital system ( Figures 33E View FIGURE 33 , 34B View FIGURE 34 , 37A–B View FIGURE 37 ): As for family. Carrefour and talon both not embedded in albumen gland. Free oviduct medium to long; capsular gland present; very thick internal longitudinal pilasters present. Bursa copulatrix inserted on vagina, short, less than half spermoviduct length; duct of bursa copulatrix narrow, distinguishable from bursa copulatrix, internally with longitudinal pilasters. Vagina very short; internally with longitudinal pilasters. Stimulator absent. Penis large, short; epiphallus enters penis through simple pore, at base of penis; penis internally smooth, two longitudinal penis pilasters present, penial diverticulum absent. Penial sheath absent; penis retractor muscle attached to penis. Epiphallus much longer than penis, internally with longitudinal pilasters. Epiphallic retractor caecum very long, positioned in middle of epiphallus. Lime-sac present. Spermatophore soft capsule with firm tail pipe; capsule very long and coiled; tail pipe open at one end, long, sculptured with longitudinal ridges.
Radula ( Figure 36D–F View FIGURE 36 ): Relatively long and narrow. Central tooth with very small ectocones; mesocone very short and rounded; much shorter than tooth base. Lateral and marginal tooth fields distinguishable. Lateral teeth with endocone much smaller than central tooth ectocones; ectocone equal in size to those on central tooth; mesocone much longer than tooth base. Marginal teeth with endocones absent; ectocones shorter and narrower than the mesocone, not subdivided into extra teeth. Radular formula (28.37.1.37.28) × 125 rows.
Remarks. Full details of the shell, reproductive system, spermatophore, jaw and radula of Elisolimax flavescens were presented by van Goethem (1977). Details of 17 other species belonging to the genus [including the type species, E. belli (Heynemann, 1882) ] were also presented ( van Goethem 1977).
Elisolimax is distributed throughout E and SE Africa, Madagascar and the Comoro Islands and contains 15–18 species ( Schileyko 2002b). This species has previously been placed in Urocyclidae in the subfamily Urocyclinae but, recently, Schileyko (2002b) included it in Helicarionidae in the subfamily Urocyclinae and tribe Buettneriini . In the current study it grouped with Sheldonia poepiggii ( Trochonanininae , Urocyclidae ) in the phylogenetic analysis ( Figure 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
| NMSA |
KwaZulu-Natal Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |