Gekko vietnamensis, Sang, Nguyen Ngoc, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.293940 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5670016 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/623B87CF-FFF6-FFBD-FF25-F939FAB83981 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Gekko vietnamensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Gekko vietnamensis sp. nov.
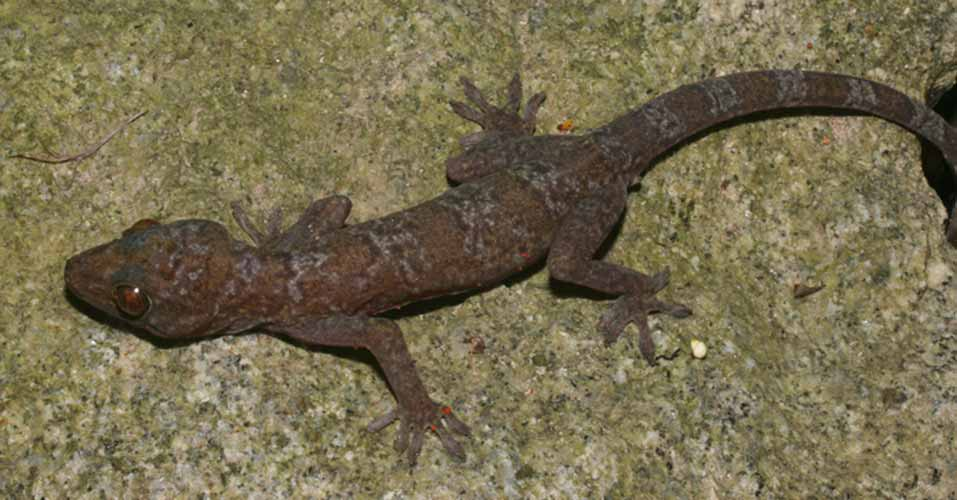
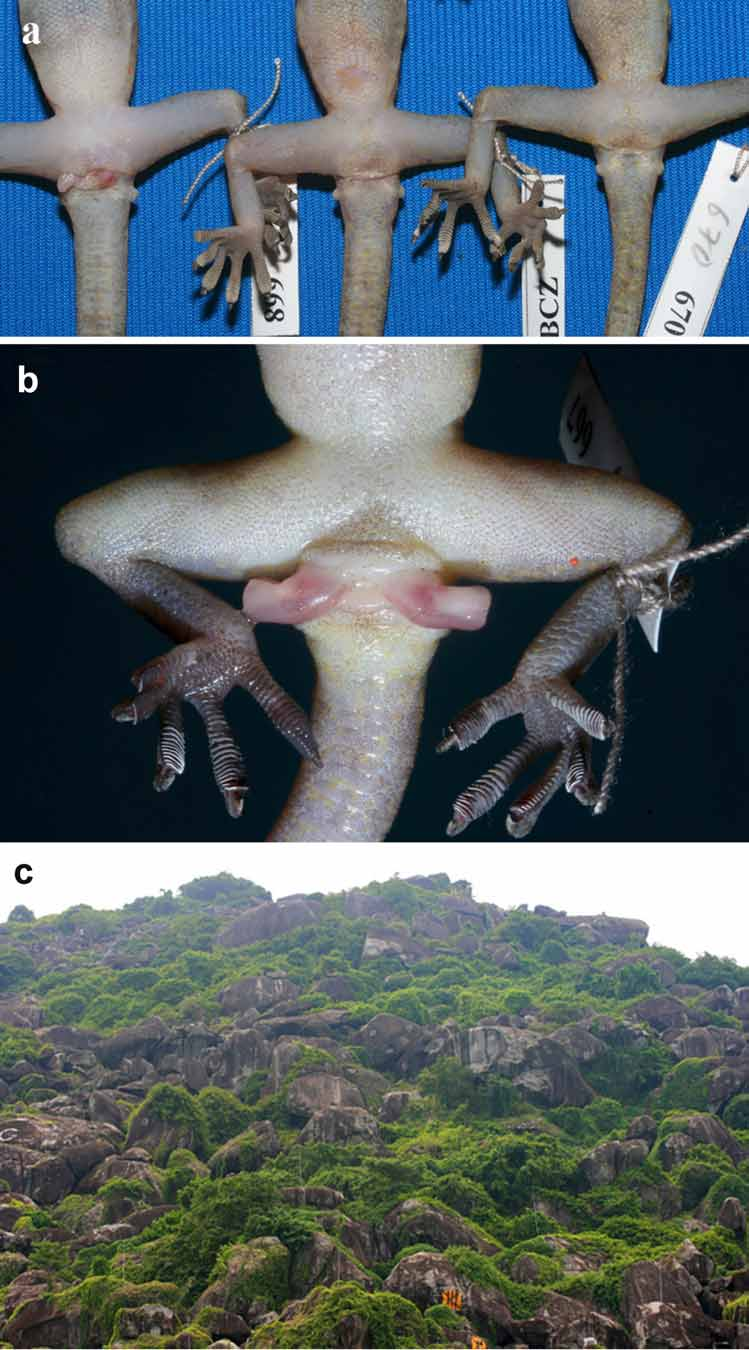
Holotype ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). ITBCZ 667, adult male, colleted at Tức Dụp Hill ( 10o22'35.1"N, 104o57'35.3"E; 43 m a.s.l.), An Giang Province, southern Vietnam, on 2 August 2008, by Nguyen Ngoc Sang GoogleMaps .
Paratypes. ITBCZ GoogleMaps 668 GoogleMaps –670, GoogleMaps ITBCZ 700 GoogleMaps –702—six GoogleMaps adult males, GoogleMaps ITBCZ 671—adult female, same data as holotype GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. Gekko vietnamensis sp. nov. has the following diagnostic characters: a medium size (SVL up to 91 mm); lack of precloacal and femoral pores, no enlarged femoral scales; rostral touching nostril; 11–12 supralabials, 10–11 infralabials; body slender with four unclear transverse bands on the back and 28–30 scales across mid-belly; 18–20 undivided transverse lamellae under the fourth toe, digits free; and tail longer than snout-vent length with enlarged undivided transverse subcaudal scales.
Holotype Paratypes
Description of holotype. Adult male, snout-vent length 83.02 mm. Head relatively depressed (HeadH/ HeadW ratio 0.62; HeadH/HeadL ratio 0.51), distinct from neck. Eyes medium (OrbD/HeadH ratio 0.57), brown, pupil vertical. A row of 12 supralabials continued as a small scale row extending to jaw, the first touching the nostril. 10 infralabials also continued as a small scale rows extending to jaw. Rostral broader than high, touching the nostril. Small scales between internasals present. Mental nearly triangular, narrower than the rostral. Three pairs of postmentals. Gular region with small flat granules. Head covered above with small granular scales. Ear opening oval, smaller than eye (EarL/OrbD ratio 0.36).
Body slender, elongate (TrunkL/SVL ratio 0.45). Dorsal scales small, intermixed with larger smooth tubercles. Belly with hexagonal to round smooth scales, larger than dorsal scales. 28 scales across the belly in the middle of the body, between two lateral folds.
Precloacal region with round and smooth scales, larger than scales in dorsum and limbs. No precloacal pores, no femoral pores as well as enlarged femoral scales ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 b).
Digits free and compressed. Inner digit well developed, without claw. 19 undivided transverse lamellae under the fourth toe. Tail elongate, round section, longer than snout-vent length (TailL/SVL ratio 1.19). 91 enlarged undivided transverse subcaudal scales. One smooth cloacal spur on the each side of the tail base.
Colour in life. Dark brown above with four unclear transverse bands on the back. Venter whitish, uniform. Tail with alternating bands of dark brown and grey, the dark brown bands being broader than the grey ones. Seven grey bands on tail.
Colour in preservative. In 75% ethanol, coloration and pattern do not significantly differ.
Variation. Holotype and paratypes have the same color pattern in life and in preservation. Six male paratypes also without precloacal pores as well as femoral pores. The maximum size recorded in paratype ITBCZ 701 with 90.96 mm in snout-vent length. Variation in size and arranging scale are presented in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Habitat. All specimens were found in rocky caves. The type locality is an isolated hill in Mekong Delta with outcrop sandstone rock and covered partly by lianas ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 c). In the dry season, this hill virtually becomes a barren rocky area.
Distribution. Recorded only from type locality - at Tức Dụp Hill, An Giang Province, southern Vietnam ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 c).
Etymology. This new gecko is named after the nation of Vietnam.
Comparisons. Gekko vietnamensis sp. nov. is distinguished from all other congeneric species except for other poreless forms by the lack of distinct precloacal pores in adult males. The new species may be distinguished from G. vertebralis by its larger body size (max. SVL 90.96 mm versus 69.2 mm), the number of transverse lamellae under the fourth toe (18–20 versus 9–17), and the absence of numerous brown dots on ventral surfaces of body (present in G. vertebralis ). From G. s h i b a t a i, the new species differs by its larger body size (max. SVL 90.96 mm versus 70.9 mm), the number of transverse lamellae under the fourth toe (18–20 versus 9–16), and ventral surface of head without dark irregular spots (present in G. shibatai ). From G. tawaensis , the new species differs by possessing enlarged dorsal tubercles on body (absent in G. t a w a e n s i s).
Gekko vietnamensis sp. nov. differs from other Vietnamese congeners in its lack of precloacal pores. Among these Vietnamese congeners, Gekko vietnamensis sp. nov. may be also distinguished from G. badenii and G. ulikovskii by its coloration, dark brown above with four transverse broad bands (versus yellowishgreen above with narrow, light dorsal bands); from G. canhi by the presence of one (versus two or three) cloacal spur on each side of tail base, and a larger number of subdigital lamellae below the fourth toe (18–20 versus 14–17); from G. c h i n e n s i s by a larger number of subdigital lamellae below the fourth toe (18–20 versus 12–16), and the shape of dorsal tubercles (smooth and round versus subconical); from G. gecko by rostral contact of the nostril (versus not in contact), and lack of subconical tubercles on the back and conical tubercles on the tail; from G. grossmanni by the presence of broad transverse bands on dorsum (versus blotches); from G. palmatus by the lack of broad webbing between the toes; from G. russelltraini by the presence of one (versus two) cloacal spur on each side of tail base, a larger number of interorbital scale rows (38–46 versus 30–34), and the shape of dorsal pattern (transverse broad bands versus vertebral blotches and short, white bands on the flanks); from G. scientiadventura by the presence of dorsal tubercles, and larger body size (max. SVL 90.96 mm versus 73.0 mm); and from G. takouensis by the presence of one (versus two or three) cloacal spur on each side of tail base, a larger number of interorbital scale rows (38–46 versus 27–34), and the shape of dorsal pattern (transverse broad bands versus vertebral blotches and short, white bars on the flanks).
TABLE 1. Measurements and pholidosis of the type series of Gekko vietnamensis sp. nov. For abbreviations see Materials and Methods.
| Sex | ITBCZ 667 Male | ITBCZ 668 Male | ITBCZ 669 Male | ITBCZ 670 Male | ITBCZ 671 Female | ITBCZ 700 Male | ITBCZ 701 Male | ITBCZ 702 Male | Mean±S.D. Min – Max n = 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVL | 83.02 | 85.58 | 80.56 | 82.48 | 79.86 | 90.90 | 90.96 | 89.62 | 85.37±4.59 |
| HeadL HeadW | 21.26 17.44 | 22.76 17.64 | 18.71 16.13 | 22.44 16.64 | 21.36 15.68 | 22.99 18.41 | 23.07 18.54 | 22.96 18.30 | 21.94±1.49 17.35±1.09 |
| HeadH | 10.78 | 11.33 | 10.25 | 10.41 | 9.86 | 10.94 | 11.33 | 10.94 | 10.73±0.52 |
| OrbD SnEye | 6.18 8.81 | 5.87 9.25 | 5.70 8.15 | 5.81 8.89 | 5.58 8.88 | 6.61 9.70 | 6.35 9.64 | 6.13 9.53 | 6.03±0.35 9.11±0.53 |
| NarEye | 7.75 | 8.23 | 7.34 | 7.53 | 7.34 | 8.20 | 8.14 | 8.26 | 7.85±0.41 |
| EarL TrunkL | 2.22 37.50 | 2.87 39.88 | 2.76 33.75 | 2.87 37.60 | 2.71 37.62 | 2.66 42.91 | 2.93 39.98 | 2.69 39.42 | 2.71±0.22 38.58±2.66 |
| TailL | 98.60 | 98.24 | - | - | - | 105.02 | 108.00 | 102.11 | 102.40±4.18 (n = 5) |
| CrusL ForeaL | 15.51 11.73 | 15.81 11.91 | 14.67 11.31 | 15.77 11.71 | 14.43 11.55 | 15.98 12.64 | 16.35 12.39 | 15.86 12.52 | 15.55±0.66 11.97±0.49 |
| TailW | 7.20 | 7.89 | 6.88 | 6.62 | 6.27 | 7.58 | 8.35 | 7.62 | 7.30±0.69 |
| Internar Interorb | 2.76 8.36 | 2.77 8.59 | 2.85 8.07 | 2.80 8.38 | 2.90 7.91 | 3.08 7.98 | 3.04 8.78 | 3.08 8.58 | 2.91±0.14 8.33±0.32 |
| EyeEar | 6.36 | 7.26 | 6.32 | 6.38 | 6.04 | 6.41 | 7.06 | 6.74 | 6.57±0.41 |
| SPL IFL | 12 10 | 12 11 | 12 11 | 12 11 | 11 11 | 12 10 | 11 10 | 12 10 | 11–12 10–11 |
| IntOrb | 45 | 46 | 38 | 39 | 43 | 38 | 43 | 38 | 38–46 |
| SDL IV PP | 19 0 | 19 0 | 18 0 | 20 0 | 19 - | 19 0 | 18 0 | 19 0 | 18–20 0 |
| FP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CaS SC | 1/1 91 | 1/1 77 | 1/1 - | 1/1 - | 1/1 - | 1/1 73 | 1/1 81 | 1/1 76 | 1/1 73–91 |
| SB | 28 | 30 | 28 | 30 | 30 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28–30 |
| ITBCZ |
ITBCZ |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.