Lipotactes (Sublipotactes) khmericus Gorochov, 1998
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.25221/fee.434.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2A2352F6-0505-4F83-9040-56E8D5560D6E |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5569A62B-FFDA-0F6E-FF04-FA59A4FCB158 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Lipotactes (Sublipotactes) khmericus Gorochov, 1998 |
| status |
|
Lipotactes (Sublipotactes) khmericus Gorochov, 1998 View in CoL
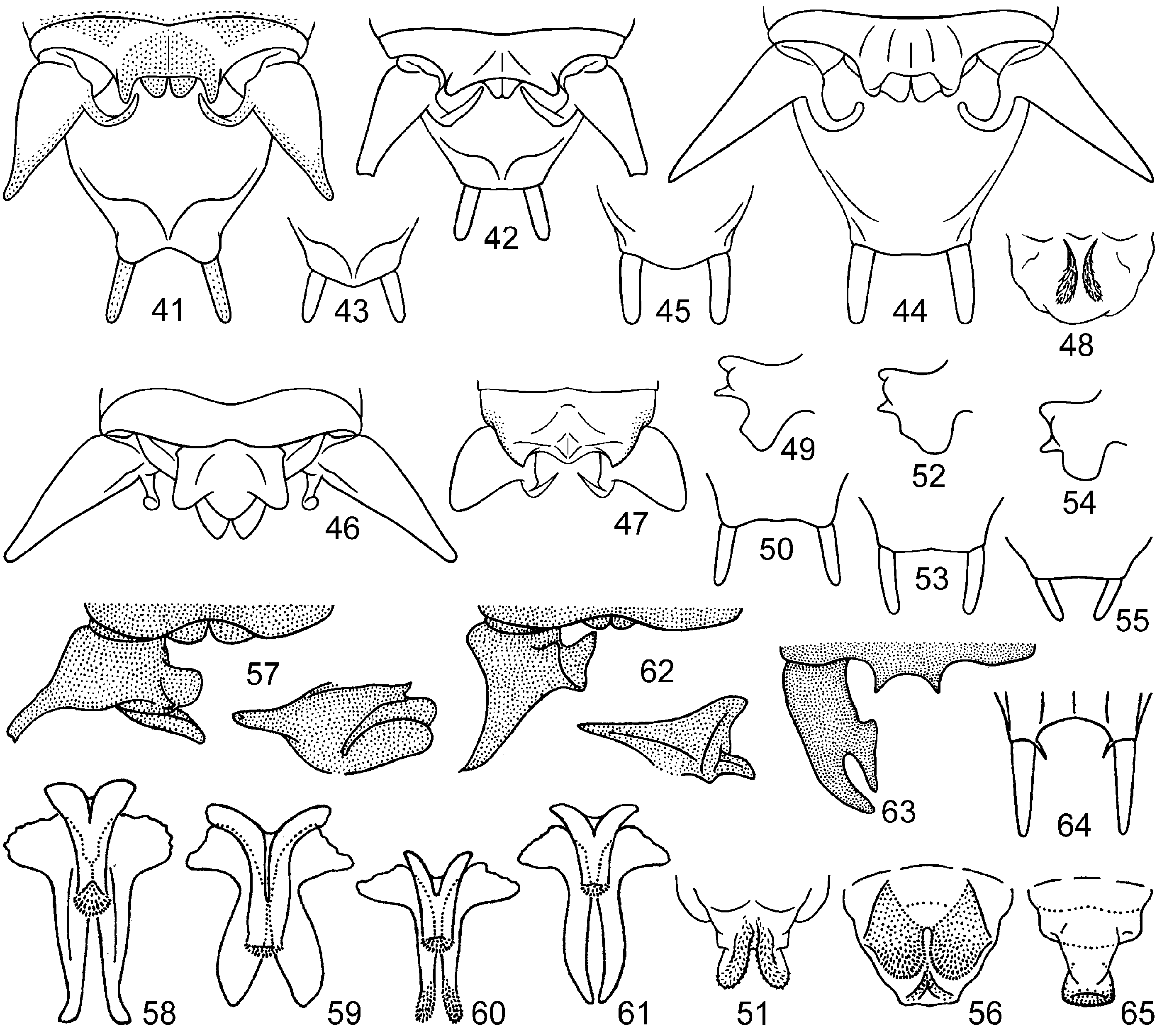
Figs 49–55 View Figs 41–65
MATERIAL. Cambodia: 7 ♂, 6 ♀ , western part, environs of Sihanoukville Town near Siam Bay , secondary forest, 22–26.VIII 2003, A. Gorochov, L. Anisyutkin; 2 ♂ ,
1 ♀, 10–15 km NEE of Sihanoukville Town , environs of waterfall, ~ 200 m, secondary forest, 11–12.IX 2003, A. Gorochov ; 3 ♂, 2 ♀, southern part of Elefan Mts ,
Bokor National Park on Phnom-Bokor Mt, 700–1000 m, forest, 18–22.IX 2003, A.
Gorochov, M. Berezin; 4 ♂, 3 ♀, central part of Elefan Mts, ~ 100 km NE of Sihanoukville Town , environs of Styeng-Chkhral Vill., 300–500 m, forest, 27.VIII–6.IX
2003, A. Gorochov, L. Anisyutkin; 1 ♂, 1 ♀, northern part of Elefan Mts , ~ 150 km
NNE of Sihanoukville Town, Kiri-Rom National Park, ~ 600–800 m, remnants of forest, 7–10.X 2003, A. Gorochov, M. Berezin.
NOTE. These specimens are very similar to the holotype of L. (S.) khmericus ,
but the medial cercal lamella of their males are less deeply notched near its apical spinule (compare Figs 49 and 52, 54 View Figs 41–65 ). The males from Elefan Mts have the genital plate styles almost as long as in this holotype ( Figs 50, 53 View Figs 41–65 ), and some of them are practically indistinguishable from males of L. samkos Ingrisch, 2021 in the cercal lamella ( Fig. 52 View Figs 41–65 ). The other males from my material are with these styles somewhat shorter ( Fig. 55 View Figs 41–65 ), and these males are very similar to those of L. saengeri Ingrisch, 2021
in the shape of this lamella ( Fig. 54 View Figs 41–65 ). However, all these differences are very insig-
nificant and only imply a subspecies status. So, here I subdivide L. (S.) khmericus into three subspecies: nominotypical one ( Figs 49, 50 View Figs 41–65 ) characteristic of the eastern part of Cambodia; L. (S.) kh. samkos stat. n. ( Figs 52, 53 View Figs 41–65 ) living in mountains of the western part of Cambodia; L. (S.) kh. saengeri stat. n. ( Figs 54, 55 View Figs 41–65 ) distributed in the western sea coast of Cambodia and the nearest part of Thailand.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.