Euconocephalus malabaricum Tiwari and Diwakar, 2024
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5405.2.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6943C3BB-F5BC-4B8B-91F4-EB069E1D8D5E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10603377 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/407C87E0-FF84-FF99-91B8-AB6BFDC073D9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Euconocephalus malabaricum Tiwari and Diwakar |
| status |
sp. nov. |
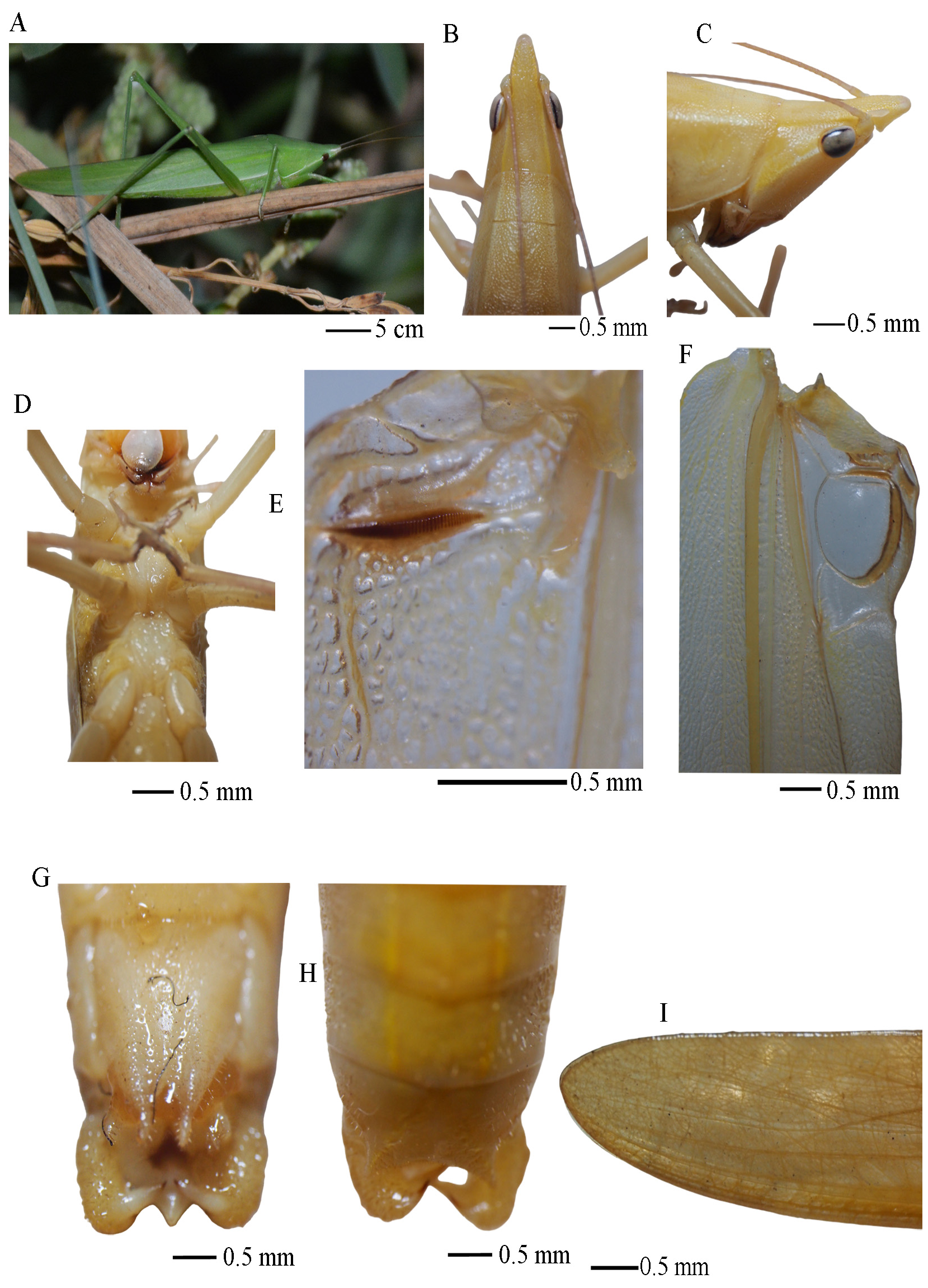
Euconocephalus malabaricum Tiwari and Diwakar sp. n.
( Figs. 5–6 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 )
Material examined: Holotype: Male. INDIA. Kerala, Varnam P.O. Puthanangady, Cherthala , Alleppey . ~ 2 m a.s.l. 2020, Coll. Chandranshu Tiwari, Department of Environmental Studies, University of Delhi, 110007 (Delhi), India . Paratype: Kerala, Varnam P.O. Puthanangady , Cherthala , Alleppey . ~ 2 m a.s.l. 2020, Coll. Chandranshu Tiwari (2 ♂) .
Type locality: Varnam P.O. Puthanangady, Cherthala, Alleppey Kerela.
Measurements: Body 33.1 (1.3); tegmen 40.3 (3.6); fastigium 2.0 (0.4); pronotum 8.1 (0.9), fore-femora 5.7 (0.7); mid-femora 7.3 (0.3); post-femora 20.1 (1.7); fore-tibia 6.1 (0.4); mid-tibia 7.0 (0.2); post-tibia 20.4 (0.3), file 2.6 (0.2).
Distribution: Crepescular-Nocturnal. Recorded from rice fields and fallow lands. Likely distributed throughout the Malabar coast.
Seasonal occurrence: The species was recorded during the dry season preceding the monsoon.
Etymology: The species is named after Malabar coast where it was recorded from. Adjective following Euconocephalus in neuter.
Differential diagnosis: The species is similar to Euconocephalus incertus ( Walker 1869) but differs in the following character: shorter fastigium, tegmen, and apex of supra-anal plate obtuse. Subgenital plate smaller without the lateral ridges.
Description:
Male: Body slender. Head. Fastigium of vertex conical, elongate 2.0 mm in length, apex rounded. Fastigium of vertex separated from fastigium of frons by a notch with a small ventral tubercle present at the base of fastigium. Eyes suboval and prominent. Pronotum with anterior dorsal margin almost straight, posterior margin broadly rounded; transverse sulcus distinct before the middle of pronotum; lateral carinae present. Lateral lobes of pronotum inclined; longer than high with distinct humeral sinus. Prosternum armed with a pair of spines, mesosternal and metasternal lobes triangular. Legs genicular lobes of fore femora unarmed on both side; genicular lobes of mid femora armed on the inner side with a single spine and unarmed on outer side; genicular lobes of hind femora armed with a single spine on both inner and outer side. Fore coxae armed with a long projected spine.All femora dorsally unarmed. Fore femora ventrally armed with 2 minute spines on inner margin and unarmed on outer margin. Mid femora ventrally unarmed on outer margin and 3 minute spines on inner margin. Hind femora ventrally armed with 9 minute to small spines on inner margin and 7 minute to small spines on outer margin. Tympanum on fore tibia conchate, tympanal slits facing forward with a pair of small elongated pits laterally just below the tympanum. Fore and mid tibiae dorsally unarmed. Fore tibiae ventrally armed with 6 small spines each on inner and outer margin. Mid tibiae ventrally armed with 7 small spines each on inner and outer margin. Hind tibiae dorsally armed with 15 small sized spines on inner and 19 spines on outer margin. Hind tibiae ventrally armed with 9 small spines on inner margin and 17 small more spaced spines on outer margin. Single dorsal pair of spurs and two ventral pairs (inner small and outer large) of spurs present at the apical region of hind tibiae. Male tenth abdominal tergite with two incurved lobes on apical margin. Wings. Tegmina longer than hind wings but not extending beyond the hind wings; apices obtusely rounded. Wings reaching beyond the middle of hind tibia when folded. Hind wings pellucid. Stridulatory file with 76 teeth on the ventral side of left tegmen; file slightly curved. relatively narrow on distal end than the proximal end.
Male genitalia. Supra-anal plate triangular with dorsal basal groove, apex obtuse. Subgenital plate broad with well developed medial ridge. Apical margin with triangular excision; styles conical and short. Cerci thick with two incurved apical teeth, dorsal tooth shorter than ventral tooth.
Female. Unknown. Supposedly similar to E.incertus .
Coloration. Green to Yellow Green when alive. Antennae yellow to pale green. Lateral margin of fastigium of vertex on both sides with narrow yellow band which extends on the vertex above eye level and reaching up to the posterior margin of pronotum. Tegmen appears green/yellow when live with anterior external margin of the tegmen pale or translucent. All femora same color as tegmen. Tibia pale yellow to white. Claws and tarsal joints pale.
Depositories: The specimens are deposited in the Department of Environmental Studies, Faculty of Science , University of Delhi .
Acoustic Description
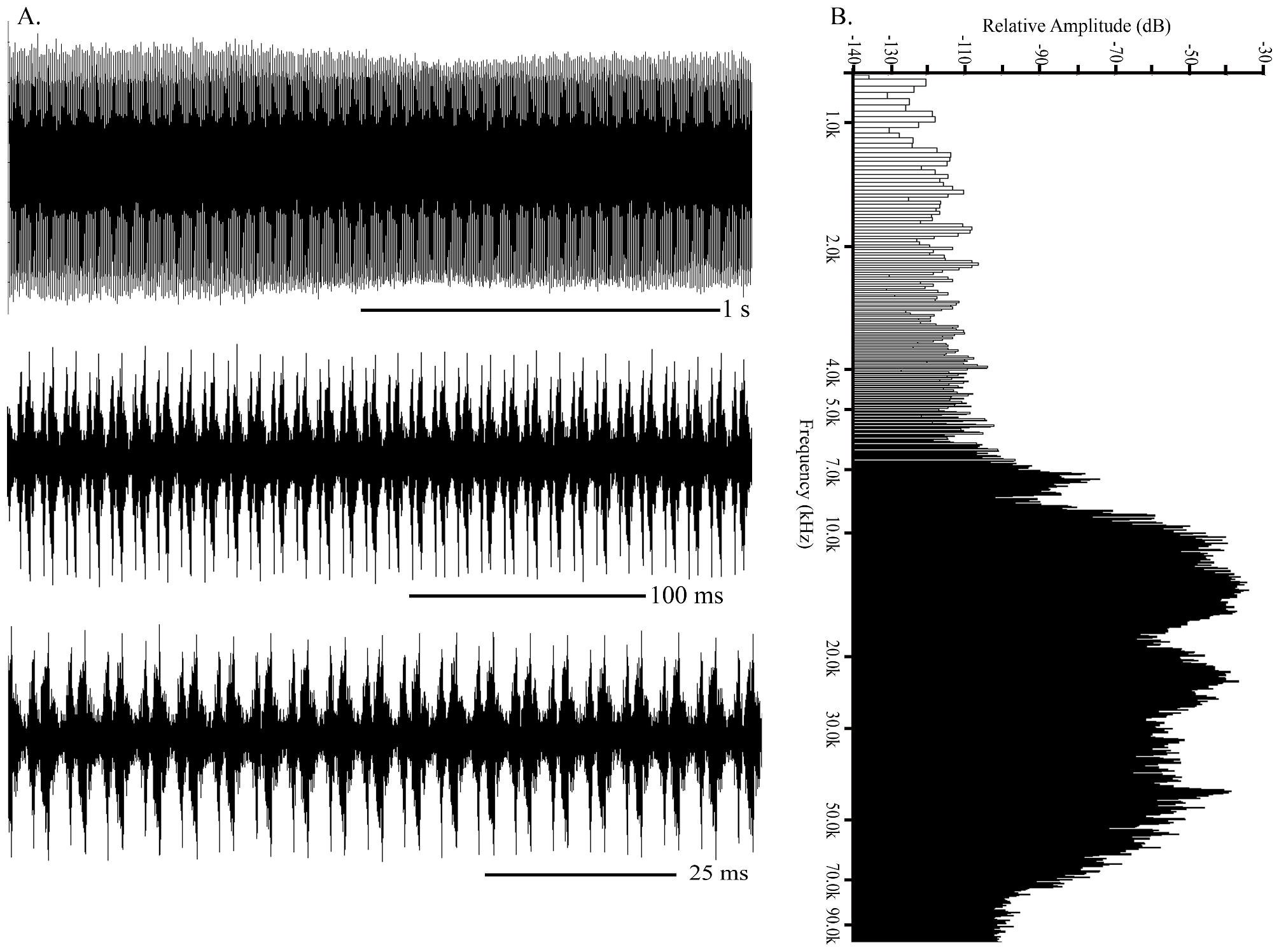
The call of E. malabaricum consists of a buzzing call typical to Conocephalinae family, with a two part echeme (SD=4±1 ms) produced at a very high rate (209±37 echeme/s). The call had the peak frequency of 12 kHz and a bandwidth of 7±1.5 kHz ( Figure 6 View FIGURE 6 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |